Abstract
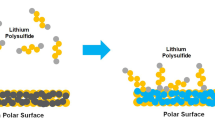
Lithium/sulfur (Li/S) cells have great potential to become mainstream secondary batteries due to their ultra-high theoretical specific energy. The major challenge for Li/S cells is the unstable cycling performance caused by the sulfur’s insulating nature and the high-solubility of the intermediate polysulfide products. Several years of efforts to develop various fancy carbon nanostructures, trying to physically encapsulate the polysulfides, did not yet push the cell’s cycle life long enough to compete with current Li ion cells. The focus of this review is on the recent progress in chemical bonding strategy for trapping polysulfides through employing functional groups and additives in carbon matrix. Research results on understanding the working mechanism of chemical interaction between polysulfides and functional groups (e.g. O–, B–, N–and S–) in carbon matrix, metal-based additives, or polymer additives during charge/discharge are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner, J. A. A realizable renewable energy future. Science 1999, 285, 687–689.
Goodenough, J. B. Evolution of strategies for modern rechargeable batteries. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1053–1061.
Li, N.; Weng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Cheng, H. M.; Zhou, H. An aqueous dissolved polysulfide cathode for lithium–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3307–3312.
Zhang, S.; Liu, M. N.; Ma, F.; Ye, F. M.; Li, H. F.; Zhang, X. Y.; Hou, Y.; Qiu, Y. C.; Li, W. F.; Wang, J. et al. A high energy density Li2S@C nanocomposite cathode with a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube top current collector. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18913–18919.
Xu, J.; Shui, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, H. K.; Dou, S. X.; Jeon, I. Y.; Seo, J. M.; Baek, J. B.; Dai, L. Sulfur-graphene nanostructured cathodes via ball-milling for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10920–10930.
Ji, X. L.; Lee, K. T.; Nazar, L. F. A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 500–506.
Nan, C. Y.; Lin, Z.; Liao, H. G.; Song, M. K.; Li, Y. D.; Cairns, E. J. Durable carbon-coated Li2S core–shell spheres for high performance lithium/sulfur cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4659–4663.
Moon, S.; Jung, Y. H.; Jung, W. K.; Jung, D. S.; Choi, J. W.; Kim, D. K. Encapsulated monoclinic sulfur for stable cycling of Li–S rechargeable batteries. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6547–6553.
Zhang, C. F.; Wu, H. B.; Yuan, C. Z.; Guo, Z. P.; Lou, X. W. Confining sulfur in double-shelled hollow carbon spheres for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9592–9595.
Elazari, R.; Salitra, G.; Garsuch, A.; Panchenko, A.; Aurbach, D. Sulfur-impregnated activated carbon fiber cloth as a binder-free cathode for rechargeable Li–S batteries. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5641–5644.
Li, H. F.; Yang, X. W.; Wang, X. M.; Liu, M. N.; Ye, F. M.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y. C.; Li, W. F.; Zhang, Y. G. Dense integration of graphene and sulfur through the soft approach for compact lithium/sulfur battery cathode. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 468–475.
Ji, L. W.; Rao, M. M.; Aloni, S.; Wang, L.; Cairns, E. J.; Zhang, Y. G. Porous carbon nanofiber–sulfur composite electrodes for lithium/sulfur cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 5053–5059.
Ye, F. M.; Hou, Y.; Liu, M. N.; Li, W. F.; Yang, X. W.; Qiu, Y. C.; Zhou, L. S.; Li, H. F.; Xu, Y. J.; Zhang, Y. G. Fabrication of mesoporous Li2S–C nanofibers for high performance Li/Li2S cell cathodes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9472–9476.
Zheng, G. Y.; Yang, Y.; Cha, J. J.; Hong, S. S.; Cui, Y. Hollow carbon nanofiber-encapsulated sulfur cathodes for high specific capacity rechargeable lithium batteries. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4462–4467.
Wang, H. L.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Y. Y.; Robinson, J. T.; Li, Y. G.; Jackson, A.; Cui, Y.; Dai, H. J. Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium–sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2644–2647.
Xin, S.; Gu, L.; Zhao, N. H.; Yin, Y. X.; Zhou, L. J.; Guo, Y. G.; Wan, L. J. Smaller sulfur molecules promise better lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18510–18513.
Yang, C. P.; Yin, Y. X.; Guo, Y. G.; Wan, L. J. Electrochemical (de)lithiation of 1D sulfur chains in Li–S batteries: Amodel system study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2215–2218.
Li, L.; Ruan, G.; Peng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Fei, H.; Raji, A. R. O.; Samuel, E. L. G.; Tour, J. M. Enhanced cycling stability of lithium sulfur batteries using sulfur-polyaniline-graphene nanoribbon composite cathodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 15033–15039.
Zheng, S. Y.; Yi, F.; Li, Z. P.; Zhu, Y. J.; Xu, Y. H.; Luo, C.; Yang, J. H.; Wang, C. S. Copper-stabilized sulfur–microporous carbon cathodes for Li–S batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4156–4163.
Xiao, L. F.; Cao, Y. L.; Xiao, J.; Schwezer, B.; Engelhard, M. H.; Saraf, L. V.; Nie, Z. M.; Exarhos, G. J.; Liu, J. A soft approach to encapsulate sulfur: Polyaniline nanotubes for lithium–sulfur batteries with long cycle life. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1176–1181.
Ji, L. W.; Rao, M. M.; Zheng, H. M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. C.; Duan, W. H.; Guo, J. H.; Cairns, E. J.; Zhang, Y. G. Graphene oxide as a sulfur immobilizer in high performance lithium/sulfur cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18522–18525.
Qiu, Y. C.; Rong, G. L.; Yang, J.; Li, G. Z.; Ma, S.; Wang, X. L.; Pan, Z. H.; Hou, Y.; Liu, M. N.; Ye, F. M. et al. Highly nitridated graphene–Li2S cathodes with stable modulated cycles. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501369.
Demir-Cakan, R.; Morcrette, M.; Nouar, F.; Davoisne, C.; Devic, T.; Gonbeau, D.; Dominko, R.; Serre, C.; Gerey, G.; Tarascon, J. M. Cathode composites for Li–S batteries via the use of oxygenated porous architectures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16154–16160.
Evers, S.; Yim, T.; Nazar, L. F. Understanding the nature of absorption/adsorption in nanoporous polysulfide sorbents for the Li–S battery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19653–19658.
Chung, S. H.; Manthiram, A. A natural carbonized leaf as polysulfide diffusion inhibitor for high-performance lithium–sulfur battery cells. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1655–1661.
Song, M. K.; Zhang, Y. G.; Cairns, E. J. A long-life, high-rate lithium/sulfur cell: Amultifaceted approach to enhancing cell performance. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5891–5899.
Qiu, Y. C.; Li, W. F.; Zhao, W.; Li, G. Z.; Hou, Y.; Liu, M. N.; Zhou, L. S.; Ye, F. M.; Li, H. F.; Wie, Z. H. et al. High-rate, ultralong cycle-life lithium/sulfur batteries enabled by nitrogen-doped graphene. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4821–4827.
Manthiram, A.; Fu, Y.Z.; Chung, S. H.; Zu, C. X.; Su, Y. S. Rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11751–11787.
Song, M. K.; Cairns, E. J.; Zhang, Y. G. Lithium/sulfur batteries with high specific energy: Old challenges and new opportunities. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2186–2204.
Kim, H.; Lee, J. T.; Lee, D. C.; Magasinski, A.; Cho, W.; Yushin, G. Plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of ultrathin oxide coatings for stabilized lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 1308–1315.
Yin, Y. X.; Xin, S.; Guo, Y. G.; Wan, L. J. Lithium–sulfur batteries: Electrochemistry, materials, and prospects. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13186–13200.
Fronczek, D. N.; Bessler, W. G. Insight into lithium–sulfur batteries: Elementary kinetic modeling and impedance simulation. J. Power Source 2013, 244, 183–188.
Fu, Y. Z.; Su, Y. S.; Manthiram, A. Highly reversible lithium/dissolved polysulfide batteries with carbon nanotube electrodes. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6930–6935.
Chung, S. H.; Singhal, R.; Kalra, V.; Manthiram, A. Porous carbon mat as an electrochemical testing platform for investigating the polysulfide retention of various cathode configurations in Li–S cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2163–2169.
Su, Y. S.; Fu, Y. Z.; Guo, B. K.; Dai, S.; Manthiram, A. Fast, reversible lithium storage with a sulfur/long-chainpolysulfide redox couple. Chem.—Eur. J. 2013, 19, 8621–8626.
Xu, R.; Lu, J.; Amine, K. Progress in mechanistic understanding and characterization techniques of Li–S batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500408.
Zhang, S. G.; Ueno, K.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe M. Recent advances in electrolytes for lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500117.
Evers, S.; Nazar, L. F. New approaches for high energy density lithium–sulfur battery cathodes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1135–1143.
Manthiram, A.; Fu, Y. Z.; Su, Y. S. Challenges and prospects of lithium–sulfur batteries. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1125–1134.
Zheng, G. Y.; Zhang, Q. F.; Cha, J. J.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Y.; Seh, Z. W.; Cui, Y. Amphiphilic surface modification of hollow carbon nanofibers for improved cycle life of lithium sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1265–1270.
Zhou, W. D.; Yu, Y. C.; Chen, H.; Disalvo, F. J.; Abruña, H. D. Yolk–shell structure of polyaniline-coated sulfur for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16736–16743.
Barchasz, C.; Lepretre, J. C.; Alloin, F.; Patoux, S. New insights into the limiting parameters of the Li/S rechargeable cell. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 322–330.
Sun, H.; Xu, G. L.; Xu, Y. F.; Sun, S. G.; Zhang, X. F.; Qiu, Y. C.; Yang, S. H. A composite material of uniformly dispersed sulfur on reduced graphene oxide: Aqueous one-pot synthesis, characterization and excellent performance as the cathode in rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 726–738.
Zhao, C. Y.; Liu, L. J.; Zhao, H. L.; Krall, A.; Wen, Z. H.; Chen, J. H.; Hurley, P.; Jiang, J. W.; Li, Y. Sulfur-infiltrated porous carbon microspheres with controllable multi-modal pore size distribution for high energy lithium–sulfur batteries. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 882–888.
Chung, S. H.; Han, P.; Singhal, R.; Kalra, V.; Manthiram, A. Electrochemically stable rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries with a microporous carbon nanofiber filter for polysulfide. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500738.
Chung, S. H.; Manthiram, A. Bifunctional separator with a light-weight carbon-coating for dynamically and statically stable lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5299–5306.
Chung, S. H.; Manthiram, A. High-performance Li–S batteries with an ultra-lightweight MWCNT-coated separator. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1978–1983.
Chung, S. H.; Manthiram, A. A polyethylene glycolsupported microporous carbon coating as a polysulfide trap for utilizing pure sulfur cathodes in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7352–7357.
Bruce, P. G.; Freunberger, S. A.; Hardwick, L. J.; Tarascon, J. M. Li–O2 and Li–S batteries with high energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 19–29.
Mikhaylik, Y. V.; Akridge, J. R. Polysulfide shuttle study in the Li/S battery system. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A1969?A1976.
Huang, J. Q.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, H. J.; Liu, X. Y.; Qian, W. Z.; Wie, F. Ionic shield for polysulfides towards highly-stable lithium–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 347–353.
Liang, X.; Hart, C.; Pang, Q.; Garsuch, A.; Weiss, T.; Nazar, L. F. A highly efficient polysulfide mediator for lithium–sulfur batteries. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5682.
Oschatz, M.; Borchardt, L.; Pinkert, K.; Thieme, S.; Lohe, M. R.; Hoffmann, C.; Benusch, M.; Wisser, F. M.; Ziegler, C.; Giebeler, L. et al. Hierarchical carbide-derived carbon foams with advanced mesostructure as a versatile electrochemical energy-storage material. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1300645.
Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, L. X.; Yi, Z. Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Strasser, P.; Huang, Y. H. A highly ordered meso@microporous carbon-supported sulfur@smaller sulfur core–shell structured cathode for Li–S batteries. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9295–9303.
Jayaprakash, N.; Shen, J.; Moganty, S. S.; Corona, A.; Archer, L. A. Porous hollow carbon@sulfur composites for high-power lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5904–5908.
He, G.; Evers, S.; Liang, X.; Cuisinier, M.; Garsuch, A.; Nazar, L. F. Tailoring porosity in carbon nanospheres for lithium–sulfur battery cathodes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10920–10930.
Zhou, G. M.; Li, L.; Wang, D. W.; Shan, X. Y.; Pei, S. F.; Li, F.; Cheng, H. M. A flexible sulfur-graphene-polypropylene separator integrated electrode for advanced Li–S batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 641–647.
Chen, H. W.; Dong, W. L.; Ge, J.; Wang, C. H.; Wu, X. D.; Lu, W.; Chen, L. W. Ultrafine sulfur nanoparticles in conducting polymer shell as cathode materials for high performance lithium/sulfur batteries. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1910.
Chen, Y. M.; Li, X. Y.; Park, K. S.; Hong, J. H.; Song, J.; Zhou, L. M.; Mai, Y. W.; Huang, H. T.; Goodenough, J. B. Sulfur encapsulated in porous hollow CNTs@CNFs for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10126–10130.
Zhang, L.; Ji, L. W.; Glans, P. A.; Zhang, Y. G.; Zhu, J. F.; Guo, J. H. Electronic structure and chemical bonding of a graphene oxide–sulfur nanocomposite for use in superior performance lithium–sulfur cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 13670–13675.
Zhou, G. M.; Yin, L. C.; Wang, D. W.; Li, L.; Pei, S. F.; Gentle, I. R.; Li, F.; Cheng, H. M. Fibrous hybrid of graphene and sulfur nanocrystals for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5367–5375.
Feng, X. F.; Song, M. K.; Stolte, W. C.; Gardenghi, D.; Zhang, D.; Sun, X. H.; Zhu, J. F.; Cairns, E. J.; Guo, J. H. Understanding the degradation mechanism of rechargeable lithium/sulfur cells: A comprehensive study of the sulfur–graphene oxide cathode after discharge–charge cycling. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 16931–16940.
Yang, C. P.; Yin, Y. X.; Ye, H.; Jiang, K. C.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y. G. Insight into the effect of boron doping on sulfur/carbon cathode in lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8789–8795.
Seh, Z. W.; Wang, H. T.; Hsu, P. C.; Zhang, Q. F.; Li, W. Y.; Zheng, G. Y.; Yao, H. B.; Cui, Y. Facile synthesis of Li2S–polypyrrole composite structures for high-performance Li2S cathodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 672–676.
Song, J. X.; Xu, T.; Gordin, M. L.; Zhu, P. Y.; Lv, D. P.; Jiang, Y. B.; Chen, Y. S.; Duan, Y. H.; Wang, D. H. Nitrogendoped mesoporous carbon promoted chemical adsorption of sulfur and fabrication of high-areal-capacity sulfur cathode with exceptional cycling stability for lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1243–1250.
Guo, J. C.; Yang, Z. C.; Yu, Y. C.; Abruña, H. D.; Archer, L. A. Lithium–sulfur battery cathode enabled by lithium–nitrile interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 763–767.
Song, J. X.; Gordin, M. L.; Xu, T.; Chen, S. R.; Yu, Z. X.; Sohn, H.; Lu, J.; Ren, Y.; Duan, Y. H.; Wang, D. H. Strong lithium polysulfide chemisorption on electroactive sites of nitrogen-doped carbon composites for high-performance lithium–sulfur battery cathodes. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4325–4329.
Tang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M. Q.; Huang, J. Q.; Cheng, X. B.; Tian, G. L.; Peng, H. J.; Wei, F. Nitrogen-doped aligned carbon nanotube/graphene sandwiches: Facile catalytic growth on bifunctional natural catalysts and their applications as scaffolds for high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6100–6105.
Pang, Q.; Tang, J. T.; Huang, H.; Liang, X.; Hart, C.; Tam, K. C.; Nazar, L. F. A nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped carbon derived from polyrhodanine@cellulose for advanced lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6021–6028.
Zhou, G. M.; Paek, E.; Hwang, G. S.; Manthiram, A. Longlife Li/polysulphide batteries with high sulphur loading enabled by lightweight three-dimensional nitrogen/sulphurcodoped graphene sponge. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7760.
Seh, Z. W.; Li, W. Y.; Cha, J. J.; Zheng, G. Y.; Yang, Y.; McDowell, M. T.; Hsu, P. C.; Cui, Y. Sulphur–TiO2 yolk–shell nanoarchitecture with internal void space for long-cycle lithium–sulfur batteries. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1331.
Yao, H. B.; Zheng, G. Y.; Hsu, P. C.; Kong, D. S.; Cha, J. J.; Li, W. Y.; Seh, Z. W.; McDowell, M. T.; Yan, K.; Liang, Z. et al. Improving lithium–sulphur batteries through spatial control of sulphur species deposition on a hybrid electrode surface. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3943.
Tao, X. Y.; Wang, J. G.; Ying, Z. G.; Cai, Q. X.; Zheng, G. Y.; Gan, Y. P.; Huang, H.; Xia, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, W. K. et al. Strong sulfur binding with conducting magnéli-phase TinO2n–1 nanomaterials for improving lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5288–5294.
Pang, Q.; Kundu, D.; Cuisinier, M.; Naza, L. F. Surfaceenhanced redox chemistry of polysulphides on a metallic and polar host for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Commun. 2015, 5, 4759.
Song, M. S.; Han, S. C.; Kim, H. S.; Kim, J. H.; Kim, K. T.; Kang, Y. M.; Ahn, H. J.; Dou, S. X.; Lee, J. Y. Effects of nanosized adsorbing material on electrochemical properties of sulfur cathodes for Li/S secondary batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A791–A795.
Zhang, Y. G.; Zhao, Y.; Yermukhambetova, A.; Bakenov, Z.; Chen, P. J. Ternary sulfur/polyacrylonitrile/Mg0.6Ni0.4O composite cathodes for high performance lithium/sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 295–301.
Choi, Y. J.; Jung, B. S.; Lee, D. J.; Kim, K. W.; Ahn, H. J.; Cho, K. K.; Gu, H. B. Electrochemical properties of sulfur electrode containing nano Al2O3 for lithium/sulfur cell. Phys. Scr. 2007, T129, 62.
Ji, X. L.; Evers, S.; Black, R.; Nazar, L. F. Stabilizing lithium–sulphur cathodes using polysulphide reservoirs. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 325.
Liang, Z.; Zheng, G. Y.; Li, W. Y.; Seh, Z. W.; Yao, H. B.; Yan, K.; Kong, D. S.; Cui, Y. Sulfur cathodes with hydrogen reduced titanium dioxide inverse opal structure. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5249–5256.
Sun, F. G.; Wang, J. T.; Long, D. H.; Qiao, W. M.; Ling, L. C.; Lv, C. X.; Cai, R. A high-rate lithium–sulfur battery assisted by nitrogen-enriched mesoporous carbons decorated with ultrafine La2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13283–13289.
Qu, Q. T.; Gao, T.; Zheng, H. Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Y.; Li, X. X.; Chen, J. M.; Han, Y. Y.; Shao, J.; Zheng, H. Z. Strong surface-bound sulfur in conductive MoO2 matrix for enhancing Li–S battery performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500048.
Liang, X.; Garsuch, A.; Nazar, L. F. Sulfur cathodes based on conductive MXene nanosheets for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3907–3911.
Zhang, Q. F.; Wang, Y. F.; Seh, Z. W.; Fu, Z. H.; Zhang, R. F.; Cui, Y. Understanding the anchoring effect of twodimensional layered materials for lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3780–3786.
Gu, M. S.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J. S.; Jang, B. Y.; Lee, K. T.; Kim, B. S. Inhibiting the shuttle effect in lithium–sulfur batteries using a layer-by-layer assembled ion-permselective separator. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 46940–46946.
She, Z. W.; Zhang, Q. F.; Li, W. Y.; Zheng, G. Y.; Yao, H. B.; Cui, Y. Stable cycling of lithium sulfide cathodes through strong affinity with a bifunctional binder. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3673–3677.
Park, K.; Cho, J. H.; Jang, J. H.; Yu, B. C.; De La Hoz, A. T.; Miller, K. M.; Ellison, C. J.; Goodenough, J. B. Trapping lithium polysulfides of a Li–S battery by forming lithium bonds in a polymer matrix. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2389–2395.
Chen, H. W.; Wang, C. H.; Dai, Y. F.; Qiu, S. Q.; Yang, J. L.; Lu, W.; Chen, L. W. Rational design of cathode structure for high rate performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5443–5448.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Ye, F., Li, W. et al. Chemical routes toward long-lasting lithium/sulfur cells. Nano Res. 9, 94–116 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1027-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1027-8