Abstract
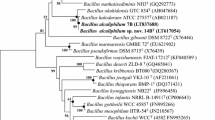
A Gram-positive, rod-shaped, endospore-forming organism, strain BL3-6T, was isolated from tidal flat sediments of the Yellow Sea in the region of Tae-An. A 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis demonstrated that this isolate belongs to the Bacillus cereus group, and is closely related to Bacillus mycoides (99.0% similarity), Bacillus thuringiensis (99.0%), Bacillus weihenstephanensis (99.0%), Bacillus cereus (98.9%), Bacillus anthracis (98.8%), and Bacillus pseudomycoides (98.1%). The phylogenetic distance from any validly described Bacillus species outside the Bacillus cereus group was less than 95.6%. The DNA G+C content of the strain was 39.4 mol% and the major respiratory quinone was menaquinone-7. The major cellular fatty acids were iso-C14:0 (17.8%), iso-C16:0 (15.8%), and iso-C12:0 (11.3%). The diagnostic amino acid of the cell wall was meso-diaminopimelic acid and the major cell wall sugar was galactose. The results of DNA-DNA hybridization (<55.6%) and physiological and biochemical tests allowed genotypic and phenotypic differentiation of strain BL3-6T from the published Bacillus species. BL3-6T therefore represents a new species, for which the name Bacillus gaemokensis sp. nov. is proposed, with the type strain BL3-6T (=KCTC 13318T =JCM 15801T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, I., A. Yokota, A. Yamazoe, and T. Fujiwara. 2007. Proposal of Lysinibacillus boronitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., and transfer of Bacillus fusiformis to Lysinibacillus fusiformis comb. nov. and Bacillus sphaericus to Lysinibacillus sphaericus comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1117–1125.
Ash, C., J.A. Farrow, M. Dorsch, E. Stackebrandt, and M.D. Collins. 1991. Comparative analysis of Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and related species on the basis of reverse transcriptase sequencing of 16S rRNA. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 41, 343–346.
Cardazzo, B., E. Negrisolo, L. Carraro, L. Alberghini, T. Patarnello, and V. Giaccone. 2008. Multiple-locus sequence typing and analysis of toxin genes in Bacillus cereus food-borne isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 850–860.
Chang, Y.H., J. Han, J. Chun, K.C. Lee, M.S. Rhee, Y.B. Kim, and K.S. Bae. 2002. Comamonas koreensis sp. nov., a non-motile species from wetland in Woopo, Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 377–381.
Chang, Y.H., M.Y. Jung, I.S. Park, and H.M. Oh. 2008. Sporolactobacillus vineae sp. nov., a spore-forming lactic acid bacterium isolated from vineyard soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 2316–2320.
Claus, D. and R.C.W. Berkeley. 1986. Genus Bacillus Cohn 1872, pp. 1105–1140. In P.H.A. Sneath, N.S. Mair, M.E. Sharpe, and J.G. Holt (eds.), Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 2. The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore, USA.
Drobniewski, F.A. 1993. Bacillus cereus and related species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 6, 324–338.
Ezaki, T., Y. Hashimoto, and E. Yabuuchi. 1989. Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 224–229.
Felsenstein, J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 368–376.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 40, 783–791.
Felsenstein, J. 1993. PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package), version 3.5c, Seattle: Department of Genetics, University of Washington, USA.
Fitch, W.M. 1971. Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20, 406–416.
Gonzalez, J.M. and C. Saiz-Jimenez. 2002. A fluorimetric method for the estimation of G+C mol% content in microorganisms by thermal denaturation temperature. Environ. Microbiol. 4, 770–773.
Granum, P.E. and T. Lund. 1997. Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 157, 223–228.
Henderson, I., C.J. Duggleby, and P.C.B. Turnbull. 1994. Differentiation of Bacillus antliracis from other Bacillus cereus group bacteria with the PCR. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44, 99–105.
Jackson, P.J., E.A. Walthers, A.S. Kalif, K.L. Richmond, D.M. Adair, K.K. Hill, C.R. Kuske, G.L. Andersen, K.H. Wilson, M. Hugh-Jones, and P. Keim. 1997. Characterization of the variable-number tandem repeats in vrrA from different Bacillus anthracis isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 1400–1405.
Jukes, T.H. and C.R. Cantor. 1969. Evolution of protein molecules. In Mammalian Protein Metabolism, pp. 21–132. In H.N. Munro (ed.). Academic Press, New York, USA.
Kaneko, T., R. Nozaki, and K. Aizawa. 1978. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness between Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol. Immunol. 22, 639–641.
Kim, W., J.Y. Kim, S.L. Cho, S.W. Nam, J.W. Shin, Y.S. Kim, and H.S. hin. 2008. Glycosyltransferase — a specific marker for the discrimination of Bacillus anthracis from the Bacillus cereus group. J. Med. Microbiol. 57, 279–286.
Komagata, K. and K. Suzuki. 1987. Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. In Method in Microbiology, vol. 19, pp. 161–207. R.R. Colwell and R. Grigorova (eds.). Academic press, London, UK.
Lechner, S., R. Mayr, K.P. Francis, B.M. Pruss, T. Kaplan, E. Wiessner-Gunkel, G.S. Stewart, and S. Scherer. 1998. Bacillus weihenstephanensis sp. nov. is a new psychrotolerant species of the Bacillus cereus group. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1373–1382.
Nakamura, L.K. 1998. Bacillus pseudomycoides sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1031–1035.
Nakamura, L.K. and M.A. Jackson. 1995. Clarification of the taxonomy of Bacillus mycoides. J. Appl. Microbiol. 45, 46–49.
Priest, F.G., M. Goodfellow, and C. Todd. 1988. A numerical classification of the genus Bacillus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134, 1847–1882.
Saitou, N. and M. Nei. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Schleifer, K.H. and O. Kandler. 1972. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol. Rev. 36, 407–477.
Seki, T., C. Chung, H. Mikami, and Y. Oshima. 1978. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology and taxonomy of the genus Bacillus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 28, 182–189.
Smibert, R.M. and N.R. Krieg. 1994. Phenotypic characterization, pp. 607–654. In P. Gerhardt, R.G.E. Murray, W.A. Wood, and N.R. Krieg (eds.), Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., USA.
Stackebrandt, E. and B.M. Goebel. 1994. Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Microbiol. 44, 846–849.
Staneck, J.L. and G.D. Roberts. 1974. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin layer chromatography. Appl. Microbiol. 28, 226–231.
Stenfors Arnesen, L.P., A. Fagerlund, and P.E. Granum. 2008. From soil to gut: Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 32, 579–606.
Venkateswaran, K., M. Kempf, F. Chen, M. Satomi, W. Nicholson, and R. Kern. 2003. Bacillus nealsonii sp. nov., isolated from a spacecraft-assembly facility, whose spores are gamma-radiation resistant. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53, 165–172.
von Stetten, F., R. Mayr, and S. Scherer. 1999. Climatic influence on mesophilic Bacillus cereus and psychrotolerant Bacillus weihenstephanensis population in tropical temperate and alpine soil. Environ. Microbiol. 1, 503–515.
Wayne, L.G., D.J. Brenner, R.R. Colwell, P.A.D. Grimont, O. Kandler, M.I. Krichevsky, L.H. Moore, and et al. 1987. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12275-011-0548-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, MY., Paek, W.K., Park, IS. et al. Bacillus gaemokensis sp. nov., isolated from foreshore tidal flat sediment from the Yellow Sea. J Microbiol. 48, 867–871 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0148-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0148-0