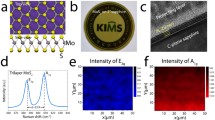
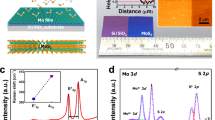
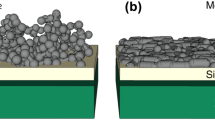
Abstract
Layered semiconductors with atomic thicknesses are becoming increasingly important as active elements in high-performance electronic devices owing to their high carrier mobilities, large surface-to-volume ratios, and rapid electrical responses to their surrounding environments. Here, we report the first implementation of a highly sensitive chemical-vapor-deposition-grown multilayer MoSe2 field-effect transistor (FET) in a NO2 gas sensor. This sensor exhibited ultra-high sensitivity (S = ca. 1,907 for NO2 at 300 ppm), real-time response, and rapid on–off switching. The high sensitivity of our MoSe2 gas sensor is attributed to changes in the gap states near the valence band induced by the NO2 gas absorbed in the MoSe2, which leads to a significant increase in hole current in the off-state regime. Device modeling and quantum transport simulations revealed that the variation of gap states with NO2 concentration is the key mechanism in a MoSe2 FET-based NO2 gas sensor. This comprehensive study, which addresses material growth, device fabrication, characterization, and device simulations, not only indicates the utility of MoSe2 FETs for high-performance chemical sensors, but also establishes a fundamental understanding of how surface chemistry influences carrier transport in layered semiconductor devices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui, Y.; Wei, Q. Q.; Park, H.; Lieber, C. M. Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 2001, 293, 1289–1292.
Lavrik, N. V.; Sepaniak, M. J.; Datskos, P. G. Cantilever transducers as a platform for chemical and biological sensors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 2229–2253.
Liu, Y. X.; Dong, X. C.; Chen, P. Biological and chemical sensors based on graphene materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2283–2307.
Lee, J.; Dak, P.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Choi, W.; Alam, M. A.; Kim, S. Two-dimensional layered MoS2 biosensors enable highly sensitive detection of biomolecules. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7352.
Kong, J.; Franklin, N. R.; Zhou, C. W.; Chapline, M. G.; Peng, S.; Cho, K.; Dai, H. J. Nanotube molecular wires as chemical sensors. Science 2000, 287, 622–625.
Tamvakos, A.; Korir, K.; Tamvakos, D.; Calestani, D.; Cicero, G.; Pullini, D. NO2 gas sensing mechanism of ZnO thin-film transducers: Physical experiment and theoretical correlation study. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 406–412.
Collins, P. G.; Bradley, K.; Ishigami, M.; Zettl, A. Extreme oxygen sensitivity of electronic properties of carbon nanotubes. Science 2000, 287, 1801–1804.
Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Liu, G.; Abbas, A. N.; Fathi, M.; Zhou, C. W. High-performance chemical sensing using Schottky-contacted chemical vapor deposition grown monolayer MoS2 transistors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5304–5314.
Lu, G. H.; Park, S.; Yu, K. H.; Ruoff, R. S.; Ocola, L. E.; Rosenmann, D.; Chen, J. H. Toward practical gas sensing with highly reduced graphene oxide: A new signal processing method to circumvent run-to-run and device-to-device variations. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1154–1164.
Zhang, J.; Boyd, A.; Tselev, A.; Paranjape, M.; Barbara, P. Mechanism of NO2 detection in carbon nanotube field effect transistor chemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 123112.
Cho, B.; Hahm, M. G.; Choi, M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, A. R.; Lee, Y.-J.; Park, S.-G.; Kwon, J.-D.; Kim, C. S.; Song, M. et al. Charge-transfer-based gas sensing using atomic-layer MoS2. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8052.
Late, D. J.; Huang, Y.-K.; Liu, B.; Acharya, J.; Shirodkar, S. N.; Luo, J. J.; Yan, A. M.; Charles, D.; Waghmare, U. V.; Dravid, V. P. et al. Sensing behavior of atomically thinlayered MoS2 transistors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4879–4891.
Li, H.; Yin, Z. Y.; He, Q. Y.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Lu, G.; Fam, D. W. H.; Tok, A. I. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Fabrication of single- and multilayer MoS2 film-based field-effect transistors for sensing NO at room temperature. Small 2012, 8, 63–67.
Boarino, L.; Baratto, C.; Geobaldo, F.; Amato, G.; Comini, E.; Rossi, A. M.; Faglia, G.; Lérondel, G.; Sberveglieri, G. NO2 monitoring at room temperature by a porous silicon gas sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2000, 69–70, 210–214.
Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G.; Pan, Z. W.; Wang, Z. L. Stable and highly sensitive gas sensors based on semiconducting oxide nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 1869–1871.
Das, A.; Dost, R.; Richardson, T.; Grell, M.; Morrison, J. J.; Turner, M. L. A nitrogen dioxide sensor based on an organic transistor constructed from smorphous semiconducting polymers. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4018–4023.
McAlpine, M. C.; Ahmad, H.; Wang, D. W.; Heath, J. R. Highly ordered nanowire arrays on plastic substrates for ultrasensitive flexible chemical sensors. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 379–384.
Zhang, D. H.; Liu, Z. Q.; Li, C.; Tang, T.; Liu, X. L.; Han, S.; Lei, B.; Zhou, C. W. Detection of NO2 down to ppb levels using individual and multiple In2O3 nanowire devices. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1919–1924.
Cho, B.; Yoon, J.; Lim, S. K.; Kim, A. R.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Kwon, J.-D.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, B. H. et al. Chemical sensing of 2D graphene/MoS2 heterostructure device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16775–16780.
Late, D. J.; Doneux, T.; Bougouma, M. Single-layer MoSe2 based NH3 gas sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 233103.
Samnakay, R.; Jiang, C.; Rumyantsev, S. L.; Shur, M. S.; Balandin, A. A. Selective chemical vapor sensing with fewlayer MoS2 thin-film transistors: Comparison with graphene devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 023115.
Rhyee, J.-S.; Kwon, J.; Dak, P.; Kim, J. H.; Kim, S. M.; Park, J.; Hong, Y. K.; Song, W. G.; Omkaram, I.; Alam, M. A. et al. High-mobility transistors based on large-area and highly crystalline CVD-grown MoSe2 films on insulating substrates. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2316–2321.
Datta, S. Quantum Transport: Atom to Transistor, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2005.
Yun, W. S.; Han, S. W.; Hong, S. C.; Kim, I. G.; Lee, J. D. Thickness and strain effects on electronic structures of transition metal dichalcogenides: 2H-MX2 semiconductors (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se, Te). Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 033305.
Kumar, A.; Ahluwalia, P. K. Tunable dielectric response of transition metals dichalcogenides MX2 (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se, Te): Effect of quantum confinement. Phys. B-Condens. Matter 2012, 407, 4627–4634.
Tongay, S.; Zhou, J.; Ataca, C.; Lo, K.; Matthews, T. S.; Li, J. B.; Grossman, J. C.; Wu, J. Q. Thermally driven crossover from indirect toward direct bandgap in 2D semiconductors: MoSe2 versus MoS2. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5576–5580.
Bissessur, R.; Xu, H. Nanomaterials based on molybdenum diselenide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 117, 335–337.
Tonndorf, P.; Schmidt, R.; Böttger, P.; Zhang, X.; Börner, J.; Liebig, A.; Albrecht, M.; Kloc, C.; Gordan, O.; Zahn, D. R. T. et al. Photoluminescence emission and raman response of monolayer MoS2, MoSe2, and WSe2. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 4908–4916.
Zhao, Y. Y.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Araujo, P. T.; Gan, C. K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Quek, S. Y.; Dresselhaus, M. S. et al. Interlayer breathing and shear modes in few-trilayer MoS2 and WSe2. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1007–1015.
Jung, C.; Kim, S. M.; Moon, H.; Han, G.; Kwon, J.; Hong, Y. K.; Omkaram, I.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, J. Highly crystalline CVD-grown multilayer MoSe2 thin film transistor for fast photodetector. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15313.
Xia, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.-Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Zhu, D.-D.; Li, J.-J.; Gu, C.-Z.; Meng, X.-M. CVD synthesis of large-area, highly crystalline MoSe2 atomic layers on diverse substrates and application to photodetectors. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8949–8955.
Yue, Q.; Shao, Z.; Chang, S.; Li, J. Adsorption of gas molecules on monolayer MoS2 and effect of applied electric field. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 425.
Sharma, M.; Jamdagni, P.; Kumar, A.; Ahluwalia, P. Interactions of gas molecules with monolayer MoSe2: A first principle study. In AIP Conference Proceedings, Dae Solid State Physics Symposium 2015; AIP Publishing: Uttar Pradesh, India, 2016; pp 140045.
Fan, Z. Y.; Lu, J. G. Gate-refreshable nanowire chemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 123510.
Fan, S.-W.; Srivastava, A. K.; Dravid, V. P. UV-activated room-temperature gas sensing mechanism of polycrystalline ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 142106.
Fowler, J. D.; Allen, M. J.; Tung, V. C.; Yang, Y.; Kaner, R. B.; Weiller, B. H. Practical chemical sensors from chemically derived graphene. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 301–306.
Li, J.; Lu, Y. J.; Ye, Q.; Cinke, M.; Han, J.; Meyyappan, M. Carbon nanotube sensors for gas and organic vapor detection. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 929–933.
Some, S.; Xu, Y.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Qin, H. Y.; Kulkarni, A.; Kim, T.; Lee, H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensor using hydrophilic and hydrophobic graphenes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1868.
Wöllenstein, J.; Böttner, H.; Jaegle, M.; Becker, W. J.; Wagner, E. Material properties and the influence of metallic catalysts at the surface of highly dense SnO2 films. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2000, 70, 196–202.
Ryzhikov, A.; Labeau, M.; Gaskov, A. Al2O3 (M = Pt, Ru) catalytic membranes for selective semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2005, 109, 91–96.
Fleischer, M.; Meixner, H. Selectivity in high-temperature operated semiconductor gas-sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 1998, 52, 179–187.
Matsuguchi, M.; Uno, T. Molecular imprinting strategy for solvent molecules and its application for QCM-based VOC vapor sensing. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2006, 113, 94–99.
Dubois, M.; Brunet, J.; Pauly, A.; Spinelle, L.; Ndiaye, A.; Guérin, K.; Varenne, C.; Lauron, B.; Klyushin, A. Y.; Vinogradov, A. S. A carbonaceous chemical filter for the selective detection of NO2 in the environment. Carbon 2013, 52, 17–29.
Pauly, A.; Dubois, M.; Brunet, J.; Spinelle, L.; Ndiaye, A.; Guérin, K.; Varenne, C.; Vinogradov, A. S.; Klyushin, A. Y. An innovative gas sensor system designed from a sensitive organic semiconductor downstream a nanocarbonaceous chemical filter for selective detection of NO2 in an environmental context. Part II: Interpretations of O3/ nanocarbons and NO2/nanocarbons interactions. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2012, 173, 652–658.
Brunet, J.; Pauly, A.; Varenne, C.; Ndiaye, A. L.; Dubois, M. Nanocarbonaceous filters for the achievement of highly sensitive and selective NO2 monitoring by means of phthalocyanine-based resistive sensors. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 29–32.
Acknowledgements
This research is also supported in part by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Nos. NRF-2013M3C1A3059590, NRF-2014M3A9D7070732, and NRF-2015R1A5A1037548). This work was supported in part by U.S. National Science Foundation under grant CMMI 826276, and in part by NSERC Discovery Grant (No. RGPIN-05920-2014). This research was supported by the Commercializations Promotion Agency for R&D Outcomes (COMPA) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MISP) and in part by the fund from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) institutional program. Computing resources were provided by SHARCNET through Compute Canada. D. Y. acknowledges the financial support by WIN Nanofellowship. The authors would like to thank Prof. Jong-Soo Rhyee for supporting CVD MoSe2 flakes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1725-x.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, J., Yin, D., Liu, N. et al. A highly sensitive chemical gas detecting transistor based on highly crystalline CVD-grown MoSe2 films. Nano Res. 10, 1861–1871 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1291-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1291-7