Abstract
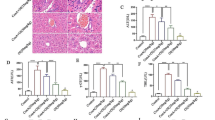
Drug repositioning is a strategy that explores new pharmaceutical applications of previously launched or failed drugs, and is advantageous since it saves capital and time. In this study, we examined the inhibition of TLR2 signaling by drug candidates. HEK-Blue™-hTLR2 cells were pretreated with drugs and stimulated using the TLR2 ligand, Pam3CSK4. Among the drugs that inhibited TLR2 signaling, we selected TRIAC, which is yet to be patented. Pretreatment with TRIAC decreased the TLR2 level and the phosphorylation of Akt and MAPKs in HEK-Blue™-hTLR2 cells. Since TLR2 is overexpressed in patients with acute hepatitis, we confirmed that TRIAC alleviates necrosis in a mouse model of Con A-induced acute hepatitis. The serum AST and ALT levels are indicators of liver damage, and are increased in Con A-induced hepatitis. Additionally, TLR2 and inflammatory cytokine levels are increased following administration of Con A and lead to liver damage. TRIAC decreased the serum levels of AST and ALT, and reduced liver tissue necrosis in mice with Con A-induced acute fulminant liver damage, by reducing the levels of inflammatory cytokines. In conclusion, TRIAC alleviates inflammation in mouse models of Con A-induced hepatitis by inhibiting the phosphorylation of Akt and MAPKs, the sub-mechanisms underlying TLR2 signaling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinolfi LE, Nevola R, Lus G, Restivo L, Guerrera B, Romano C, Zampino R, Rinaldi L, Sellitto A, Giordano M, Marrone A (2015) Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and neurological and psychiatric disorders: an overview. World J Gastroenterol 21:2269–2280
Akira S (2003) Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 278:38105–38108
Anastasiou O, Sydor S, Sowa JP, Manka P, Katsounas A, Syn WK, Fuhrer D, Gieseler RK, Bechmann LP, Gerken G, Moeller LC, Canbay A (2015) Higher thyroid-stimulating hormone, triiodothyronine and thyroxine values are associated with better outcome in acute liver failure. PLoS ONE 10:e0132189
Ashburn TT, Thor KB (2004) Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:673–683
Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2003) Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 300:1524–1525
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Du X, Ulevitch RJ (2003) How we detect microbes and respond to them: the Toll-like receptors and their transducers. J Leukoc Biol 74:479–485
Boldt DH, MacDermott RP, Jorolan EP (1975) Interaction of plant lectins with purified human lymphocyte populations: binding characteristics and kinetics of proliferation. J Immunol 114:1532–1536
Bozza M, Bliss JL, Maylor R, Erickson J, Donnelly L, Bouchard P, Dorner AJ, Trepicchio WL (1999) Interleukin-11 reduces T-cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice. Hepatology 30:1441–1447
Cameron AR, Nelson J, Forman HJ (1983) Depolarization and increased conductance precede superoxide release by concanavalin A-stimulated rat alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:3726–3728
Chang S, Dolganiuc A, Szabo G (2007) Toll-like receptors 1 and 6 are involved in TLR2-mediated macrophage activation by hepatitis C virus core and NS3 proteins. J Leukoc Biol 82:479–487
Das K, Chainy GB (2001) Modulation of rat liver mitochondrial antioxidant defence system by thyroid hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta 1537:1–13
Heymann F, Hamesch K, Weiskirchen R, Tacke F (2015) The concanavalin A model of acute hepatitis in mice. Lab Anim 49:12–20
Horn S, Kersseboom S, Mayerl S, Muller J, Groba C, Trajkovic-Arsic M, Ackermann T, Visser TJ, Heuer H (2013) Tetrac can replace thyroid hormone during brain development in mouse mutants deficient in the thyroid hormone transporter mct8. Endocrinology 154:968–979
Huang MJ, Liaw YF (1995) Clinical associations between thyroid and liver diseases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:344–350
Huang TH, Chen CC, Liu HM, Lee TY, Shieh SH (2017) Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates concanavalin a-induced hepatitis through reverse of aberration in the immune response and regenerative capacity in aged mice. Sci Rep 7:2705
Kaneko Y, Harada M, Kawano T, Yamashita M, Shibata Y, Gejyo F, Nakayama T, Taniguchi M (2000) Augmentation of Valpha14 NKT cell-mediated cytotoxicity by interleukin 4 in an autocrine mechanism resulting in the development of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J Exp Med 191:105–114
Kuzuhara H, Nishiyama S, Minowa N, Sasaki K, Omoto S (2000) Protective effects of soyasapogenol A on liver injury mediated by immune response in a concanavalin A-induced hepatitis model. Eur J Pharmacol 391:175–181
Lee JH, Won JH, Choi JM, Cha HH, Jang YJ, Park S, Kim HG, Kim HC, Kim DK (2014) Protective effect of ellagic acid on concanavalin A-induced hepatitis via toll-like receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappaB signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem 62:10110–10117
Li J, Xia Y, Liu T, Wang J, Dai W, Wang F, Zheng Y, Chen K, Li S, Abudumijiti H, Zhou Z, Lu W, Zhu R, Yang J, Zhang H, Yin Q, Wang C, Zhou Y, Lu J, Guo C (2015) Protective effects of astaxanthin on ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis by the JNK/p-JNK pathway-mediated inhibition of autophagy and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 10:e0120440
Li X, Liu HC, Yao QY, Xu BL, Zhang SC, Tu CT (2016) Quercetin protects mice from ConA-induced hepatitis by inhibiting HMGB1-TLR expression and down-regulating the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Inflammation 39:96–106
Lien E, Ingalls RR (2002) Toll-like receptors. Crit Care Med 30:S1–S11
Malik R, Hodgson H (2002) The relationship between the thyroid gland and the liver. QJM 95:559–569
Massol J, Martin P, Soubrie P, Puech AJ (1988) Triiodothyroacetic acid (TRIAC) potentiation of antidepressant-induced reversal of learned helplessness in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 152:347–351
Mullur R, Liu YY, Brent GA (2014) Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol Rev 94:355–382
Nair AB, Jacob S (2016) A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm 7:27–31
Sang XX, Wang RL, Zhang CE, Liu SJ, Shen HH, Guo YM, Zhang YM, Niu M, Wang JB, Bai ZF, Xiao XH (2017) Sophocarpine protects mice from ConA-Induced hepatitis via inhibition of the IFN-Gamma/STAT1 Pathway. Front Pharmacol 8:140
Sesmilo G, Simo O, Choque L, Casamitjana R, Puig-Domingo M, Halperin I (2011) Serum free triiodothyronine (T3) to free thyroxine (T4) ratio in treated central hypothyroidism compared with primary hypothyroidism and euthyroidism. Endocrinol Nutr 58:9–15
Shinderman-Maman E, Cohen K, Moskovich D, Hercbergs A, Werner H, Davis PJ, Ellis M, Ashur-Fabian O (2017) Thyroid hormones derivatives reduce proliferation and induce cell death and DNA damage in ovarian cancer. Sci Rep 7:16475
Sodhi A, Tarang S, Kesherwani V (2007) Concanavalin A induced expression of Toll-like receptors in murine peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol 7:454–463
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A (1992) A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Inv 90:196–203
Visvanathan K, Skinner NA, Thompson AJ, Riordan SM, Sozzi V, Edwards R, Rodgers S, Kurtovic J, Chang J, Lewin S, Desmond P, Locarnini S (2007) Regulation of Toll-like receptor-2 expression in chronic hepatitis B by the precore protein. Hepatology 45:102–110
Wang ZL, Wu XH, Song LF, Wang YS, Hu XH, Luo YF, Chen ZZ, Ke J, Peng XD, He CM, Zhang W, Chen LJ, Wei YQ (2009) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma inhibitor ameliorates concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:569–574
Xue J, Chen F, Wang J, Wu S, Zheng M, Zhu H, Liu Y, He J, Chen Z (2015) Emodin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibiting activation of the p38 MAPK-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:1557–1570
Zhang D, Zhang G, Hayden MS, Greenblatt MB, Bussey C, Flavell RA, Ghosh S (2004) A toll-like receptor that prevents infection by uropathogenic bacteria. Science 303:1522–1526
Zhang B, Zhang A, Zhou X, Webb P, He W, Xia X (2012) Thyroid hormone analogue stimulates keratinocyte proliferation but inhibits cell differentiation in epidermis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 25:859–869
Zhou M, Zhu X, Ye S, Zhou B (2014) Blocking TLR2 in vivo attenuates experimental hepatitis induced by concanavalin A in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 21:241–246
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (Grant Numbers NRF-2013M3A9B6075890, NRF-2015M3A9C7030121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, H.C., Jang, J.M., Zhou, D. et al. 3, 5, 3′-Triiodothyroacetic acid (TRIAC) is an anti-inflammatory drug that targets toll-like receptor 2. Arch. Pharm. Res. 41, 995–1008 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1057-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1057-8