Abstract
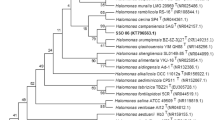
A moderately halophilic bacterial strain 15-13T, which was isolated from soda meadow saline soil in Daqing City, Heilongjiang Province, China, was subjected to a polyphasic taxonomic study. The cells of strain 15–13 were found to be Gram-negative, rod-shaped, and motile. The required growth conditions for strain 15–13T were: 1–23% NaCl (optimum, 7%), 10–50°C (optimum, 35°C), and pH 7.0–11.0 (optimum, pH 9.5). The predominant cellular fatty acids were C18:1 ω7c (60.48%) and C16:0 (13.96%). The DNA G+C content was 67.6 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons indicated that strain 15–13T clustered within a branch comprising species of the genus Halomonas. The closest phylogenetic neighbor of strain 15–13T was Halomonas pantelleriensis DSM 9661T (98.9% 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity). The level of DNA-DNA relatedness between the novel isolated strain and H pantelleriensis DSM 9661T was 33.8%. On the basis of the phenotypic and phylogenetic data, strain 15–13T represents a novel species of the genus Halomonas, for which the name Halomonas alkalitolerans sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain for this novel species is 15–13T (=CGMCC 1.9129T =NBRC 106539T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahal, D.R., R.H. Vreeland, C.D. Litchfield, M.R. Mormile, B.J. Tindall, A. Oren, V. Bejar, E. Quesada, and A. Ventosa. 2007. Recommended minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Halomonadaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2436–2446.
Berendes, F., G. Gottcswhalk, E. Heine-Dobbernack, E.R.B. Moore, and B.J. Tindall. 1996. Halomonas desiderata sp. nov., a new alkaliphilic, halotolerant and denitrifying bacterium isolated from a municipal sewage works. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 19, 158–167.
Boltyanskaya, Y.V., V.V. Kevbrin, A.M. Lysenko, T.V. Kolganova, T.P. Tourova, G.A. Osipov, and T.N. Zhilina. 2007. Halomonas mongoliensis sp. nov. and Halomonas kenyensis sp. nov., new hal oalkaliphilic denitrifiers capable of N2O reduction, isolated from soda lakes. Microbiology (English translation of Mikrobiologiia). 76, 739–747.
De Ley, J., H. Cattoir, and A. Reynaerts. 1970. The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur. J. Biochem. 12, 143–153.
Duckworth, A.M., W.D. Grant, B.E. Jones, D. Meijer, M.C. Màrques, and A. Ventosa. 2000. Halomonas magadii sp. nov., a new member of the genus Halomonas, isolated from a soda lake of the East African Rift Valley. Extremophiles 4, 53–60.
Dussault, H.P. 1955. An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 70, 484–485.
Felsenstein, J. 2004. PHYLIP-Phylogeny Inference Package documentation files, version 3.62c. Distributed by the author. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA.
Heyrman, J., A. Balcaen, P. De Vos, and J. Swings. 2002. Halomonas muralis sp. nov., isolated from microbial biofilms colonizing the walls and murals of the Saint-Catherine chapel (Castle Herberstein, Austria). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 2049–2054.
Huß, V.A.R., H. Festl, and K.H. Schleifer. 1983. Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 4, 184–192.
Kaye, J.Z., C. Màrquez, A. Ventosa, and J.A. Baross. 2004. Halomonas neptunia sp. nov., Halomonas sulfidaeris sp. nov., Halomonas axialensis sp. nov., and Halomonas hydrothermalis sp. nov.: halophilic bacteria isolated from widely distributed deep-sea hydrothermalvent environments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 499–511.
Kumar, S., K. Tamura, and M. Nei. 2004. MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 5, 150–163.
Marmur, J. 1961. A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J. Mol. Biol. 3, 208–218.
Marmur, J. and P. Doty. 1962. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J. Mol. Biol. 5, 109–118.
Mata, J.A., J. Martinez-Cánovas, E. Quesada, and V. Béjar. 2002. A detailed phenotypic characterization of the type strains of Halomonas species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 25, 360–375.
Mormile, M.R., M.F. Romine, M.T. Garcìa, A. Ventosa, T.J. Bailey, and B.M. Peyton. 1999. Halomonas campisalis sp. nov., a denitrifying, moderately haloalkaliphilic bacterium. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 22, 551–558.
Quillaguamán, J., R. Hatti-Kaul, B. Mattiason, M.T. Alvarez, and O. Delgado. 2004. Halomonas boliviensis sp. nov., an alkalitolerant, moderate halophile isolated from soil around a Bolivian hypersaline lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 721–725.
Reysenbach, A.L., K. Longnecker, and J. Kirshtein. 2000. Novel bacterial and archaeal lineages from an in situ growth chamber deployed at a mid-Atlantic ridge hydrothermal vent. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 3798–3806.
Romano, I., A. Giordano, L. Lama, B. Nicolaus, and A. Gambacorta. 2005. Halomonas campaniensis sp. nov., a haloalkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a mineral pool of Campania region, Italy. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 28, 610–618.
Romano, I., L. Lama, B. Nicolaus, A. Poli, A. Gambacorta, and A. Giordano. 2006. Halomonas alkaliphila sp. nov., a novel halotolerant alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a salt pool in Campania (Italy). J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 52, 339–348.
Romano, I., B. Nicolaus, L. Lama, M.C. Manca, and A. Gambacorta. 1996. Characterization of a haloalkaliphilic strictly aerobic bacterium, isolated from Pantelleria Island. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 19, 326–333.
Sehgal, S.N. and N.E. Gibbons. 1960. Effect of some metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can. J. Microbiol. 6, 165–169.
Ventosa, A., E. Quesada, F. Rodriguez-Valera, F. Ruiz-Berraquero, and A. Ramos-Cormenzana. 1982. Numerical taxonomy of moderately halophilic Gram-negative rods. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128, 1959–1968.
Vreeland, R.H. 2005. Genus I. Halomonas. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd (ed.), vol. 2, pp. 300–313. In D.J. Brenner, N.R. Krieg, J.T. Staley and G.M. Garrity (eds.). Springer, New York, N.Y., USA.
Vreeland, R.H., C.D. Litchfield, E.L. Martin, and E. Elliot. 1980. Halomonas elongata, a new genus and species of extremely salt tolerant bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 30, 485–495.
Wang, Y.N., H. Cai, S.L. Yu, Z.Y. Wang, and X.L. Wu. 2007. Halomonas gudaonensis sp. nov., isolated from a saline soil contaminated by crude oil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 911–915.
Wang, S., Q. Yang, Z.H. Liu, L. Sun, D. Wei, J.J. Zhang, J.Z. Song, and H.F. Yuan. 2010. Haloterrigena daqingensis sp. nov., an extremely haloalkaliphilic archaeon isolated from salt-alkaline soils in Daqing, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 2267–2271.
Wayne, L.G., D.J. Brenner, R.R. Colwell, P.A.D. Grimont, O. Kandler, M.I. Krichevsky, L.H. Moore, and et al. 1987. International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464.
Wu, G., X.Q. Wu, Y.N. Wang, C.Q. Chi, Y.Q. Tang, K. Kida, X.L. Wu, and Z.K. Luan. 2008. Halomonas daqingensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from an oilfield soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 2859–2865.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springer.com/content/120956
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Yang, Q., Liu, ZH. et al. Halomonas alkalitolerans sp. nov., a novel moderately halophilic bacteriun isolated from soda meadow saline soil in Daqing, China. J Microbiol. 49, 24–28 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-011-0197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-011-0197-z