Abstract
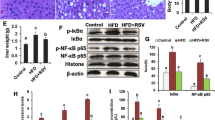
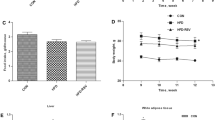
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with inhibited AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and activation of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (SREBP-1). AMPK phosphorylation inhibits SREBP-1, a major transcription factor of de novo lipogenesis, by inhibiting the liver X receptor (LXR) or by direct phosphorylation. Resveratrol, a polyphenol, has regulatory effects on hepatic lipid metabolism as a potent AMPK activator. In this study, we evaluated the anti-steatogenic effects of resveratrol and its derivatives and identified the molecular mechanism in vitro and in vivo. Resveratrol and its derivatives decreased lipid accumulation by free fatty acids (FFA mixture; 0.5 mM, oleic acid:palmitic acid = 2: 1) in H4IIEC3 cells. Synthesized derivatives of resveratrol had lower cytotoxicity than the parental molecule with similar potency. SY-102 suppressed SREBP-1 maturation by T0901317, an LXR agonist, and decreased SRE luciferase activity and the mRNA levels of lipogenic genes. Inhibition of AMPK by pre-treatment with compound C completely blocked the effects of SY-102. To evaluate their efficacy in vivo, mice were fed a high-fat diet for 5 days, and resveratrol or SY-102 was administered orally for the last 2 days. Oral administration of the SY-102 increased AMPK phosphorylation, followed by reduced hepatic triglyceride accumulation to a similar extent as resveratrol. These data demonstrate that SY-102, a synthesized derivative of resveratrol, might provide a promising therapeutic effect against fatty liver disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmo, J.M., X. Liang, C.Q. Rogers, B. Pennock, and M. You. 2008. Resveratrol alleviates alcoholic fatty liver in mice. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 295: 833–842.
Angulo, P. 2002. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. New England Journal of Medicine 346: 1221–1231.
Baur, J.A., and D.A. Sinclair. 2006. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 5: 493–506.
Bellentani, S., G. Saccoccio, F. Masutti, L.S. Crocè, G. Brandi, F. Sasso, G. Cristanini, and C. Tiribelli. 2000. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in Northern Italy. Annals of Internal Medicine 132: 112–117.
Borra, M.T., B.C. Smith, and J.M. Denu. 2005. Mechanism of human SIRT1 activation by resveratrol. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280: 17187–17195.
Chun, Y.J., C. Lim, S.O. Ohk, J.M. Lee, J.H. Lee, S. Choi, and S. Kim. 2011. trans-Stilbenoids: Potent and selective inhibitors for human cytochrome P4501B1. Medicinal Chemistry Communications 2: 402–405.
Gómez-Lechón, M.J., M.T. Donato, A. Martínez-Romero, N. Jiménez, J.V. Castell, and J.E. O’Connor. 2007. A human hepatocellular in vitro model to investigate steatosis. Chemico-Biological Interactions 165: 106–116.
Hou, X., S. Xu, K.A. Maitland-Toolan, K. Sato, B. Jiang, Y. Ido, F. Lan, K. Walsh, M. Wierzbicki, T.J. Verbeuren, R.A. Cohen, and M. Zang. 2008. SIRT1 regulates hepatocyte lipid metabolism through activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 283: 20015–20026.
Hwahng, S.H., S.H. Ki, E.J. Bae, H.E. Kim, and S.G. Kim. 2009. Role of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-p70 ribosomal S6 kinase-1 pathway in repression of liver X receptor-alpha-dependent lipogenic gene induction and hepatic steatosis by a novel class of dithiolethiones. Hepatology 49: 1913–1925.
Kraegen, E.W., P.W. Clark, A.B. Jenkins, E.A. Daley, D.J. Chisholm, and L.H. Storlien. 1991. Development of muscle insulin resistance after liver insulin resistance in high-fat-fed rats. Diabetes 40: 1397–1403.
Khanal, T., J.H. Choi, Y.P. Hwang, Y.C. Chung, and H.G. Jeong. 2009. Protective effects of saponins from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum against fatty liver in chronic ethanol feeding via the activation of AMP-dependent protein kinase. Food and Chemical Toxicology 47: 2749–2754.
Lee, M.S., D. Kim, K. Jo, and J.K. Hwang. 2010. Nordihydroguaiaretic acid protects against high-fat diet-induced fatty liver by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in obese mice. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 401: 92–97.
Li, S., M.S. Brown, and J.L. Goldstein. 2010. Bifurcation of insulin signaling pathway in rat liver: mTORC1 required for stimulation of lipogenesis, but not inhibition of gluconeogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 3441–3446.
Li, Y., S. Xu, M.M. Mihaylova, B. Zheng, X. Hou, B. Jiang, O. Park, Z. Luo, E. Lefai, J.Y. Shyy, B. Gao, M. Wierzbicki, T.J. Verbeuren, R.J. Shaw, R.A. Cohen, and M. Zang. 2011. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metabolism 13: 376–388.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Manna, S.K., A. Mukhopadhyay, and B.B. Aggarwal. 2000. Resveratrol suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-κB, activator protein-1, and apoptosis: Potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. The Journal of Immunology 164: 6509–6519.
McMillian, M.K., E.R. Grant, Z. Zhong, J.B. Parker, L. Li, R.A. Zivin, M.E. Burczynski, and M.D. Johnson. 2001. Nile red binding to HepG2 cells: An improved assay for in vitro studies of hepatosteatosis. In Vitro and Molecular Toxicology 14: 177–190.
Olas, B., B. Wachowicz, J. Saluk-Juszczak, and T. Zieliński. 2002. Effect of resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, on platelet activation induced by endotoxin or thrombin. Thrombosis Research 107: 141–145.
Rossmeisl, M., J.S. Rim, R.A. Koza, and L.P. Kozak. 2003. Variation in type 2 diabetes-related traits in mouse strains susceptible to diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 52: 1958–1966.
Samuel, V.T., Z.X. Liu, X. Qu, B.D. Elder, S. Bilz, D. Befroy, A.J. Romanelli, and G.I. Shulman. 2004. Mechanism of hepatic insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 32345–32353.
Schultz, J.R., H. Tu, A. Luk, J.J. Repa, J.C. Medina, L. Li, S. Schwendner, S. Wang, M. Thoolen, D.J. Mangelsdorf, K.D. Lustig, and B. Shan. 2000. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes and Development 14: 2831–2838.
Shang, J., L.L. Chen, F.X. Xiao, H. Sun, H.C. Ding, and H. Xiao. 2008. Resveratrol improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 29: 698–706.
Wang, G.L., Y.C. Fu, W.C. Xu, Y.Q. Feng, S.R. Fang, and X.H. Zhou. 2009. Resveratrol inhibits the expression of SREBP1 in cell model of steatosis via Sirt1–FOXO1 signaling pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 380: 644–649.
Yahagi, N., H. Shimano, A.H. Hasty, T. Matsuzaka, T. Ide, T. Yoshikawa, M. Amemiya-Kudo, S. Tomita, H. Okazaki, Y. Tamura, Y. Iizuka, K. Ohashi, J. Osuga, K. Harada, T. Gotoda, R. Nagai, S. Ishibashi, and N. Yamada. 2002. Absence of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) ameliorates fatty livers but not obesity or insulin resistance in Lep(ob)/Lep(ob) mice. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277: 19353–19357.
Yoshikawa, T., H. Shimano, M. Amemiya-Kudo, N. Yahagi, A.H. Hasty, T. Matsuzaka, H. Okazaki, Y. Tamura, Y. Iizuka, K. Ohashi, J. Osuga, K. Harada, T. Gotoda, S. Kimura, S. Ishibashi, and N. Yamada. 2001. Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter. Molecular and Cellular Biology 21: 2991–3000.
You, M., M. Fischer, M.A. Deeg, and D.W. Crabb. 2002. Ethanol induces fatty acid synthesis pathways by activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP). Journal of Biological Chemistry 277: 29342–29347.
Zang, M.W., S.Q. Xu, K.A. Maitland-Toolan, A. Zuccollo, X.Y. Hou, B.B. Jiang, M. Wierzbicki, T.J. Verbeuren, and R.A. Cohen. 2006. Polyphenols stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase, lower lipids, and inhibit accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetic LDL receptor-deficient mice. Diabetes 55: 2180–2191.
Zhou, G., R. Myers, Y. Li, Y. Chen, X. Shen, J. Fenyk-Melody, M. Wu, J. Ventre, T. Doebber, N. Fujii, N. Musi, M.F. Hirshman, L.J. Goodyear, and D.E. Moller. 2001. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. Journal of Clinical Investigation 108: 1167–1174.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A121185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YJ., Suh, HR., Yoon, Y. et al. Protective effect of resveratrol derivatives on high-fat diet induced fatty liver by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 1169–1176 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0347-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0347-z