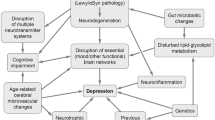
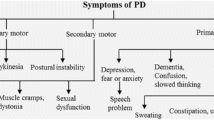
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, including bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. Recent clinical findings recognize PD as a complex disease with diverse neuropsychiatric complications. Depression is the most frequent non-motor psychiatric symptom experienced in PD, and it is associated with poor quality of life. While the pathophysiology of PD-associated depression is not directly related to neurodegenerative processes in the substantia nigra, underlying mechanisms remain unclear and there are few symptomatic treatments. Altered adult hippocampal neurogenesis is considered crucial for the development and treatment of depression. In genetic animal models and human postmortem studies of PD, severely impaired adult neurogenesis has been observed, with patients showing hippocampal atrophy and disrupted hippocampal neurogenesis. Because adult newborn neurons appear to exert various functions, which relate to non-motor symptoms observed in PD, there might be a close correlation between malformation of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus and depressive symptoms. Here, we discuss current concepts regarding impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and non-motor symptoms of PD, and review PD-associated pathophysiological factors regulating neurogenesis, including inflammatory signaling and autophagy. We present a novel framework for targeting adult hippocampal neurogenesis, which could provide a promising treatment for PD-associated depression.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Erviti L, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Cooper JM, Caballero C, Ferrer I, Obeso JA, Schapira AH (2010) Chaperone-mediated autophagy markers in Parkinson disease brains. Arch Neurol 67:1464–1472
Bang Y, Kim KS, Seol W, Choi HJ (2016) LRRK2 interferes with aggresome formation for autophagic clearance. Mol Cell Neurosci 75:71–80
Ben-Hur T, Ben-Menachem O, Furer V, Einstein O, Mizrachi-Kol R, Grigoriadis N (2003) Effects of proinflammatory cytokines on the growth, fate, and motility of multipotential neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:623–631
Boldrini M, Underwood MD, Hen R, Rosoklija GB, Dwork AJ, John Mann J, Arango V (2009) Antidepressants increase neural progenitor cells in the human hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2376–2389
Boldrini M, Hen R, Underwood MD, Rosoklija GB, Dwork AJ, Mann JJ, Arango V (2012) Hippocampal angiogenesis and progenitor cell proliferation are increased with antidepressant use in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 72:562–571
Boldrini M, Santiago AN, Hen R, Dwork AJ, Rosoklija GB, Tamir H, Arango V, John Mann J (2013) Hippocampal granule neuron number and dentate gyrus volume in antidepressant-treated and untreated major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1068–1077
Bremner JD, Narayan M, Anderson ER, Staib LH, Miller HL, Charney DS (2000) Hippocampal volume reduction in major depression. Am J Psychiatry 157:115–118
Brochard V, Combadiere B, Prigent A, Laouar Y, Perrin A, Beray-Berthat V, Bonduelle O, Alvarez-Fischer D, Callebert J, Launay JM, Duyckaerts C, Flavell RA, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 119:182–192
Brown JP, Couillard-Despres S, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J, Aigner L, Kuhn HG (2003) Transient expression of doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 467:1–10
Bruck A, Kurki T, Kaasinen V, Vahlberg T, Rinne JO (2004) Hippocampal and prefrontal atrophy in patients with early non-demented Parkinson’s disease is related to cognitive impairment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1467–1469
Cambiaghi M, Cursi M, Magri L, Castoldi V, Comi G, Minicucci F, Galli R, Leocani L (2013) Behavioural and EEG effects of chronic rapamycin treatment in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Neuropharmacology 67:1–7
Castano A, Herrera AJ, Cano J, Machado A (2002) The degenerative effect of a single intranigral injection of LPS on the dopaminergic system is prevented by dexamethasone, and not mimicked by rh-TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IFN-gamma. J Neurochem 81:150–157
Chao Y, Wong SC, Tan EK (2014) Evidence of inflammatory system involvement in Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:308654
Chen H, Zhang SM, Hernan MA, Schwarzschild MA, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Ascherio A (2003) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 60:1059–1064
Couillard-Despres S, Aigner L (2011) In vivo imaging of adult neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 33:1037–1044
Crews L, Mizuno H, Desplats P, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Patrick C, Winner B, Winkler J, Masliah E (2008) Alpha-synuclein alters Notch-1 expression and neurogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells and in the hippocampus of transgenic mice. J Neurosci 28:4250–4260
Czeh B, Lucassen PJ (2007) What causes the hippocampal volume decrease in depression? Are neurogenesis, glial changes and apoptosis implicated? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257:250–260
Czeh B, Michaelis T, Watanabe T, Frahm J, de Biurrun G, van Kampen M, Bartolomucci A, Fuchs E (2001) Stress-induced changes in cerebral metabolites, hippocampal volume, and cell proliferation are prevented by antidepressant treatment with tianeptine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12796–12801
Dean J, Keshavan M (2017) The neurobiology of depression: an integrated view. Asian J Psychiatry 27:101–111
Dong H, Gao Z, Rong H, Jin M, Zhang X (2014) Beta-asarone reverses chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior and promotes hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. Molecules 19:5634–5649
Elhwuegi AS (2004) Central monoamines and their role in major depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:435–451
Encinas JM, Enikolopov G (2008) Identifying and quantitating neural stem and progenitor cells in the adult brain. Methods Cell Biol 85:243–272
Encinas JM, Vaahtokari A, Enikolopov G (2006) Fluoxetine targets early progenitor cells in the adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8233–8238
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4:1313–1317
Farrell KF, Krishnamachari S, Villanueva E, Lou H, Alerte TN, Peet E, Drolet RE, Perez RG (2014) Non-motor parkinsonian pathology in aging A53T alpha-synuclein mice is associated with progressive synucleinopathy and altered enzymatic function. J Neurochem 128:536–546
Fava M, Johe K, Ereshefsky L, Gertsik LG, English BA, Bilello JA, Thurmond LM, Johnstone J, Dickerson BC, Makris N, Hoeppner BB, Flynn M, Mischoulon D, Kinrys G, Freeman MP (2016) A phase 1B, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, multiple-dose escalation study of NSI-189 phosphate, a neurogenic compound, in depressed patients. Mol Psychiatry 21:1372–1380
Ferguson JM (2001) SSRI antidepressant medications: adverse effects and tolerability. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 3:22–27
Fukuda S, Kato F, Tozuka Y, Yamaguchi M, Miyamoto Y, Hisatsune T (2003) Two distinct subpopulations of nestin-positive cells in adult mouse dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 23:9357–9366
Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287:1433–1438
Gao HM, Zhang F, Zhou H, Kam W, Wilson B, Hong JS (2011) Neuroinflammation and alpha-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Environ Health Perspect 119:807–814
Gerhard A, Pavese N, Hotton G, Turkheimer F, Es M, Hammers A, Eggert K, Oertel W, Banati RB, Brooks DJ (2006) In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 21:404–412
Ghosal K, Stathopoulos A, Pimplikar SW (2010) APP intracellular domain impairs adult neurogenesis in transgenic mice by inducing neuroinflammation. PLoS ONE 5:e11866
Goncalves JT, Schafer ST, Gage FH (2016) Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus: from Stem cells to behavior. Cell 167:897–914
Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ben-Menachem-Zidon O, Licht T, Weidenfeld J, Ben-Hur T, Yirmiya R (2008) Brain interleukin-1 mediates chronic stress-induced depression in mice via adrenocortical activation and hippocampal neurogenesis suppression. Mol Psychiatry 13:717–728
Guo JD, Zhao X, Li Y, Li GR, Liu XL (2018) Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (review). Int J Mol Med 41:1817–1825
Gyorfi O, Nagy H, Bokor M, Moustafa AA, Rosenzweig I, Kelemen O, Keri S (2017) Reduced CA2-CA3 hippocampal subfield volume is related to depression and normalized by l-DOPA in newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol 8:84
Hirschfeld RM (2000) History and evolution of the monoamine hypothesis of depression. J Clin Psychiatry 61(Suppl 6):4–6
Ho NF, Hooker JM, Sahay A, Holt DJ, Roffman JL (2013) In vivo imaging of adult human hippocampal neurogenesis: progress, pitfalls and promise. Mol Psychiatry 18:404–416
Hoban DB, Connaughton E, Connaughton C, Hogan G, Thornton C, Mulcahy P, Moloney TC, Dowd E (2013) Further characterisation of the LPS model of Parkinson’s disease: a comparison of intra-nigral and intra-striatal lipopolysaccharide administration on motor function, microgliosis and nigrostriatal neurodegeneration in the rat. Brain Behav Immun 27:91–100
Hoglinger GU, Rizk P, Muriel MP, Duyckaerts C, Oertel WH, Caille I, Hirsch EC (2004) Dopamine depletion impairs precursor cell proliferation in Parkinson disease. Nat Neurosci 7:726–735
Jayatissa MN, Bisgaard C, Tingstrom A, Papp M, Wiborg O (2006) Hippocampal cytogenesis correlates to escitalopram-mediated recovery in a chronic mild stress rat model of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2395–2404
Jessberger S, Kempermann G (2003) Adult-born hippocampal neurons mature into activity-dependent responsiveness. Eur J Neurosci 18:2707–2712
Jin J, Kim S-N, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhang C, Seo J-S, Kim Y, Sun T (2016) miR-17-92 cluster regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis, anxiety, and depression. Cell Rep 16(6):1653–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.101
Jurgenson M, Aonurm-Helm A, Zharkovsky A (2012) Partial reduction in neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) in heterozygous mice induces depression-related behaviour without cognitive impairment. Brain Res 1447:106–118
Kanaan NM, Kordower JH, Collier TJ (2008) Age and region-specific responses of microglia, but not astrocytes, suggest a role in selective vulnerability of dopamine neurons after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine exposure in monkeys. Glia 56:1199–1214
Kang E, Wen Z, Song H, Christian KM, Ming GL (2016) Adult neurogenesis and psychiatric disorders. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8:a019026
Kempermann G, Krebs J, Fabel K (2008) The contribution of failing adult hippocampal neurogenesis to psychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 21:290–295
Keohane A, Ryan S, Maloney E, Sullivan AM, Nolan YM (2010) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha impairs neuronal differentiation but not proliferation of hippocampal neural precursor cells: role of Hes1. Mol Cell Neurosci 43:127–135
Kim HJ, Kim W, Kong SY (2013) Antidepressants for neuro-regeneration: from depression to Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 36:1279–1290
Kim S, Park JM, Moon J, Choi HJ (2014) Alpha-synuclein interferes with cAMP/PKA-dependent upregulation of dopamine beta-hydroxylase and is associated with abnormal adaptive responses to immobilization stress. Exp Neurol 252:63–74
Kohl Z, Ben Abdallah N, Vogelgsang J, Tischer L, Deusser J, Amato D, Anderson S, Muller CP, Riess O, Masliah E, Nuber S, Winkler J (2016) Severely impaired hippocampal neurogenesis associates with an early serotonergic deficit in a BAC alpha-synuclein transgenic rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 85:206–217
Kohler O, Benros ME, Nordentoft M, Farkouh ME, Iyengar RL, Mors O, Krogh J (2014) Effect of anti-inflammatory treatment on depression, depressive symptoms, and adverse effects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Psychiatry 71:1381–1391
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, Iwata J, Tanida I, Ueno T, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Tanaka K (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 441:880–884
Komitova M, Eriksson PS (2004) Sox-2 is expressed by neural progenitors and astroglia in the adult rat brain. Neurosci Lett 369:24–27
Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, Litwin T, Joniec I, Ciesielska A, Przybylkowski A, Czlonkowski A, Czlonkowska A (2004) Dexamethasone protects against dopaminergic neurons damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Int Immunopharmacol 4:1307–1318
Lafenetre P, Leske O, Ma-Hogemeie Z, Haghikia A, Bichler Z, Wahle P, Heumann R (2010) Exercise can rescue recognition memory impairment in a model with reduced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Behav Neurosci 3:34
Lang UE, Heger J, Willbring M, Domula M, Matschke K, Tugtekin SM (2009) Immunosuppression using the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor everolimus: pilot study shows significant cognitive and affective improvement. Transplant Proc 41:4285–4288
Leentjens AF, Van den Akker M, Metsemakers JF, Lousberg R, Verhey FR (2003) Higher incidence of depression preceding the onset of Parkinson’s disease: a register study. Mov Disord 18:414–418
Lieberwirth C, Liu Y, Jia X, Wang Z (2012) Social isolation impairs adult neurogenesis in the limbic system and alters behaviors in female prairie voles. Horm Behav 62:357–366
Lim J, Bang Y, Choi JH, Han A, Kwon MS, Hyeon Liu K, Jin Choi H (2018) LRRK2 G2019S induces anxiety/depression-like behavior prior to the onset of motor dysfunction with 5-HT1A receptor upregulation in mice. J Neurosci 38:1611–1621
Lindgren L, Bergdahl J, Nyberg L (2016) Longitudinal evidence for smaller hippocampus volume as a vulnerability factor for perceived stress. Cereb Cortex 26:3527–3533
Liu H, Song N (2016) Molecular mechanism of adult neurogenesis and its association with human brain diseases. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis 8:5–11
Liu J, Dong J, Wang L, Su Y, Yan P, Sun S (2013) Comparative efficacy and acceptability of antidepressants in Parkinson’s disease: a network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 8:e76651
Liu Q, Xin W, He P, Turner D, Yin J, Gan Y, Shi FD, Wu J (2014) Interleukin-17 inhibits adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Sci Rep 4:7554
Lucassen PJ, Stumpel MW, Wang Q, Aronica E (2010) Decreased numbers of progenitor cells but no response to antidepressant drugs in the hippocampus of elderly depressed patients. Neuropharmacology 58:940–949
Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2000) Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:9104–9110
Malykhin NV, Carter R, Seres P, Coupland NJ (2010) Structural changes in the hippocampus in major depressive disorder: contributions of disease and treatment. J Psychiatry Neurosci 35:337–343
Mao Y, Ge X, Frank CL, Madison JM, Koehler AN, Doud MK, Tassa C, Berry EM, Soda T, Singh KK, Biechele T, Petryshen TL, Moon RT, Haggarty SJ, Tsai LH (2009) Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 regulates neuronal progenitor proliferation via modulation of GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling. Cell 136:1017–1031
Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Sadeghian M, Broom L, Davis JB, Medhurst AD, Dexter DT (2009) Relationship between microglial activation and dopaminergic neuronal loss in the substantia nigra: a time course study in a 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 110:966–975
Marsh L (2013) Depression and Parkinson’s disease: current knowledge. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 13:409
Marxreiter F, Regensburger M, Winkler J (2013) Adult neurogenesis in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:459–473
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1291
Mignone JL, Kukekov V, Chiang AS, Steindler D, Enikolopov G (2004) Neural stem and progenitor cells in nestin-GFP transgenic mice. J Comp Neurol 469:311–324
Ming GL, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70:687–702
Mogi M, Kondo T, Mizuno Y, Nagatsu T (2007) p53 protein, interferon-gamma, and NF-kappaB levels are elevated in the parkinsonian brain. Neurosci Lett 414:94–97
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD (2003) Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 302:1760–1765
Muller N, Schwarz MJ, Dehning S, Douhe A, Cerovecki A, Goldstein-Muller B, Spellmann I, Hetzel G, Maino K, Kleindienst N, Moller HJ, Arolt V, Riedel M (2006) The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib has therapeutic effects in major depression: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, add-on pilot study to reboxetine. Mol Psychiatry 11:680–684
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A (2000) Changes in cytokines and neurotrophins in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 60:277–290
Okubadejo NU, Ojo OO, Oshinaike OO (2010) Clinical profile of parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease in Lagos, Southwestern Nigeria. BMC Neurol 10:1
Parent JM (2003) Injury-induced neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Neuroscientist 9:261–272
Perera TD, Dwork AJ, Keegan KA, Thirumangalakudi L, Lipira CM, Joyce N, Lange C, Higley JD, Rosoklija G, Hen R, Sackeim HA, Coplan JD (2011) Necessity of hippocampal neurogenesis for the therapeutic action of antidepressants in adult nonhuman primates. PLoS ONE 6:e17600
Petri R, Pircs K, Jonsson ME, Akerblom M, Brattas PL, Klussendorf T, Jakobsson J (2017) let-7 regulates radial migration of new-born neurons through positive regulation of autophagy. EMBO J 36:1379–1391
Poewe W (2008) Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 15(Suppl 1):14–20
Qin XY, Zhang SP, Cao C, Loh YP, Cheng Y (2016) Aberrations in peripheral inflammatory cytokine levels in Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol 73:1316–1324
Rajkowska G, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Wei J, Dilley G, Pittman SD, Meltzer HY, Overholser JC, Roth BL, Stockmeier CA (1999) Morphometric evidence for neuronal and glial prefrontal cell pathology in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 45:1085–1098
Ravina B, Camicioli R, Como PG, Marsh L, Jankovic J, Weintraub D, Elm J (2007) The impact of depressive symptoms in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 69:342–347
Rideout HJ, Lang-Rollin I, Stefanis L (2004) Involvement of macroautophagy in the dissolution of neuronal inclusions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2551–2562
Rusch BD, Abercrombie HC, Oakes TR, Schaefer SM, Davidson RJ (2001) Hippocampal morphometry in depressed patients and control subjects: relations to anxiety symptoms. Biol Psychiatry 50:960–964
Sahay A, Hen R (2007) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in depression. Nat Neurosci 10:1110–1115
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301:805–809
Sarkar S, Rubinsztein DC (2006) Inositol and IP3 levels regulate autophagy: biology and therapeutic speculations. Autophagy 2:132–134
Sato S, Uchihara T, Fukuda T, Noda S, Kondo H, Saiki S, Komatsu M, Uchiyama Y, Tanaka K, Hattori N (2018) Loss of autophagy in dopaminergic neurons causes Lewy pathology and motor dysfunction in aged mice. Sci Rep 8:2813
Sawada M, Imamura K, Nagatsu T (2006) Role of cytokines in inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:373–381
Schoenfeld TJ, McCausland HC, Morris HD, Padmanaban V, Cameron HA (2017) Stress and loss of adult neurogenesis differentially reduce hippocampal volume. Biol Psychiatry 82(12):914–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.05.013
Schondorf DC, Aureli M, McAllister FE, Hindley CJ, Mayer F, Schmid B, Sardi SP, Valsecchi M, Hoffmann S, Schwarz LK, Hedrich U, Berg D, Shihabuddin LS, Hu J, Pruszak J, Gygi SP, Sonnino S, Gasser T, Deleidi M (2014) iPSC-derived neurons from GBA1-associated Parkinson’s disease patients show autophagic defects and impaired calcium homeostasis. Nat Commun 5:4028
Schrag A (2006) Quality of life and depression in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 248:151–157
Schrag A, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N (2000) What contributes to quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69:308–312
Silva R, Mesquita AR, Bessa J, Sousa JC, Sotiropoulos I, Leao P, Almeida OF, Sousa N (2008) Lithium blocks stress-induced changes in depressive-like behavior and hippocampal cell fate: the role of glycogen-synthase-kinase-3beta. Neuroscience 152:656–669
Singh S, Mishra A, Mishra SK, Shukla S (2017) ALCAR promote adult hippocampal neurogenesis by regulating cell-survival and cell death-related signals in rat model of Parkinson’s disease like-phenotypes. Neurochem Int 108:388–396
Son H, Yu IT, Hwang SJ, Kim JS, Lee SH, Lee YS, Kaang BK (2003) Lithium enhances long-term potentiation independently of hippocampal neurogenesis in the rat dentate gyrus. J Neurochem 85:872–881
Song H, Stevens CF, Gage FH (2002) Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature 417:39–44
Spencer B, Potkar R, Trejo M, Rockenstein E, Patrick C, Gindi R, Adame A, Wyss-Coray T, Masliah E (2009) Beclin 1 gene transfer activates autophagy and ameliorates the neurodegenerative pathology in alpha-synuclein models of Parkinson’s and Lewy body diseases. J Neurosci 29:13578–13588
Steffens DC, Byrum CE, McQuoid DR, Greenberg DL, Payne ME, Blitchington TF, MacFall JR, Krishnan KR (2000) Hippocampal volume in geriatric depression. Biol Psychiatry 48:301–309
Stoykova A, Gruss P (1994) Roles of Pax-genes in developing and adult brain as suggested by expression patterns. J Neurosci 14:1395–1412
Sung YH (2015) Effects of treadmill exercise on hippocampal neurogenesis in an MPTP/probenecid-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J Phys Ther Sci 27:3203–3206
Tajiri N, Quach DM, Kaneko Y, Wu S, Lee D, Lam T, Hayama KL, Hazel TG, Johe K, Wu MC, Borlongan CV (2017) NSI-189, a small molecule with neurogenic properties, exerts behavioral, and neurostructural benefits in stroke rats. J Cell Physiol 232:2731–2740
Takamura N, Nakagawa S, Masuda T, Boku S, Kato A, Song N, An Y, Kitaichi Y, Inoue T, Koyama T, Kusumi I (2014) The effect of dopamine on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 50:116–124
Tang MM, Lin WJ, Zhang JT, Zhao YW, Li YC (2017) Exogenous FGF2 reverses depressive-like behaviors and restores the suppressed FGF2-ERK1/2 signaling and the impaired hippocampal neurogenesis induced by neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun 66:322–331
Tashiro A, Sandler VM, Toni N, Zhao C, Gage FH (2006) NMDA-receptor-mediated, cell-specific integration of new neurons in adult dentate gyrus. Nature 442:929–933
Todorova A, Jenner P, Ray Chaudhuri K (2014) Non-motor Parkinson’s: integral to motor Parkinson’s, yet often neglected. Pract Neurol 14:310–322
Troeung L, Egan SJ, Gasson N (2013) A meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled treatment trials for depression and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 8:e79510
Uchida S, Hara K, Kobayashi A, Fujimoto M, Otsuki K, Yamagata H, Hobara T, Abe N, Higuchi F, Shibata T, Hasegawa S, Kida S, Nakai A, Watanabe Y (2011) Impaired hippocampal spinogenesis and neurogenesis and altered affective behavior in mice lacking heat shock factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1681–1686
Valero J, Mastrella G, Neiva I, Sanchez S, Malva JO (2014) Long-term effects of an acute and systemic administration of LPS on adult neurogenesis and spatial memory. Front Neurosci 8:83
Vallieres L, Campbell IL, Gage FH, Sawchenko PE (2002) Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in adult transgenic mice with chronic astrocytic production of interleukin-6. J Neurosci 22:486–492
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH (1999) Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 2:266–270
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415:1030–1034
Wang C, Liang CC, Bian ZC, Zhu Y, Guan JL (2013) FIP200 is required for maintenance and differentiation of postnatal neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 16:532–542
Wexler EM, Geschwind DH, Palmer TD (2008) Lithium regulates adult hippocampal progenitor development through canonical Wnt pathway activation. Mol Psychiatry 13:285–292
Whitney NP, Eidem TM, Peng H, Huang Y, Zheng JC (2009) Inflammation mediates varying effects in neurogenesis: relevance to the pathogenesis of brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurochem 108:1343–1359
Williams-Gray CH, Wijeyekoon R, Yarnall AJ, Lawson RA, Breen DP, Evans JR, Cummins GA, Duncan GW, Khoo TK, Burn DJ, Barker RA, Icicle-Pd study group (2016) Serum immune markers and disease progression in an incident Parkinson’s disease cohort (ICICLE-PD). Mov Disord 31:995–1003
Winner B, Winkler J (2015) Adult neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a021287
Winner B, Desplats P, Hagl C, Klucken J, Aigner R, Ploetz S, Laemke J, Karl A, Aigner L, Masliah E, Buerger E, Winkler J (2009) Dopamine receptor activation promotes adult neurogenesis in an acute Parkinson model. Exp Neurol 219:543–552
Winner B, Melrose HL, Zhao C, Hinkle KM, Yue M, Kent C, Braithwaite AT, Ogholikhan S, Aigner R, Winkler J, Farrer MJ, Gage FH (2011) Adult neurogenesis and neurite outgrowth are impaired in LRRK2 G2019S mice. Neurobiol Dis 41:706–716
Xi Y, Dhaliwal JS, Ceizar M, Vaculik M, Kumar KL, Lagace DC (2016) Knockout of Atg5 delays the maturation and reduces the survival of adult-generated neurons in the hippocampus. Cell Death Dis 7:e2127
Xiong N, Xiong J, Jia M, Liu L, Zhang X, Chen Z, Huang J, Zhang Z, Hou L, Luo Z, Ghoorah D, Lin Z, Wang T (2013) The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease: rotenone-based modeling. Behav Brain Funct 9:13
Yazdankhah M, Farioli-Vecchioli S, Tonchev AB, Stoykova A, Cecconi F (2014) The autophagy regulators Ambra1 and Beclin 1 are required for adult neurogenesis in the brain subventricular zone. Cell Death Dis 5:e1403
Zhang H, Duan C, Yang H (2015) Defective autophagy in Parkinson’s disease: lessons from genetics. Mol Neurobiol 51:89–104
Zhao C, Teng EM, Summers RG Jr, Ming GL, Gage FH (2006) Distinct morphological stages of dentate granule neuron maturation in the adult mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 26:3–11
Zhuo C, Xue R, Luo L, Ji F, Tian H, Qu H, Lin X, Jiang R, Tao R (2017) Efficacy of antidepressive medication for depression in Parkinson disease: a network meta-analysis. Medicine 96:e6698
Zonis S, Ljubimov VA, Mahgerefteh M, Pechnick RN, Wawrowsky K, Chesnokova V (2013) p21Cip restrains hippocampal neurogenesis and protects neuronal progenitors from apoptosis during acute systemic inflammation. Hippocampus 23:1383–1394
Zonis S, Pechnick RN, Ljubimov VA, Mahgerefteh M, Wawrowsky K, Michelsen KS, Chesnokova V (2015) Chronic intestinal inflammation alters hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neuroinflammation 12:65
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the GRRC program of Gyeonggi province (#GRRC-CHA2017-A02, Validity and Safety Evaluation of Regional Specialized Resources) and the Grants #2015R1D1A1A01059598, #2015M3A9E1028326, #2016R1C1B1011117 and #2016M3A9E8941671 from the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J., Bang, Y. & Choi, H.J. Abnormal hippocampal neurogenesis in Parkinson’s disease: relevance to a new therapeutic target for depression with Parkinson’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 41, 943–954 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1063-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1063-x