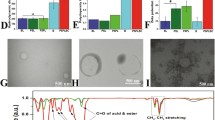
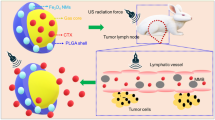
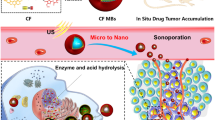
Abstract
Applying ultrasound (US) to drug delivery and disease therapy is important work. Sonodynamic therapy (SDT)—a comprehensive therapy using US and a sonosensitizer—exhibits antineoplastic activity in many tumors. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of using a new sonosensitizer (sinoporphyrin sodium, DVDMS) loaded into liposome–microbubble complexes (DLMBs) as a possible candidate to enhance SDT against breast cancer. DLMBs were synthesized via the biotin–avidin linkage and confirmed to have good US response. US-induced cavitation played a key role to trigger a boosted payload release from DLMBs and improve the cellular uptake and intratumoral diffusion of DVDMS to realize better SDT effect. The combination of DLMBs and US treatment resulted in significant changes to cell morphology, mitochondria damage, and cell apoptosis in vitro. In vivo, the combined treatment markedly inhibited tumor growth, which appeared to result from increased apoptosis and reduced proliferation activity. The significant increase in the antitumor effect of DLMBs plus US suggests their potential use as a new approach to promote the killing activity of SDT against breast cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood, A. K. W.; Sehgal, C. M. A review of low-intensity ultrasound for cancer therapy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 905–928.
Antonelli, A.; Sfara, C.; Magnani, M. Intravascular contrast agents in diagnostic applications: Use of red blood cells to improve the lifespan and efficacy of blood pool contrast agents. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 731–766.
Di, J.; Yu, J. C.; Wang, Q.; Yao S. S.; Suo, D. J.; Ye, Y. Q.; Pless, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Gu, Z. Ultrasound-triggered noninvasive regulation of blood glucose levels using microgels integrated with insulin nanocapsules. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1393–1402.
McHale, A. P.; Callan, J. F.; Nomikou, N.; Fowley, C.; Callan, B. Sonodynamic therapy: Concept, mechanism and application to cancer treatment. In Therapeutic Ultrasound; Escoffre, J. M.; Bouakaz, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Switzerland, 2016; pp 429–450.
Trendowski, M. The promise of sonodynamic therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 143–160.
Lv, Y. H.; Zheng, J. H.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, L. M.; Wang, C. Y.; Liu, N. A.; Zhao, H.; Ji, H.; Li, B. X.; Cao, W. W. Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing effect of exoprotoporphyrin IX based sonodynamic therapy on human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40967.
Sun, H. Z.; Ge, W. J; Gao, X.; Wang, S. S.; Jiang, S. J.; Hu, Y.; Yu, M.; Hu, S. S. Apoptosis-promoting effects of hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether-sonodynamic therapy (HMME-SDT) on endometrial cancer. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0137980.
Inui, T.; Amitani, H.; Kubo, K.; Kuchiike, D.; Uto, Y.; Nishikata, T.; Mette, M. Case report: A non-small cell lung cancer patient treated with GcMAF, sonodynamic therapy and tumor treating fields. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 3767–3770.
Jia, Y. L.; Wang, X. B.; Liu, Q. H.; Leung, A. W.; Wang, P.; Xu, C. S. Sonodynamic action of hypocrellin B triggers cell apoptoisis of breast cancer cells involving caspase pathway. Ultrasonics 2017, 73, 154–161.
Li, Y. X.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. B.; Su, X. M.; Liu, Q. H. Involvement of mitochondrial and reactive oxygen species in the sonodynamic toxicity of chlorin e6 in human leukemia K562 cells. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 990–1000.
Wang, X. J.; Mitchell, D.; Lewis, T. J. Primary clinical use of sonodynamic therapy (SDT) for advanced breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 12029.
Huang, P.; Qian, X. Q.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. D.; Lin, H.; Wang, L. Y.; Zhu, Y. F.; Shi, J. L. Metalloporphyrin-encapsulated biodegradable nanosystems for highly efficient magnetic resonance imaging-guided sonodynamic cancer therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1275–1284.
Deepagan, V. G.; You, D. G.; Um, W.; Ko, H.; Kwon, S.; Choi, K. Y.; Yi, G. R.; Lee, J. Y.; Lee, D. S.; Kim, K. et al. Long-circulating Au-TiO2 nanocomposite as a sonosensitizer for ROS-mediated eradication of cancer. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6257–6264.
Wang, H. P.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X. B.; Liu, Q. H. Microbubbles enhance the antitumor effects of sinoporphyrin sodium mediated sonodynamic therapy both in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 1401–1409.
McEwan, C.; Kamila, S.; Owen, J.; Nesbitt, H.; Callan, B.; Borden, M.; Nomikou, N.; Hamoudi, R. A.; Taylor, M. A.; Stride, E. et al. Combined sonodynamic and antimetabolite therapy for the improved treatment of pancreatic cancer using oxygen loaded microbubbles as a delivery vehicle. Biomaterials 2016, 80, 20–32.
McEwan, C.; Fowley, C.; Nomikou, N.; McCaughan, B.; McHale, A. P.; Callan, J. F. Polymeric microbubbles as delivery vehicles for sensitizers in sonodynamic therapy. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14926–14930.
Chen, H.; Hwang, J. H. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction for chemotherapeutic drug delivery to solid tumors. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2013, 1, 10.
Fu, Z. W.; Popov, V. Parametric study of acoustically-driven microbubble cavitations in a sonochemical reactor. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 415–427.
Yoon, Y. I.; Kwon, Y. S.; Cho, H. S.; Heo, S. H.; Park, K. S.; Park, S. G.; Lee, S. H.; Hwang, S. I.; Kim, Y. I.; Jae, H. J. et al. Ultrasound-mediated gene and drug delivery using a microbubble-liposome particle system. Theranostics 2014, 4, 1133–1144.
Ibsen, S.; Schutt, C. E.; Esener, S. Microbubble-mediated ultrasound therapy: A review of its potential in cancer treatment. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2013, 7, 375–388.
Wang, Q. X.; Manmi, K.; Liu, K. K. Cell mechanics in biomedical cavitation. Interface Focus 2015, 5, 20150018.
Zhang, L.; Sun, Z. X.; Ren, P. P.; You, M. J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L. Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. H.; Yan, F.; Zheng, H. R. et al. Localized delivery of shRNA against PHD2 protects the heart from acute myocardial infarction through ultrasoundtargeted cationic microbubble destruction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 51–66.
Dewitte, H.; Vanderperren, K.; Haers, H.; Stock, E.; Duchateau, L.; Hesta, M.; Saunders, J. H.; De Smedt, S. C.; Lentacker, I. Theranostic mRNA-loaded microbubbles in the lymphatics of dogs: Implications for drug delivery. Theranostics 2015, 5, 97–109.
Kheirolomoom, A.; Dayton, P. A.; Lum, A. F. H.; Little, E.; Paoli, E. E.; Zheng, H. R.; Ferrara, K. W. Acoustically-active microbubbles conjugated to liposomes: Characterization of a proposed drug delivery vehicle. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 275–284.
Geers, B.; Lentacker, I.; Sanders, N. N.; Demeester, J.; Meairs, S.; De Smedt, S. C. Self-assembled liposome-loaded microbubbles: The missing link for safe and efficient ultrasound triggered drug-delivery. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 249–256.
Deng, Z. T.; Yan, F.; Jin, Q. F.; Li, F.; Wu, J. R.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H. R. Reversal of multidrug resistance phenotype in human breast cancer cells using doxorubicin-liposomemicrobubble complexes assisted by ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 109–116.
Zhu, X.; Guo, J.; He, C. C.; Geng, H. X.; Yu, G. S.; Li, J. Q.; Zheng, H. R.; Ji, X. J.; Yan, F. Ultrasound triggered image-guided drug delivery to inhibit vascular reconstruction via paclitaxel-loaded microbubbles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21683.
Fang, Q.; Yang, D. A porphyrin dimer salt combined with the ether bond and its manufacturing method. China Patent ZL200910179116.5, Aug 29, 2012.
Wang, X. B.; Hu, J. M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S. L.; Liu, Y. C.; Xiong, W. L.; Liu, Q. H. Analysis of the in vivo and in vitro effects of photodynamic therapy on breast cancer by using a sensitizer, sinoporphyrin sodium. Theranostics 2015, 5, 772–786.
Yan, X. F.; Hu, H.; Lin, J.; Jin, A. J.; Niu, G.; Zhang, S. L.; Huang, P.; Shen, B. Z.; Chen, X. Y. Optical and photoacoustic dual-modality imaging guided synergistic photodynamic/photothermal therapies. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2520–2526.
Yan, X. F.; Niu, G.; Lin, J.; Jin, A. J.; Hu, H.; Tang, Y. X.; Zhang, Y. J.; Wu, A. G.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S. L. et al. Enhanced fluorescence imaging guided photodynamic therapy of sinoporphyrin sodium loaded graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2015, 42, 94–102.
Xiong, W. L.; Wang, P.; Hu, J. M.; Jia, Y. L.; Wu, L. J.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, Q. H.; Wang, X. B. A new sensitizer DVDMS combined with multiple focused ultrasound treatments: An effective antitumor strategy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17485.
Li, C. F.; Zhang, K.; Wang, P.; Hu, J. M.; Liu, Q. H.; Wang, X. B. Sonodynamic antitumor effect of a novel sonosensitizer on S180 solid tumor. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 50–59.
Li, Y. X.; Wang, P.; Chen, X. Y.; Hu, J. M.; Liu, Y. C.; Wang, X. B.; Liu, Q. H. Activation of microbubbles by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound enhances the cytotoxicity of curcumin involving apoptosis induction and cell motility inhibition in human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 26–36.
Mihaljević, B.; Katušin-Ražem, B.; Ražem, D. The reevaluation of the ferric thiocyanate assay for lipid hydroperoxides with special considerations of the mechanistic aspects of the response. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 21, 53–63.
Jia, Y. L.; Yuan, W. J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Q. H.; Wang, X. B. Comparison of cell membrane damage induced by the therapeutic ultrasound on human breast cancer MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR cells. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 128–135.
Pulaski, B. A.; Terman, D. S.; Khan, S.; Muller, E.; Ostrand- Rosenberg, S. Cooperativity of Staphylococcal aureus enterotoxin B superantigen, major histocompatibility complex class II, and CD80 for immunotherapy of advanced spontaneous metastases in a clinically relevant postoperative mouse breast cancer model. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2710–2715.
Lentacker, I.; Geers, B.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S. C.; Sanders, N. N. Design and evaluation of doxorubicincontaining microbubbles for ultrasound-triggered doxorubicin delivery: Cytotoxicity and mechanisms involved. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 101–108.
Yan, F.; Li, L.; Deng, Z. T.; Jin, Q. F.; Chen, J. J.; Yang, W.; Yeh, C. K.; Wu, J. R.; Shandas, R.; Liu, X. et al. Paclitaxelliposome–microbubble complexes as ultrasound-triggered therapeutic drug delivery carriers. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 246–255.
Emmer, M.; van Wamel, A.; Goertz, D. E.; de Jong, N. The onset of microbubble vibration. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 941–949.
McLaughlan, J. R.; Harput, S.; Abou-Saleh, R. H.; Peyman, S. A.; Evans, S.; Freear, S. Characterisation of liposomeloaded microbubble populations for subharmonic imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 346–356.
Wang, P.; Wang, X. B.; Zhang, K.; Gao, K. L.; Song, M.; Liu, Q. H. The spectroscopy analyses of PpIX by ultrasound irradiation and its sonotoxicity in vitro. Ultrasonics 2013, 53, 935–942.
Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. B.; Su, X. M.; Liu, Q. H. Activation of microbubbles by low-level therapeutic ultrasound enhances the antitumor effects of doxorubicin. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2739–2753.
Sennoga, C. A.; Kanbar, E.; Auboire, L.; Dujardin, P. A.; Fouan, D.; Escoffre, J. M.; Bouakaz, A. Microbubblemediated ultrasound drug-delivery and therapeutic monitoring. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 11, 1–13.
Qin, J. L.; Wang, T. Y.; Willmann, J. K. Sonoporation: Applications for cancer therapy. In Therapeutic Ultrasound; Escoffre, J. M.; Bouakaz, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Switzerland, 2016; pp 263–291.
Meijering, B. D. M.; Juffermans, L. J. M.; van Wamel, A.; Henning, R. H.; Zuhorn, I. S.; Emmer, M.; Versteilen, A. M. G.; Paulus, V. W. J.; van Gilst, W. H.; Kooiman, K. et al. Ultrasound and microbubble-targeted delivery of macromolecules is regulated by induction of endocytosis and pore formation. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 679–687.
Wang, H. P.; Wang, X. B.; Zhang, S. L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q. H. Sinoporphyrin sodium, a novel sensitizer, triggers mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in ECA-109 cells via production of reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 3077–3090.
Theek, B.; Baues, M.; Ojha, T.; Möckel, D.; Veettil, S. K.; Steitz, J.; van Bloois, L.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Sonoporation enhances liposome accumulation and penetration in tumors with low EPR. J. Control. Release 2016, 231, 77–85.
Luo, T. T.; Sun, J. C.; Zhu, S. Y.; He, J.; Hao, L.; Xiao, L. L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q. Q.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z. G. et al. Ultrasound-mediated destruction of oxygen and paclitaxel loaded dual-targeting microbubbles for intraperitoneal treatment of ovarian cancer xenografts. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 1–11.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81472846 and 81571834), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M600684), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. GK201602003), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2017JM8004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., An, H., Wang, X. et al. Ultrasound-triggered release of sinoporphyrin sodium from liposome-microbubble complexes and its enhanced sonodynamic toxicity in breast cancer. Nano Res. 11, 1038–1056 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1719-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1719-8