Abstract
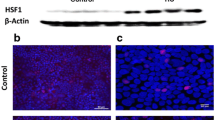
Indomethacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with clearly known side effects on the gastrointestinal tract. The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether eupatilin inhibit cell injury induced by indomethacin in cultured feline esophageal epithelial cells (EECs). EECs were used to investigate the ability of eupatilin to induce the expression of heat shock proteins (HSP27 and HSP70) and analyze its cytoprotective effect against indomethacin-induced damage. The treatment of EECs with indomethacin for 8 h decreased cell viability. Western blot analysis showed that the levels of HSPs gradually decreased in cells treated with indomethacin, while eupatilin treatment increased the levels of HSPs. When treated with both indomethacin and eupatilin, the levels of HSPs increased rapidly, and were maintained at 130–140%. In addition, treatment with the specific inhibitors of PTK, PKC, PLC, p38 MAPK, JNKs, and PI3K attenuated the eupatilin-induced expression of HSPs. Pretreatment of EECs with the inhibitors of protein synthesis, actinomycin D or cycloheximide, attenuated the cytoprotective effect of eupatilin on indomethacin-induced cell damage. Reactive oxygen species production was upregulated by indomethacin, but downregulated by eupatilin. Taken together, it was suggested that HSPs were partly responsible for the eupatilin-mediated cytoprotective activity against the indomethacin-induced damage in EECs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afroz S, Yagi A, Fujikawa K, Rahman MM, Morito K, Fukuta T, Watanabe S, Kiyokage E, Toida K, Shimizu T, Ishida T, Kogure K, Tokumura A, Tanaka T (2018) Lysophosphatidic acid in medicinal herbs enhances prostaglandin E2 and protects against indomethacin-induced gastric cell damage in vivo and in vitro. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 135:36–44
Ahn B, Ko K-H, Oh T-Y, Cho H, Kim W-B, Lee K-J, Cho S-W, Hahm K-B (2001) Efficacy of use of colonoscopy in dextran sulfate sodium induced ulcerative colitis in rats: the evaluation of the effects of antioxidant by colonoscopy. Int J Colorectal Dis 16:174–181
Arrigo AP (2007) The cellular “networking” of mammalian Hsp27 and its functions in the control of protein folding, redox state and apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 594:14–26
Arrigo AP, Virot S, Chaufour S, Firdaus W, Kretz-Remy C, Diaz-Latoud C (2005) Hsp27 consolidates intracellular redox homeostasis by upholding glutathione in its reduced form and by decreasing iron intracellular levels. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:414–422
Banerjee RK (1990) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit gastric peroxidase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1034:275–280
Beck PL, Xavier R, Lu N, Nanda NN, Dinauer M, Podolsky DK, Seed B (2000) Mechanisms of NSAID-Induced gastrointestinal injury defined using mutant mice. Gastroenterology 119:699–705
Binder RJ, Vatner R, Srivastava P (2004) The heat-shock protein receptors: some answers and more questions. Tissue Antigens 64:442–451
Carvalho NS, Silva MM, Silva RO, Nicolau LA, Sousa FB, Damasceno SR, Silva DA, Barbosa AL, Leite JR, Medeiros JV (2015) Gastroprotective properties of cashew gum, a complex heteropolysaccharide of Anacardium occidentale, in naproxen-induced gastrointestinal damage in rats. Drug Dev Res 76:143–151
Chen KC-W, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Lou MF (2007) Control of PDGF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and signal transduction in human lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis 13:374
Das D, Bandyopadhyay D, Bhattacharjee M, Banerjee RK (1997) Hydroxyl radical is the major causative factor in stress-induced gastric ulceration. Free Radic Biol Med 23:8–18
De Magalhaes JP, Church GM (2006) Cells discover fire: employing reactive oxygen species in development and consequences for aging. Exp Gerontol 41:1–10
Ebert M, Schäfer C, Chen J, Hoffmann J, Gu P, Kubisch C, Carl-Mcgrath S, Treiber G, Malfertheiner P, Röcken C (2005) Protective role of heat shock protein 27 in gastric mucosal injury. J Pathol 207:177–184
Ha HS, Lee SE, Lee HS, Kim GH, Yoon CJ, Han JS, Lee JY, Sohn UD (2017) The signaling of protease-activated receptor-2 activating peptide-induced contraction in cat esophageal smooth muscle cells. Arch Pharmacal Res 40:1443–1454
Hahm KB, Park IS, Kim YS, Kim JH, Cho SW, Lee SI, Youn JK (1997) Role of rebamipide on induction of heat-shock proteins and protection against reactive oxygen metabolite-mediated cell damage in cultured gastric mucosal cells. Free Radic Biol Med 22:711–716
Hawkey C (1993) Gastroduodenal problems associated with non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Scand J Gastroenterol 28:94–95
Hayes SA, Dice JF (1996) Roles of molecular chaperones in protein degradation. J Cell Biol 132:255–258
Hirakawa T, Rokutan K, Nikawa T, Kishi K (1996) Geranylgeranylacetone induces heat shock proteins in cultured guinea pig gastric mucosal cells and rat gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 111:345–357
Ialenti A, Di Meglio P, D’acquisto F, Pisano B, Maffia P, Grassia G, Di Rosa M, Ianaro A (2005) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression by the heat shock response in J774 murine macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 509:89–96
Jang HS, Um SI, Lee SH, Whang WK, Min YS, Park SY, Sohn UD (2017) The protective mechanism of QGC in feline esophageal epithelial cells by interleukin-1beta treatment. Arch Pharmacal Res 40:204–213
Kim JM, Lee DH, Kim JS, Lee JY, Park HG, Kim YJ, Oh YK, Jung HC, Kim SI (2009) 5,7-Dihydroxy-3,4,6-trimethoxyflavone inhibits the inflammatory effects induced by Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin via dissociating the complex of heat shock protein 90 and I kappaB alpha and I kappaB kinase-gamma in intestinal epithelial cell culture. Clin Exp Immunol 155:541–551
Kim EJ, Kim GT, Kim BM, Lim EG, Kim SY, Kim YM (2017) Apoptosis-induced effects of extract from Artemisia annua Linne by modulating PTEN/p53/PDK1/Akt/signal pathways through PTEN/p53-independent manner in HCT116 colon cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:236
Kruse CA, Varella-Garcia M, Kleinschmidt-Demasters BK, Owens GC, Spector EB, Fakhrai H, Savelieva E, Liang BC (1998) Receptor expression, cytogenetic, and molecular analysis of six continuous human glioma cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 34:455–462
Lee S, Lee M, Kim S-H (2008) Eupatilin inhibits H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2865–2870
Lim JC, Park SY, Nam Y, Nguyen TT, Sohn UD (2012) The protective effect of eupatilin against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury involving 5-lipoxygenase in feline esophageal epithelial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 16:313–320
Liu H-Y, Dicksved J, Lundh T, Lindberg JE (2014) Expression of heat shock proteins 27 and 72 correlates with specific commensal microbes in different regions of porcine gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 306:G1033–G1041
Luz CCF, Noguti J, De Araújo LB, Dos Santos GMS, Gomes TS, Neto RA (2017) Hsp27 and Hsp70 expression in esophageal squamous. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 18:789
Manwell LA, Heikkila JJ (2007) Examination of KNK437- and quercetin-mediated inhibition of heat shock-induced heat shock protein gene expression in Xenopus laevis cultured cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:521–530
Menon S, Goswami P (2007) A redox cycle within the cell cycle: ring in the old with the new. Oncogene 26:1101
Minowada G, Welch WJ (1995) Clinical implications of the stress response. J Clin Investig 95:3–12
Oh T, Lee J, Ahn B, Cho H, Kim W, Kim Y, Surh Y, Cho S, Lee K, Hahm K (2001) Oxidative stress is more important than acid in the pathogenesis of reflux oesophagitis in rats. Gut 49:364–371
Ohkawara T, Nishihira J, Nagashima R, Takeda H, Asaka M (2006) Polaprezinc protects human colon cells from oxidative injury induced by hydrogen peroxide: relevant to cytoprotective heat shock proteins. World J Gastroenterol 12:6178
Park SY, Lee YJ, Min Y, Kim HR, Jeong JH, Sohn UD (2011) The mechanism of MAP kinase activation under acidic condition in feline esophageal smooth muscle cells. Arch Pharmacal Res 34:1759–1768
Pockley AG (2003) Heat shock proteins as regulators of the immune response. Lancet 362:469–476
Préville X, Salvemini F, Giraud S, Chaufour S, Paul C, Stepien G, Ursini MV, Arrigo A-P (1999) Mammalian small stress proteins protect against oxidative stress through their ability to increase glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and by maintaining optimal cellular detoxifying machinery. Exp Cell Res 247:61–78
Rainsford K (1993) Mechanisms of gastrointestinal damage by NSAIDS. Agents Actions Suppl 44:59–64
Ran R, Lu A, Zhang L, Tang Y, Zhu H, Xu H, Feng Y, Han C, Zhou G, Rigby AC (2004) Hsp70 promotes TNF-mediated apoptosis by binding IKKγ and impairing NF-κB survival signaling. Genes Dev 18:1466–1481
Saini J, Sharma P (2017) Prognostic and therapeutic significance of heat shock proteins in cancer. Curr Drug Targets. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450118666170823121248
Satoh H, Amagase K, Takeuchi K (2014) Mucosal protective agents prevent exacerbation of NSAID-induced small intestinal lesions caused by antisecretory drugs in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 348:227–235
Seo H-J, Surh Y-J (2001) Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Mutat Res/Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 496:191–198
Slotta-Huspenina J, Becker K-F, Feith M, Walch A, Langer R (2014) Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) and Her2 in adenocarcinomas of the esophagus. Cancers 6:1382–1393
Sohn US, Lee SE, Lee SH, Nam Y, Hwang WK, Sohn UD (2016) The protective mechanism of quercetin-3-O-beta-d-glucuronopyranoside (QGC) in H2O2-induced injury of feline esophageal epithelial cells. Arch Pharmacal Res 39:1324–1334
Song HJ, Shin CY, Oh TY, Sohn UD (2008) The protective effect of eupatilin on indomethacin-induced cell damage in cultured feline ileal smooth muscle cells: involvement of HO-1 and ERK. J Ethnopharmacol 118:94–101
Song HJ, Shin CY, Oh TY, Min YS, Park ES, Sohn UD (2009) Eupatilin with heme oxygenase-1-inducing ability protects cultured feline esophageal epithelial cells from cell damage caused by indomethacin. Biol Pharm Bull 32:589–596
Tomisato W, Takahashi N, Komoto C, Rokutan K, Tsuchiya T, Mizushima T (2000) Geranylgeranylacetone protects cultured guinea pig gastric mucosal cells from indomethacin. Dig Dis Sci 45:1674–1679
Van Molle W, Wielockx B, Mahieu T, Takada M, Taniguchi T, Sekikawa K, Libert C (2002) HSP70 protects against TNF-induced lethal inflammatory shock. Immunity 16:685–695
Wallace JL (2001) Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastroduodenal mucosal injury. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 15:691–703
Wang L, Tu Y-C, Lian T-W, Hung J-T, Yen J-H, Wu M-J (2006) Distinctive antioxidant and antiinflammatory effects of flavonols. J Agric Food Chem 54:9798–9804
Wang L, Schumann U, Liu Y, Prokopchuk O, Steinacker JM (2012) Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) inhibits oxidative phosphorylation and compensates ATP balance through enhanced glycolytic activity. J Appl Physiol 113:1669–1676
Wang Y, Lin F, Zhu X, Leone VA, Dalal S, Tao Y, Messer JS, Chang EB (2017) Distinct roles of intracellular heat shock protein 70 in maintaining gastrointestinal homeostasis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 314:G164–G178
Wang Y, Lin F, Zhu X, Leone VA, Dalal S, Tao Y, Messer JS, Chang EB (2018) Distinct roles of intracellular heat shock protein 70 in maintaining gastrointestinal homeostasis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 314:G164–G178
Wenzel U, Kuntz S, Brendel MD, Daniel H (2000) Dietary flavone is a potent apoptosis inducer in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 60:3823–3831
Yokoe S, Nakagawa T, Kojima Y, Higuchi K, Asahi M (2015) Indomethacin-induced intestinal epithelial cell damage is mediated by pVHL activation through the degradation of collagen I and HIF-1alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 468:671–676
Zhang Y, Feng Z, Wang W, Dong J, Gong X, Pu H, Chen X (2017) Expression of heat shock protein-27 (Hsp27) and P38MAPK in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monit 23:5246–5253
Zheng Z, Kim JY, Ma H, Lee JE, Yenari MA (2008) Anti-inflammatory effects of the 70 kDa heat shock protein in experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:53–63
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (Grant Number 2016R1D1A1A09918019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Min, Y.S. & Sohn, U.D. Cytoprotective effect of eupatilin against indomethacin-induced damage in feline esophageal epithelial cells: relevance of HSP27 and HSP70. Arch. Pharm. Res. 41, 1019–1031 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1066-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1066-7