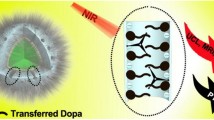
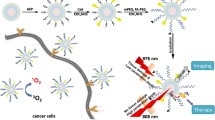
Abstract
Significant attenuation and overheating, caused by the absorption of the excitation band (980 nm) in water, are the major obstacles in the in vivo application of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). Therefore, appropriately-structured Nd3+-doped UCNPs with 808 nm excitation could be a promising alternative. Herein, we developed core–shell–shell structured Nd3+-sensitized UCNPs as imaging agents, and decorated them onto the surface of polydopamine (PDA) to construct a novel multifunctional core/satellite nanotheranostic (PDA@UCNPs) for in vivo imaging guidance photothermal therapy using single 808 nm laser irradiation. The core–shell–shell structured design enabled outstanding upconversion luminescence properties and strong X-ray attenuation, thereby making the nanocomposites potential candidates for excellent upconversion luminescence/computed tomography dual modal imaging. In addition, the PDA core not only provides high photothermal conversion efficiency and outstanding antitumor effect, but also endows the platform with robust biocompatibility owing to its natural features. Therefore, this multifunctional nanocomposite could be a promising theranostic in future oncotherapy, with high therapeutic effectiveness but low side effects. This study would stimulate interest in designing bio-application-compatible multifunctional nanocomposites, especially for cancer diagnosis and treatment in vivo.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lal, S.; Clare, S. E.; Halas, N. J. Nanoshell-enabled photothermal cancer therapy: Impending clinical impact. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1842–1851.
Robinson, J. T.; Tabakman, S. M.; Liang, Y. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Casalongue, H. S.; Vinh, D.; Dai, H. J. Ultrasmall reduced graphene oxide with high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6825–6831.
Xia, Y. N.; Li, W. Y.; Cobley, C. M.; Chen, J. Y.; Xia, X. H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, M. X.; Cho, E. C.; Brown, P. K. Gold nanocages: From synthesis to theranostic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 914–924.
Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282.
Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782.
Ke, H. T.; Wang, J. R.; Dai, Z. F.; Jin, Y. S.; Qu, E. Z.; Xing, Z. W.; Guo, C. X.; Yue, X. L.; Liu, J. B. Gold-nanoshelled microcapsules: Atheranostic agent for ultrasound contrast imaging and photothermal therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3017–3021.
Liu, H. Y.; Liu, T. L.; Wu, X. L.; Li, L. L.; Tan, L. F.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. Q. Targeting gold nanoshells on silica nanorattles: A drug cocktail to fight breast tumors via a single irradiation with near-infrared laser light. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 755–761.
Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Li, Y. G.; Chen, J. H.; Wang, C.; Shao, M. W.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z. Facile preparation of multifunctional upconversionnanoprobes for multimodal imaging and dual-targeted photothermal therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7385–7390.
Tian, Q. W.; Tang, M. H.; Sun, Y. G.; Zou, R. J.; Chen, Z. G.; Zhu, M. F.; Yang, S. P.; Wang, J. L.; Wang, J. H.; Hu, J. Q. Hydrophilic flower-like CuS superstructures as an efficient 980 nm laser-driven photothermal agent for ablation of cancer cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 23, 3542–3547.
Tian, Q. W.; Jiang, F. R.; Zou, R. J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z. G.; Zhu, M. F.; Yang, S. P.; Wang, J. L.; Wang, J. H.; Hu, J. Q. Hydrophilic Cu9S5 nanocrystals: A photothermal agent with a 25.7% heat conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells in vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9761–9771.
Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. X.; Sun, X. M.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z. Graphene in mice: Ultrahigh in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3318–3323.
Yang, K.; Feng, L. Z.; Shi, X. Z.; Liu, Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 530–547.
Li, C. X.; Bolisetty, S.; Chaitanya, K.; Adamcik, J.; Mezzenga, R. Tunable carbon nanotube/protein core-shell nanoparticles with NIR- and enzymatic-responsive cytotoxicity. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1010–1015.
Huang, X. Q.; Tang, S. H.; Mu, X. L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, G. X.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Ruan, F. X.; Yang, Z. L.; Zheng, N. F. Freestanding palladium nanosheets with plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 28–32.
Tang, S. H.; Huang, X. Q.; Zheng, N. F. Silica coating improves the efficacy of Pd nanosheets for photothermal therapy of cancer cells using near infrared laser. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3948–3950.
Yang, J.; Choi, J.; Bang, D.; Kim, E.; Lim, E.-K.; Park, H.; Suh, J.-S.; Lee, K.; Yoo, K.-H.; Kim, E.-K. et al. Convertible organic nanoparticles for near-infrared photothermal ablation of cancer cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 441–444.
Liu, Y. L.; Ai, K. L.; Liu, J. H.; Deng, M.; He, Y. Y.; Lu, L. H. Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres: An efficient near-infrared photothermal therapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1353–1359.
Stritzker, J.; Kirscher, L.; Scadeng, M.; Deliolanis, N. C.; Morscher, S.; Symvoulidis, P.; Schaefer, K.; Zhang, Q.; Buckel, L.; Hess, M. et al. Vaccinia virus-mediated melanin production allows MR and optoacoustic deep tissue imaging and laser-induced thermotherapy of cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3316–3320.
Wang, F.; Banerjee, D.; Liu, Y. S.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, X. G. Upconversion nanoparticles in biological labeling, imaging, and therapy. Analyst 2010, 135, 1839–1854.
Wang, G. F.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. D. Lanthanide-doped nanocrystals: Synthesis, optical-magnetic properties, and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 322–332.
Deng, M. L.; Wang, L. Y. Unexpected luminescence enhancement of upconverting nanocrystals by cation exchange with well retained small particle size. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 782–793.
Liu, Y. S.; Tu, D. T.; Zhu, H. M.; Chen, X. Y. Lanthanidedoped luminescent nanoprobes: Controlled synthesis, optical spectroscopy, and bioapplications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6924–6958.
Gorris, H. H.; Wolfbeis, O. S. Photon-upconverting nanoparticles for optical encoding and multiplexing of cells, biomolecules, and microspheres. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3584–3600.
Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Shao, M. W.; Lee, S.; Liu, Z. Highly-sensitive multiplexed in vivo imaging using PEGylatedupconversion nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 722–732.
Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. Upconversion nanoparticles and their composite nanostructures for biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 23–37.
Chen, G. Y.; Qiu, H. L.; Prasad, P. N.; Chen, X. Y. Upconversion nanoparticles: Design, nanochemistry, and applications in theranostics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5161–5214.
Sun, L. D.; Wang, Y. F.; Yan, C. H. Paradigms and challenges for bioapplication of rare earth upconversion luminescent nanoparticles: Small size and tunable emission/excitation spectra. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1001–1009.
Zhou, J.; Liu, Q.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Y. Upconversion luminescent materials: Advances and applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 395–465.
Chen, Y. Y.; Liu, S.; Hou, Z. Y.; Ma, P.; Yang, D. M.; Li, C. X.; Lin, J. Multifunctional electrospinning composite fibers for orthotopic cancer treatment in vivo. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1917–1931.
Ni, D. L.; Zhang, J. W.; Bu, W. B.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Z. W.; Xing, H. Y.; Wang, J.; Duan, F.; Liu, Y. Y.; Fan, W. P. et al. PEGylated NaHoF4 nanoparticles as contrast agents for both X-ray computed tomography and ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 218–225.
Weissleder, R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 316–317.
Byrnes, K. R.; Waynant, R. W.; Ilev, I. K.; Wu, X. J.; Barna, L.; Smith, K.; Heckert, R.; Gerst, H.; Anders, J. J. Light promotes regeneration and functional recovery and alters the immune response after spinal cord injury. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 36, 171–185.
Zhan, Q. Q.; Qian, J.; Liang, H. J.; Somesfalean, G.; Wang, D.; He, S. L.; Zhang, Z. G.; Andersson-Engels, S. Using 915 nm laser excited Tm3+/Er3+/Ho3+-doped NaYbF4 upconversion nanoparticles for in vitro and deeper in vivo bioimaging without overheating irradiation. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3744–3757.
Zou, W. Q.; Visser, C.; Maduro, J. A.; Pshenichnikov, M. S.; Hummelen, J. C. Broadband dye-sensitized upconversion of near-infrared light. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 560–564.
Shen, J.; Chen, G. Y.; Vu, A. M.; Fan, W.; Bilsel, O. S.; Chang, C. C.; Han, G. Engineering the upconversion nanoparticle excitation wavelength: Cascade sensitization of tridoped upconversion colloidal nanoparticles at 800 nm. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2013, 1, 644–650.
Wang, Y. F.; Liu, G. Y.; Sun, L. D.; Xiao, J. W.; Zhou, J. C.; Yan, C. H. Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanophosphors: Efficient in vivobioimaging probes with minimized heating effect. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7200–7206.
Xie, X. J.; Gao, N. Y.; Deng, R. R.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Q. H.; Liu, X. G. Mechanistic investigation of photon upconversion in Nd3+-sensitized core–shell nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12608–12611.
Wen, H. L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X.; Hung, T. F.; Wang, B. L.; Zhu, G. Y.; Yu, S. F.; Wang, F. Upconverting near-infrared light through energy management in core–shell–shell nanoparticles. Angew.Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13419–13423.
Zhong, Y. T.; Tian, G.; Gu, Z. J.; Yang, Y. J.; Gu, L.; Zhao, Y. L.; Ma, Y.; Yao, J. N. Elimination of photon quenching by a transition layer to fabricate a quenching-shield sandwich structure for 800 nm excited upconversion luminescence of Nd3+-sensitized nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2831–2837.
Chen, Y. Y.; Liu, B.; Deng, X. R.; Huang, S. S.; Hou, Z. Y.; Li, C. X.; Lin, J. Multifunctional Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanomaterials for synchronous tumor diagnosis and treatment. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8574–8583.
Wang, D.; Xue, B.; Kong, X. G.; Tu, L. P.; Liu, X. M.; Zhang, Y. L.; Chang, Y. L.; Luo, Y. S.; Zhao, H. Y.; Zhang, H. 808 nm driven Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanostructures for photodynamic therapy and simultaneous fluorescence imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 190–197.
Zou, X. M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Chen, M.; Yao, L. M.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Y. An Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanophosphor modified with a cyanine dye for the ratiometricupconversion luminescence bioimaging of hypochlorite. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4105–4113.
Liu, B.; Chen, Y. Y.; Li, C. X.; He, F.; Hou, Z. Y.; Huang, S. S.; Zhu, H. M.; Chen, X. Y.; Lin, J. Poly(acrylic acid) modification of Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanophosphors for highly efficient UCL imaging and pH-responsive drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4717–4729.
Wang, Y. H.; Wang, H. G.; Liu, D. P.; Song, S. Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. J. Graphene oxide covalently grafted upconversion nanoparticles for combined NIR mediated imaging and photothermal/photodynamic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7715–7724.
Wang, Y. H.; Song, S. Y.; Liu, J. H.; Liu, D. P.; Zhang, H. J. ZnO-functionalized upconvertingnanotheranostic agent: Multi-modality imaging-guided chemotherapy with on-demand drug release triggered by pH. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 536–540.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the financial aid from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51502284, 51372242, 51402286, 21521092, 21590794, and 21210001), the Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan Science and Technology Cooperation Special Project of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2014DFT10310), the Program of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province of China (No. 20140201007GX), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB643802), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDB20030300) and the Jilin Province Youth Foundation (No. 20150520007JH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1555_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Multifunctional core/satellite polydopamine@Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanocomposite: A single 808 nm near-infrared light-triggered theranostic platform for in vivo imaging-guided photothermal therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, X., Liu, J., Liu, D. et al. Multifunctional core/satellite polydopamine@Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanocomposite: A single 808 nm near-infrared light-triggered theranostic platform for in vivo imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 10, 3434–3446 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1555-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1555-x