Abstract
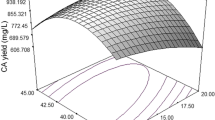
Antibiotic activity against various gram positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus was ascertained from a soil-isolated microbial strain Streptomyces sp. CS392. The antibiotic activity of the strain was maximized by using a dual-stage, multivariate statistical optimization framework based on the response surface methodology considering a lab-scale fermentation process. Multiple nutrient constituents of the fermentation broth were jointly optimized in the first stage, while the fermentation culture conditions were optimized in the subsequent stage. Based on the empirical models derived from the dual-stage statistical optimization framework, 39.79 % of cumulative enhancement in the antibiotic activity was obtained (analytically) at the concurrent optimal settings (Optimal nutrient composition for the first stage of optimization: 29.82 glucose, 7.6 peptone, 4.678 MgCl2 and 0.5005 g/l casamino acid; and optimal fermentation condition for the second stage of optimization: incubation period 47.55 h; incubation temperature 29.15 °C; and pH 8.36). The analytically depicted enhancement in the antibiotic activity was validated experimentally.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baş, D., and İ.H. Boyacı. 2007. Modeling and optimization I: Usability of response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering 78: 836–845.
Chen, X.-C., J.-X. Bai, J.-M. Cao, Z.-J. Li, J. Xiong, L. Zhang, Y. Hong, and H.-J. Ying. 2009. Medium optimization for the production of cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate by Microbacterium sp. no. 205 using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology 100: 919–924.
Cho, S.S., Y.H. Choi, J.R. Simkhada, P. Mander, and J.C. Yoo. 2012. A newly isolated Streptomyces sp. CS392 producing three antimicrobial compounds. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering 35: 247–254.
Deleo, F.R., and H.F. Chambers. 2009. Reemergence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the genomics era. Journal of Clinical Investigation 119: 2464.
Delisle, S., and T.M. Perl. 2003. Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci: A road map on how to prevent the emergence and transmission of antimicrobial resistance. Chest Journal 123: 504S–518S.
Fischbach, M.A., and C.T. Walsh. 2009. Antibiotics for emerging pathogens. Science 325: 1089–1093.
Gesheva, V. 2009. Optimization of the production medium for biosynthesis of antifungal antibiotic Ak-111-81 by phosphate-deregulated mutant of Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 158: 20–24.
Jamal Ibrahim, D., and M. Alam. 2010. Statistical optimization of fermentation conditions for cellulase production from palm oil mill effluent. American Journal of Environmental Sciences 6: 66–70.
Kammoun, R., B. Naili, and S. Bejar. 2008. Application of a statistical design to the optimization of parameters and culture medium for α-amylase production by Aspergillus oryzae CBS 819.72 grown on gruel (wheat grinding by-product). Bioresource Technology 99: 5602–5609.
Khurana, S., M. Kapoor, S. Gupta, and R. Kuhad. 2007. Statistical optimization of alkaline xylanase production from Streptomyces violaceoruber under submerged fermentation using response surface methodology. Indian Journal of Microbiology 47: 144–152.
Leardi, R. 2009. Experimental design in chemistry: A tutorial. Analytica Chimica Acta 652: 161–172.
Micek, S.T. 2007. Alternatives to vancomycin for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 45: S184–S190.
Song, J.-H., K. Hiramatsu, J.Y. Suh, K.S. Ko, T. Ito, M. Kapi, S. Kiem, Y.-S. Kim, W.S. Oh, and K.R. Peck. 2004. Emergence in asian countries of Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 48: 4926–4928.
Tiwari, H.K., and M.R. Sen. 2006. Emergence of vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) from a tertiary care hospital from northern part of India. BMC Infectious Diseases 6: 156.
Walsh, T.R., and R.A. Howe. 2002. The prevalence and mechanisms of vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annual Review of Microbiology 56: 657–675.
Wang, Y.-H., Y.-P. Li, Q. Zhang, and X. Zhang. 2008a. Enhanced antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus nematophila by medium optimization. Bioresource Technology 99: 1708–1715.
Wang, Y., X. Fang, F. An, G. Wang, and X. Zhang. 2011. Improvement of antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus bovienii by medium optimization using response surface methodology. Microbial Cell Factories 10: 1–15.
Wang, Y.H., J.T. Feng, Q. Zhang, and X. Zhang. 2008b. Optimization of fermentation condition for antibiotic production by Xenorhabdus nematophila with response surface methodology. Journal of Applied Microbiology 104: 735–744.
Watve, M.G., R. Tickoo, M.M. Jog, and B.D. Bhole. 2001. How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces? Archives of Microbiology 176: 386–390.
Weuster-Botz, D. 2000. Experimental design for fermentation media development: Statistical design or global random search? The Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 90: 473–483.
Willems, R.J., J. Top, D. Marga Van Santen, T.M. Coque, F. Baquero, H. Grundmann, and M.J. Bonten. 2005. Global spread of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium from distinct nosocomial genetic complex. Emerging Infectious Diseases 11: 821.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (2010-0029178).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Poonam Mander and Yun Hee Choi contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mander, P., Choi, Y.H., Seong, J.H. et al. Statistical optimization of a multivariate fermentation process for enhancing antibiotic activity of Streptomyces sp. CS392. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 973–980 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0140-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0140-4