Abstract
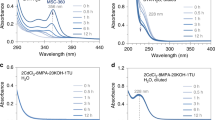
The formation pathway of aqueous-phase colloidal semiconductor magic-size clusters (MSCs) remains unrevealed. In the present work, we demonstrate, for the first time, a precursor compound (PC)-enabled formation pathway of aqueous-phase CdSe MSCs exhibiting a sharp absorption peaking at about 420 nm (MSC-420). The CdSe MSC-420 is synthesized with CdCl2 and selenourea as the respective Cd and Se sources, and with 3-mercaptopropionic acid or L-cysteine as a ligand. Absorption featureless CdSe PCs form first in the aqueous reaction batches, which transform to MSC-420 in the presence of primary amines. The coordination between primary amine and Cd2+ on PCs may be responsible to the PC-to-MSC transformation. Upon increasing the reactant concentrations or decreasing the CdCl2-ligand feed molar ratios, the Cd precursor self-assembles into large aggregates, which may encapsulate the resulting CdSe PCs and inhibit their transformation to MSC-420. The present study sheds essential light on the syntheses and formation mechanisms of nanocrystals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wan, W. S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, M.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, C. C.; Wang, S. L.; Kreouzis, T.; Fan, H. S.; Huang, W.; Yu, K. Room-temperature formation of CdS magic-size clusters in aqueous solutions assisted by primary amines. Nat. Commun.2020, 11, 4199.
He, L.; Luan, C. R.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, K. Transformations among colloidal semiconductor magic-size clusters. Acc. Chem. Res.2021, 54, 776–786.
Zhu, J. M.; Cao, Z. P.; Zhu, Y. C.; Rowell, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. L.; Zhang, C. C.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Transformation pathway from CdSe magic-size clusters with absorption doublets at 373/393 nm to clusters at 434/460 nm. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2021, 60, 20358–20365.
Yang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Luan, C. R.; Yu, K. The precursor compound of two types of ZnSe magic-sized clusters. Nano Res., in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3503-z.
Shen, Q.; Luan, C. R.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Willis, M.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, K. Reversible transformations at room temperature among three types of CdTe magic-size clusters. Inorg. Chem.2021, 60, 4243–4251.
Palencia, C.; Yu, K.; Boldt, K. The future of colloidal semiconductor magic-size clusters. ACS Nano2020, 14, 1227–1235.
Zhang, H.; Luan, C. R.; Gao, D.; Zhang, M.; Rowell, N.; Willis, M.; Chen, M.; Zeng, J. R.; Fan, H. S.; Huang, W. et al. Room-temperature formation pathway for CdTeSe alloy magic-size clusters. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2020, 59, 16943–16952.
Chen, M.; Luan, C. R.; Zhang, M.; Rowell, N.; Willis, M.; Zhang, C. C.; Wang, S. L.; Zhu, X. H.; Fan, H. S.; Huang, W. et al. Evolution of CdTe magic-size clusters with single absorption doublet assisted by adding small molecules during prenucleation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2020, 11, 2230–2240.
Li, L. J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, C. C.; Wang, S. L.; Lu, J.; Fan, H. S.; Huang, W.; Chen, X. Q. et al. Fragmentation of magic-size cluster precursor compounds into ultrasmall CdS quantum dots with enhanced particle yield at low temperatures. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2020, 59, 12013–12021.
Liu, S. P.; Yu, Q. Y.; Zhang, C. C.; Zhang, M.; Rowell, N.; Fan, H. S.; Huang, W.; Yu, K.; Liang, B. Transformation of ZnS precursor compounds to magic-size clusters exhibiting optical absorption peaking at 269 nm. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2020, 11, 75–82.
Gao, D.; Hao, X. Y.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Lockwood, D. J.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C. C.; Jiang, Y. N. et al. Formation of colloidal alloy semiconductor CdTeSe magic-size clusters at room temperature. Nat. Commun.2019, 10, 1674.
Zhang, J.; Hao, X. Y.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, C. C.; Hu, C. W.; Zhang, M.; Yu, K. Individual pathways in the formation of magic-size clusters and conventional quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2018, 9, 3660–3666.
Luan, C. R.; Tang, J. B.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, M.; Huang, W.; Fan, H. S.; Yu, K. Four types of CdTe magic-size clusters from one prenucleation stage sample at room temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2019, 10, 4345–4353.
Luan, C.; Gökçinar, Ö. Ö.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Han, S.; Zhang, M.; Fan, H. S.; Yu, K. Evolution of two types of CdTe magic-size clusters from a single induction period sample. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2018, 9, 5288–5295.
Wang, L. X.; Hui, J.; Tang, J. B.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhu, T. T.; Zhang, M.; Hao, X. Y.; Fan, H. S.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Precursor self-assembly identified as a general pathway for colloidal semiconductor magic-size clusters. Adv. Sci.2018, 5, 1800632.
Zhu, D. K.; Hui, J.; Rowell, N.; Liu, Y. Y.; Chen, Q. Y.; Steegemans, T.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, K. Interpreting the ultraviolet absorption in the spectrum of 415 nm-bandgap CdSe magic-size clusters. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2018, 9, 2818–2824.
Zhu, T. T.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.; Fan, H. S.; Rowell, N.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Han, S.; Yu, K. Two-step nucleation of CdS magic-size nanocluster MSC-311. Chem. Mater.2017, 29, 5727–5735.
Liu, M. Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. X.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Rowell, N.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Renoud, R.; Bian, F. G.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Commun.2017, 8, 15467.
Zhang, J.; Li, L. J.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Willis, M.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, C. C.; Huang, W.; Zhang, M.; Yu, K. One-step approach to single-ensemble CdS magic-size clusters with enhanced production yields. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2019, 10, 2725–2732.
Zhang, B. W.; Zhu, T. T.; Ou, M. Y.; Rowell, N.; Fan, H. S.; Han, J. T.; Tan, L.; Dove, M. T.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, X. B. et al. Thermally-induced reversible structural isomerization in colloidal semiconductor CdS magic-size clusters. Nat. Commun.2018, 9, 2499.
Liu, Z. M.; Shao, C. Y.; Jin, B.; Zhang, Z. S.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Xu, X. R.; Tang, R. K. Crosslinking ionic oligomers as conformable precursors to calcium carbonate. Nature2019, 574, 394–398.
Dey, A.; Bomans, P. H. H.; Müller, F. A.; Will, J.; Frederik, P. M.; de With, G.; Sommerdijk, N. A. J. M. The role of prenucleation clusters in surface-induced calcium phosphate crystallization. Nat. Mater.2012, 9, 1010–1014.
Han, J. S.; Luo, X. T.; Zhou, D.; Sun, H. Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B. Growth kinetics of aqueous CdTe nanocrystals in the presence of simple amines. J. Phys. Chem. C2012, 114, 6418–6425.
Zhou, D.; Lin, M.; Chen, Z. L.; Sun, H. Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H. C.; Yang, B. Simple synthesis of highly luminescent water-soluble CdTe quantum dots with controllable surface functionality. Chem. Mater.2011, 23, 4857–4862.
Lesnyak, V.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmuller, A. Colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals: The aqueous approach. Chem. Soc. Rev.2013, 42, 2905–2929.
Zhou, D.; Liu, M.; Lin, M.; Bu, X. Y.; Luo, X. T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B. Hydrazine-mediated construction of nanocrystal self-assembly materials. ACS Nano2014, 8, 10569–10581.
Jing, L. H.; Kershaw, S. V.; Li, Y. L.; Huang, X. D.; Li, Y. Y.; Rogach, A. L.; Gao, M. Y. Aqueous based semiconductor nanocrystals. Chem. Rev.2016, 116, 10623–10730.
Yao, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Advances in green colloidal synthesis of metal selenide and telluride quantum dots. Chin. Chem. Lett.2019, 30, 277–284.
Aires, A.; Möller, M.; Cortajarena, A. L. Protein design for the synthesis and stabilization of highly fluorescent quantum dots. Chem. Mater.2020, 32, 5729–5738.
Mrad, M.; Ben Chaabane, T.; Rinnert, H.; Lavinia, B.; Jasniewski, J.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. Aqueous synthesis for highly emissive 3-mercaptopropionic acid-capped AIZS quantum dots. Inorg. Chem.2020, 59, 6220–6231.
Park, Y. S.; Dmytruk, A.; Dmitruk, I.; Kasuya, A.; Okamoto, Y.; Kaji, N.; Tokeshi, M.; Baba, Y. Aqueous phase synthesized CdSe nanoparticles with well-defined numbers of constituent atoms. J. Phys. Chem. C2010, 114, 18834–18840.
Park, Y. S.; Dmytruk, A.; Dmitruk, I.; Kasuya, A.; Takeda, M.; Ohuchi, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Kaji, N.; Tokeshi, M.; Baba, Y. Size-selective growth and stabilization of small CdSe nanoparticles in aqueous solution. ACS Nano2012, 4, 121–128.
Kurihara, T.; Matano, A.; Noda, Y.; Takegoshi, K. Rotational motion of ligand-cysteine on CdSe magic-sized clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C2019, 123, 14993–14998.
Baker, J. S.; Nevins, J. S.; Coughlin, K. M.; Colón, L. A.; Watson, D. F. Influence of complex-formation equilibria on the temporal persistence of cysteinate-functionalized CdSe nanocrystals in water. Chem. Mater.2011, 23, 3546–3555.
Kurihara, T.; Noda, Y.; Takegoshi, K. Quantitative solid-state NMR study on ligand-surface interaction in cysteine-capped CdSe magic-sized clusters. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2017, 8, 2555–2559.
Kurihara, T.; Noda, Y.; Takegoshi, K. Capping structure of ligand-cysteine on CdSe magic-sized clusters. ACS Omega2019, 4, 3476–3483.
Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc.2008, 120, 215–241.
Cammi, R.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. Fast evaluation of geometries and properties of excited molecules in solution: A Tamm-Dancoff model with application to 4-dimethylaminobenzonitrile. J. Phys. Chem. A2000, 104, 5631–5637.
Marenich, A. V.; Cramer, C. J.; Truhlar, D. G. Uniform treatment of solute-solvent dispersion in the ground and excited electronic states of the solute based on a solvation model with state-specific polarizability. J. Chem. Theory Comput.2013, 9, 3649–3659.
Wang, C. L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. H.; Lv, N.; Li, M. J.; Sun, H. Z.; Yang, B. Ligand dynamics of aqueous CdTe nanocrystals at room temperature. J. Phys. Chem. C2008, 112, 6330–6336.
Wurmbrand, D.; Fischer, J. W. A.; Rosenberg, R.; Boldt, K. Morphogenesis of anisotropic nanoparticles: Self-templating via non-classical, fibrillar Cd2Se intermediates. Chem. Commun.2018, 54, 7358–7361.
Kirkwood, N.; Boldt, K. Protic additives determine the pathway of CdSe nanocrystal growth. Nanoscale2018, 10, 18238–18248.
Zhang, M.; Fives, C.; Waldron, K. C.; Zhu, X. X. Self-assembly of a bile acid dimer in aqueous solutions: From nanofibers to nematic hydrogels. Langmuir2017, 33, 1084–1089.
Zhang, M.; Ma, Z. Y.; Wang, K. J.; Zhu, X. X. CO2 sequestration by bile salt aqueous solutions and formation of supramolecular hydrogels. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng.2019, 7, 3949–3955.
Chen, Y. L.; Luo, J. T.; Zhu, X. X. Fluorescence study of inclusion complexes between star-shaped cholic acid derivatives and polycyclic aromatic fluorescent probes and the size effects of host and guest molecules. J. Phys. Chem. B2008, 112, 3402–3409.
Luo, J. T.; Chen, Y. L.; Zhu, X. X. Invertible amphiphilic molecular pockets made of cholic acid. Langmuir2009, 25, 10913–10917.
Shavel, A.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A. Factors governing the quality of aqueous CdTe nanocrystals: Calculations and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B2006, 110, 19280–19284.
Jalilehvand, F.; Leung, B. O.; Mah, V. Cadmium(II) complex formation with cysteine and penicillamine. Inorg. Chem.2009, 48, 5758–5771.
Acknowledgements
K. Y. thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21773162), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2020YJ0326), the State Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials Engineering of Sichuan University (No. sklpme2020-2-09), the Open Project of Key State Laboratory for Supramolecular Structures and Materials of Jilin University (No. SKLSSM 2021030), and the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drugs Development” (No. 2019ZX09201005-005-002). M. Z. is grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22002099), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020T130441), Sichuan University postdoctoral interdisciplinary Innovation Fund, and the Open Project of Key State Laboratory for Supramolecular Structures and Materials of Jilin University (No. SKLSSM 2021032). We would like to thank the Analytical & Testing Center of Sichuan University for both ESI-MS and NMR measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Chen, Q., Zhu, Y. et al. Precursor compound enabled formation of aqueous-phase CdSe magic-size clusters at room temperature. Nano Res. 15, 2634–2642 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3858-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3858-1