Abstract
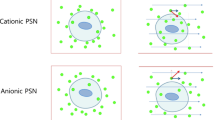
Cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment are affected by fluid shear stress generated by blood flow in the vascular microenvironment and interstitial flows in the tumor microenvironment. Thus, we investigated how fluidic shear stress affects cellular uptake as well as the endocytosis mechanism of nanoparticles using a biomimetic microfluidic system that mimics the human dynamic environment. Positively charged amino-modified polystyrene nanoparticles (PSNs) at 100 μg/mL were delivered to cancer cells under static and biomimetic dynamic conditions (0.5 dyne/cm2). Additionally, the experiment was done in the presence of endocytosis inhibitors specific for one of the endocytosis pathways. To evaluate cellular uptake of cationic PSNs, the fluorescence intensity of cationic PSNs in cancer cells was measured by flow cytometer and fluorescence images were taken using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cancer cells in dynamic conditions exhibited higher cellular uptake of PSNs and showed different cellular uptake mechanisms compared with those in static conditions. From these results, it suggested that biomimetic dynamic conditions stimulated specific endocytosis and prompted cellular uptake. It was also important to consider fluidic shear stress as one of the critical factors because cellular uptake and drug delivery could play a key role in cancer cells and metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RG (1998) The caveolae membrane system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:199–225
Araki N, Johnson MT, Swanson JA (1996) A role for phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the completion of macropinocytosis and phagocytosis by macrophages. J Cell Biol 135:1249–1260
Bhowmick T, Berk E, Cui X, Muzykantov VR, Muro S (2012) Effect of flow on endothelial endocytosis of nanocarriers targeted to ICAM-1. J Control Release 157:485–492
Bodin P, Burnstock G (2001) Evidence that release of adenosine triphosphate from endothelial cells during increased shear stress is vesicular. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 38:900–908
Brandenberger C, Muhlfeld C, Ali Z, Lenz AG, Schmid O, Parak WJ, Gehr P, Rothen-Rutishauser B (2010) Quantitative evaluation of cellular uptake and trafficking of plain and polyethylene glycol-coated gold nanoparticles. Small 6:1669–1678
Chen J, Li G, Lu J, Chen L, Huang Y, Wu H, Zhang J, Lu D (2006) A novel type of PTD, common helix–loop–helix motif, could efficiently mediate protein transduction into mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347:931–940
Chotard-Ghodsnia R, Haddad O, Leyrat A, Drochon A, Verdier C, Duperray A (2007) Morphological analysis of tumor cell/endothelial cell interactions under shear flow. J Biomech 40:335–344
Dausend J, Musyanovych A, Dass M, Walther P, Schrezenmeier H, Landfester K, Mailander V (2008) Uptake mechanism of oppositely charged fluorescent nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Macromol Biosci 8:1135–1143
Davies PF (1995) Flow-mediated endothelial mechanotransduction. Physiol Rev 75:519–560
des Rieux A, Fievez V, Theate I, Mast J, Preat V, Schneider YJ (2007) An improved in vitro model of human intestinal follicle-associated epithelium to study nanoparticle transport by M cells. Eur J Pharm Sci 30:380–391
Dong C, Slattery M, Liang S (2005) Micromechanics of tumor cell adhesion and migration under dynamic flow conditions. Front Biosci 10:379–384
Douglas KL, Piccirillo CA, Tabrizian M (2008) Cell line-dependent internalization pathways and intracellular trafficking determine transfection efficiency of nanoparticle vectors. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 68:676–687
Gratton SE, Ropp PA, Pohlhaus PD, Luft JC, Madden VJ, Napier ME, DeSimone JM (2008) The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:11613–11618
Haier J, Nicolson GL (2001) Tumor cell adhesion under hydrodynamic conditions of fluid flow. APMIS 109:241–262
Harush-Frenkel O, Debotton N, Benita S, Altschuler Y (2007) Targeting of nanoparticles to the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353:26–32
Hillaireau H, Couvreur P (2009) Nanocarriers’ entry into the cell: relevance to drug delivery. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2873–2896
Kang T, Cho Y, Park C, Kim SD, Oh E, Cui J-H, Cao Q-R, Lee B-J (2016a) Effect of biomimetic shear stress on intracellular uptake and cell-killing efficiency of doxorubicin in a free and liposomal formulation. Int J Pharm 510:42–47
Kang T, Park C, Choi J-S, Cui J-H, Lee B-J (2016b) Effects of shear stress on the cellular distribution of polystyrene nanoparticles in a biomimetic microfluidic system. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 31:130–136
Khandelwal P, Ruiz WG, Apodaca G (2010) Compensatory endocytosis in bladder umbrella cells occurs through an integrin-regulated and RhoA-and dynamin-dependent pathway. The EMBO journal 29:1961–1975
Kuhn DA, Vanhecke D, Michen B, Blank F, Gehr P, Petri-Fink A, Rothen-Rutishauser B (2014) Different endocytotic uptake mechanisms for nanoparticles in epithelial cells and macrophages. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 5:1625–1636
Lawler K, Meade G, O’Sullivan G, Kenny D (2004) Shear stress modulates the interaction of platelet-secreted matrix proteins with tumor cells through the integrin αvβ3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C1320–C1327
Lawler K, Foran E, O’Sullivan G, Long A, Kenny D (2006) Mobility and invasiveness of metastatic esophageal cancer are potentiated by shear stress in a ROCK- and Ras-dependent manner. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291:C668–C677
Lawler K, O’Sullivan G, Long A, Kenny D (2009) Shear stress induces internalization of E-cadherin and invasiveness in metastatic oesophageal cancer cells by a Src-dependent pathway. Cancer Sci 100:1082–1087
Lunov O, Syrovets T, Loos C, Beil J, Delacher M, Tron K, Nienhaus GU, Musyanovych A, Mailander V, Landfester K, Simmet T (2011) Differential uptake of functionalized polystyrene nanoparticles by human macrophages and a monocytic cell line. ACS Nano 5:1657–1669
Macia E, Ehrlich M, Massol R, Boucrot E, Brunner C, Kirchhausen T (2006) Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev Cell 10:839–850
Michor F, Liphardt J, Ferrari M, Widom J (2011) What does physics have to do with cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 11:657–670
Mineo C, Anderson RG (2001) Potocytosis. Robert Feulgen Lecture. Histochem Cell Biol 116:109–118
Nguyen KT, Eskin SG, Patterson C, Runge MS, McIntire LV (2001) Shear stress reduces protease activated receptor-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Ann Biomed Eng 29:145–152
Nichols B (2003) Caveosomes and endocytosis of lipid rafts. J Cell Sci 116:4707–4714
Panyam J, Zhou WZ, Prabha S, Sahoo SK, Labhasetwar V (2002) Rapid endo-lysosomal escape of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: implications for drug and gene delivery. FASEB J 16:1217–1226
Puri V, Watanabe R, Singh RD, Dominguez M, Brown JC, Wheatley CL, Marks DL, Pagano RE (2001) Clathrin-dependent and -independent internalization of plasma membrane sphingolipids initiates two Golgi targeting pathways. J Cell Biol 154:535–547
Qian ZM, Li H, Sun H, Ho K (2002) Targeted drug delivery via the transferrin receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway. Pharmacol Rev 54:561–587
Rejman J, Oberle V, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D (2004) Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin-and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J 377:159–169
Roberts JC, Merkle AC, Biermann PJ, Ward EE, Carkhuff BG, Cain RP, O’Connor JV (2007) Computational and experimental models of the human torso for non-penetrating ballistic impact. J Biomech 40:125–136
Saha K, Kim ST, Yan B, Miranda OR, Alfonso FS, Shlosman D, Rotello VM (2013) Surface functionality of nanoparticles determines cellular uptake mechanisms in mammalian cells. Small 9:300–305
Schwachtgen J-L, Houston P, Campbell C, Sukhatme V, Braddock M (1998) Fluid shear stress activation of egr-1 transcription in cultured human endothelial and epithelial cells is mediated via the extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Clin Invest 101:2540
Stuart AD, Brown TDK (2006) Entry of feline calicivirus is dependent on clathrin-mediated endocytosis and acidification in endosomes. J Virol 80:7500–7509
Swartz MA, Lund AW (2012) Lymphatic and interstitial flow in the tumour microenvironment: linking mechanobiology with immunity. Nat Rev Cancer 12:210–219
Thamilselvan V, Patel A, der van Voort Zyp J, Basson MD (2004) Colon cancer cell adhesion in response to Src kinase activation and actin-cytoskeleton by non-laminar shear stress. J Cell Biochem 92:361–371
Tuma P, Hubbard AL (2003) Transcytosis: crossing cellular barriers. Physiol Rev 83:871–932
Unfried K, Albrecht C, Klotz L-O, Von Mikecz A, Grether-Beck S, Schins RP (2007) Cellular responses to nanoparticles: target structures and mechanisms. Nanotoxicology 1:52–71
Zhang LW, Monteiro-Riviere NA (2009) Mechanisms of quantum dot nanoparticle cellular uptake. Toxicol Sci 110:138–155
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Grant (16173MFDS542) from Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2016, Republic of Korea. This research was partially supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2013M3A9B5075841), Korea. We would like to thank Ajou University-Central Laboratory for the use of confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, T., Park, C. & Lee, BJ. Investigation of biomimetic shear stress on cellular uptake and mechanism of polystyrene nanoparticles in various cancer cell lines. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 1663–1670 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0847-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0847-0