Abstract
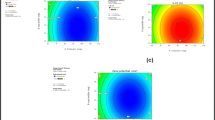
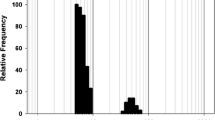
The purpose of this research was to improve oral bioavailability of poorly aqueous soluble drug lopinavir using solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Glyceryl behenate based SLNs of lopinavir were prepared using hot self-nanoemulsification (SNE) technique. The hot isotropic mixture of glyceryl behenate, Poloxamer 407 and polyethylene glycol 4000 was spontaneously self-nanoemulsify in hot water (80 °C) and SLNs were subsequently formed with rapid cooling. Hot SNE ability of isotropic mixture was visually assessed by ternary phase diagram study. Optimized SLNs were having particle size of 214.5 ± 4.07 nm, entrapment efficiency of 81.6 ± 2.3 % and zeta potential of −12.7 ± 0.87 mV. SLNs were evaluated by transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy for morphological details. Further, differential scanning calorimetry and x-ray diffraction were also performed for solid state characterization of SLNs. Higher oral bioavailability (3.56-fold) was found for lopinavir loaded SLNs in comparison to bulk lopinavir due to higher lymphatic drug transport (p < 0.05). Results indicate that SLNs of glyceryl behenate can be successfully prepared by hot SNE technique.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, S., D. Pal, and A.K. Mitra. 2007. Both P-gp and MRP2 mediate transport of lopinavir, a protease inhibitor. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 339: 139–147.
Alex, M.R.A., A.J. Chacko, S. Josea, and E.B. Souto. 2011. Lopinavir loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for intestinal lymphatic targeting. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 42: 11–18.
Amado, E., and J. Kressler. 2011. Interactions of amphiphilic block copolymers with lipid model membranes. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science 16: 491–498.
Batrakova, E.V., and A.V. Kabanov. 2008. Pluronic block copolymers: evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. Journal of Controlled Release 130: 98–106.
Boyd, M., V. Risovic, P. Jull, E. Choo, and K.M. Wasan. 2004. A stepwise surgical procedure to investigate the lymphatic transport of lipid-based oral drug formulations: Cannulation of the mesenteric and thoracic lymph ducts within the rat. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods 49: 115–120.
Das, S., and A. Choudhary. 2011. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSci Tech 12: 62–76.
Debashish, D., Rama, P.V.S., Arbinda, S. 2009. Process for preparing an amorphous form of (2S, 3S, 5S)-2-(2,6-Dimethylphenoxyacetyl- amino-3- hydroxyl-5-(2-(1-Tetrahydropyrimid-2-only)-3-methylbutanoyl)-amino-1,6-diphenyl hexane and product thereof. International Application Published under the Patent cooperation Treaty (PCT) WO 2009/004653 A2: 1–8.
Dickman, D.A., Chemburkar, S., Fort, J.J., Henry, R.F., Lechuga-Ballesteros, D., Niu, Y., Porter, W. 2005 Crystalline Pharmaceuticals. United States Patent US 6,864,369 B2.
Essa, S., J.M. Rabanel, and P. Hildgen. 2011. Characterization of rhodamine loaded PEG-g-PLA nanoparticles (NPs): Effect of poly (ethyleneglycol) grafting density. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 411: 178–187.
Kataoka, M., T. Yokoyama, Y. Masaoka, S. Sakuma, and S. Yamashita. 2011. Estimation of P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux in the oral absorption of P-gp substrate drugs from simultaneous analysis of drug dissolution and permeation. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 44: 544–551.
Kovacevic, A., S. Savica, G. Vuleta, R.H. Müller, and C.M. Keck. 2011. Poly hydroxyl surfactants for the formulation of lipid nanoparticles (SLN and NLC): Effects on size, physical stability and particle matrix structure. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 406: 163–172.
Kumar, G.N., V.K. Jayanti, M.K. Johnson, J. Uchic, S. Thomas, R.D. Lee, B.A. Grabowski, H.L. Sham, D.J. Kempf, J.F. Denissen, K.C. Marsh, E. Sun, and S.A. Roberts. 2004. Metabolism and disposition of the HIV-1 protease inhibitor lopinavir (ABT-378) given in combination with ritonavir in rats, dogs, and humans. Pharmaceutical Research 21: 1622–1630.
Manjunath, K., and V. Venkateswarlu. 2005. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and bioavailability of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles after intravenous and intraduodenal administration. Journal of Controlled Release 107: 215–228.
Mascolini, Z., What Will It Take To Replace Ritonavir as the Prime PK Booster? Debate Ritonavir v GS9350. 11th International Workshop on Clinical Pharmacology of HIV Therapy Sorrento, Italy, April 7–9 (2010). http://www.natap.org/2010/PK/PK_08.html. Accessed 17 Aug 2012.
Minocha, M., V. Khurana, B. Qin, D. Pal, and A.K. Mitra. 2012. Co-administration strategy to enhance brain accumulation of vandetanib by modulating P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp1/Abcg2) mediated efflux with m-TOR inhibitors. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 434: 306–314.
Muller, R.H., K. Mader, and S. Gohla. 2000. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 50: 161–177.
Negi, J.S., P. Chattopadhyay, A.K. Sharma, and V. Ram. 2013. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) of lopinavir using hot self nano-emulsification (SNE) technique. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 48: 231–239.
Owens, D.E., and N.A. Peppas. 2006. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 307: 93–102.
Paliwal, R., S. Rai, B. Vaidya, K. Khatri, A.K. Goyal, N. Mishra, A. Mehta, and S.P. Vyas. 2009. Effect of lipid core material on characteristics of solid lipid nanoparticles designed for oral lymphatic delivery. Nanomedicine 5: 184–191.
Ren, J., M. Zou, P. Gao, Y. Wang, and G. Cheng. 2012. Tissue distribution of borneol-modified ganciclovir-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in mice after intravenous administration. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 83: 141–148.
Rowe, R.C., P.J. Sheskey, and M.E. Quinn. 2009. Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients. London: Pharmaceutical Press and American Pharmacist Association.
Cai, S., Q. Yang, T.R. Bagby, and M.L. Forrest. 2011. Lymphatic drug delivery using engineered liposomes and solid lipid nanoparticles. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 63: 901–908.
Salvia-Trujillo, L., M.A. Rojas-Graü, R. Soliva-Fortuny, and O. Martín-Belloso. 2013. Effect of processing parameters on physicochemical characteristics of microfluidized lemongrass essential oil-alginate nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocolloids 30: 401–407.
Semete, B., L. Booysen, L. Kalombo, B. Ramalapa, R. Hayeshi, and H.S. Swai. 2012. Effects of protein binding on the biodistribution of PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles post oral administration. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 424: 115–120.
Shafran, S.D., L.D. Mashinter, and S.E. Roberts. 2005. The effect of low-dose ritonavir monotherapy on fasting serum lipid concentrations. HIV Med. 6: 421–425.
Shah, M., K. Chuttani, A.K. Mishra, and K. Pathak. 2011. Oral solid compritol 888 ATO nanosuspension of simvastatin: optimization and biodistribution studies. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 37: 526–537.
Sinha, S., M. Ali, S. Baboota, A. Ahuja, A. Kumar, and J. Ali. 2010. Solid dispersion as an approach for bioavailability enhancement of poorly water-soluble drug ritonavir. AAPS PharmSciTech 11: 518–527.
Souza, L.G., E.J. Silva, A.L.L. Martins, M.F. Mota, R.C. Braga, E.M. Lima, M.C. Valadares, S.F. Taveira, and R.N. Marreto. 2011. Development of topotecan loaded lipid nanoparticles for chemical stabilization and prolonged release. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 79: 189–196.
Trevaskis, N.L., R.M. Shanker, W.M. Charman, and C.J.H. Porter. 2010. The mechanism of lymphatic access of two cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors (CP524, 515 and CP532, 623) and evaluation of their impact on lymph lipoprotein profiles. Pharmaceutical Research 27: 1949–1964.
Vitorino, C., F.A. Carvalho, A.J. Almeida, J.J. Sousa, and A.C. Pais. 2011. The size of solid lipid nanoparticles: An interpretation from experimental design. Colloids and Surfaces B Biointerfaces 84: 117–130.
Ye, L., X. Yang, Z. Yang, S. Gao, T. Yin, W. Liu, F. Wang, M. Hu, and Z. Liu. 2013. The role of efflux transporters on the transport of highly toxic aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine, and their hydrolysates, as determined in cultured Caco-2 and transfected MDCKII cells. Toxicology Letters 216: 86–99.
Youssef, T., M. Fadel, R. Fahmy, and K. Kassab. 2012. Evaluation of hypericin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Physicochemical properties, photostability and phototoxicity. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 17: 177–186.
Zhao, Y., C. Wang, A.H.L. Chow, K. Ren, T. Gong, Z. Zhang, and Y. Zheng. 2010. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral delivery of Zedoary essential oil: Formulation and bioavailability studies. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 383: 170–177.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facilities (SAIF), Panjab Univeristy for providing XRD, TEM facilities and SMITA lab, IIT Dehli for providing particle size, AFM and DSC facilities. Authors also would like to acknowledge Uttarakhand technical University, Dehradun for their kind support.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declaration of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Negi, J.S., Chattopadhyay, P., Sharma, A.K. et al. Development and evaluation of glyceryl behenate based solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) using hot self-nanoemulsification (SNE) technique. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 361–370 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0154-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0154-y