Abstract
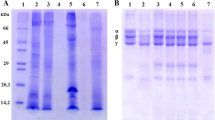
Venom of Agkistrodon halys Pallas can control severe pain such as cancer pain and neuropathic pain, but it is made up of complicated components. Aim of this study is to separate major analgesic fraction from venom of A. halys Pallas, and to reveal its biochemical and pharmacological properties. Three steps with ion exchange column first and molecular sieve columns next were used to separate and purify the fractions of venom. Analgesic effects were evaluated by hot plate tests and writhing tests in mice. The molecular weight (MW), isoelectric point, amino acid sequence, purity were respectively determined by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, isoelectric focusing, Edman degradation and HPLC. The dependence and tolerance were observed by withdrawal test in rats, and analgesic effects were observed in mice during 7 days administration. Fourteen fractions were obtained by separation; the best analgesic fraction named Pallanalgesin was selected by ED50 and LD50. It had single band in electrophoresis, relative purity 92.16 %, MW 16.6 kDa, isoelectric point 8.8, and former sequence of ten amino acids H-L-L-Q-F-R-K-M-I-K. It showed significant analgesic effect without tolerance and dependence. As a novel analgesic, Pallanalgesin has been found to explain the function of venom of A. halys Pallas on severe pain control in traditional uses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel, F.M. 1995. Short protocols in molecular biology, 3rd ed. New York: Wiley.
Beckner, T.F., and P. Idsvoog. 1975. Drug use and distribution in a pain rehabilitation center. American Journal of Hospital Pharmacy 32: 285–289.
Bliss, C. 1938. The determination of dosage mortality curve from small numbers. Quarterly Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 11: 192–216.
Chen, J., and W.R. Lariviere. 2010. The nociceptive and anti-nociceptive effects of bee venom injection and therapy: A double-edged sword. Progress in Neurobiology 92: 151–183.
Chen, R., and S.E. Robinson. 1990. The effect of cholinergic manipulations on the analgesic response to cobrotoxin in mice. Life Sciences 47: 1949–1954.
Chen, Z.X., H.L. Zhang, and Z.L. Gu. 2006. A long-form alpha-neurotoxin from cobra venom produces potent opioid-independent analgesia. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 27: 402–408.
Cura, J.E., D.P. Blanzaco, C. Brisson, M.A. Cura, R. Cabrol, L. Larrateguy, C. Mendez, C. Mendez, J.C. Sechi, J.S. Siveira, E. Theiller, A.R. de Roodt, and J.C. Vidal. 2002. Phase I and pharmacokinetics study of Cro (cytotoxin PLA2, NSC-624244) in patient with advanced cancer. Clinical Cancer Research 8: 1033–1041.
Derardt, R., S. Jougney, F. Delevalcee, and M. Falhout. 1980. Release of prostaglandins E and F in analgogenic reaction and its inhibition. European Journal of Pharmacology 61: 17–24.
Dong, X.Y. 2003. Biochemistry experiment. Beijing: Chemical Industry Publishing House.
Fontenele, J.B., G.S.B. Viana, J. Xavier-Filho, and J.W. Alencar. 1996. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of a water-soluble fraction from shark cartilage. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 29: 643–646.
Giorgi, R., M.M. Bernardi, and Y. Cury. 1993. Analgesic effect evoked by low molecular weight substances extracted from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Toxicon 31: 1257–1265.
Gutierrez, V.P., K. Katsuhiro Konno, M. Chacur, S.C. Sampaio, G. Picolo, P. Brigatte, V.O. Zambelli, and Y. Cury. 2008. Crotalphine induces potent antinociception in neuropathic pain by acting at peripheral opioid receptors. European Journal of Pharmacology 594: 84–92.
Klint, J.K., S. Senff, and D.B. Rupasinghe. 2012. Spider-venom peptides that target voltage-gated sodium channels: Pharmacological tools and potential therapeutic leads. Toxicon 60: 478–491.
Knapp, O., J.R. McArthur, and D. Adams. 2012. Conotoxins targeting neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel subtypes: potential analgesics? Toxin 4: 1236–1260.
Kokotos, G., D.A. Six, and V. Loukas. 2004. Inhibition of group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A (2) by novel 2-oxoamides in vitro, in cells, and in vivo. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 47: 14.
Kondo, K., J. Zhang, K. Xu, and H. Kagamiyama. 1989. Amino acid sequence of a presynaptic neurotoxin, agkistrodotoxin, from the venom of Agkistrodon halys Pallas. Journal of Biochemistry (Tokyo) 105: 196–203.
Levy, D.E., and G.J. Del Zoppo. 2006. Ancrod: A potential treatment for acute, ischemic stroke from snake venom. Toxin Reviews 25: 319–329.
Li, J.W., N.G. Xiong, and R.Y. Yu. 1994. Experimental principle and method of biochemistry. Beijing: Beijing University Publishing House.
Macht, D.I. 1936. Experimental and clinical study of Cobra venom as an analgesic. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 22: 61–71.
Mancin, A.C., M. Soares, S.H. Andriao-Escarso, A.M. Faca, L.J. Green, S. Zuccolotto, I.R. Pela, and J.R. Giglio. 1998. The analgesic activity of crotamine, a neurotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus (South American Ratttle snake) venom: a biochemical and pharmacological study. Toxicon 36: 1927–1937.
Markland, F.S., S. Swenson, and F. Costa. 2005. A snake venom disintegrin with potent antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Toxin Reviews 24: 113–142.
Oaklander, A.L. 2008. Mechanisms of pain and itch caused by Herpes Zoster (Shingles). Journal of Pain 9: S10–S18.
Odabsoglu, F., A. Cakir, H. Suleyman, A. Aslan, Y. Bayir, M. Halici, and C. Kazaz. 2006. Gastroprotective and antioxidant effects of usnic acid an indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 103: 59–65.
Okokon, J.E., B.S. Antia, and E. Umoh. 2008. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of ethanolic root extract of Hippocratea Africana. International Journal of Pharmacology 4: 51–55.
Perumal Samy, R., P. Gopalakrishnakone, B.H. Vincent, and T.K. Chow. 2008. Purification, characterization and bactericidal activities of basic phospholipase A2 from the venom of Agkistrodon halys (Chinese pallas). Biochimie 90: 1372–1388.
Picolo, G., R. Giorgi, and M.M. Bernardi. 1998. The antinociceptive of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom is mainly due to a supraspinally integrated response. Toxicon 36: 223–227.
Pu, X.C., P.T. Wong, and P.A. Gopalakrishnakone. 1995. Novel analgesic toxin (hannalgesin) from the venom of king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah). Toxicon 33: 1425–1431.
Quintero-Hernandez, V., E. Ortiz, and M. Redon-Anaya. 2011. Scorpion and spider venom peptides: Gene cloning and peptide expression. Toxicon 58: 644–663.
Rajendra, W., A. Armugam, and K. Jeyaseelan. 2004. Toxins in anti-nociception and anti-inflammation. Toxicon 44: 1–17.
Seiji, I., O.A. Emiko, and M. Toshiaki. 2001. Central and peripheral roles of prostaglandins in pain and their interactions with novel neuropeptides nociceptin and nocistatin. Neuroscience Research 41: 299–332.
Somchit, M.N., M.R. Sulaiman, A. Zuraini, and L. Samsuddin. 2004. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Centella asiatica. Indian Journal of Pharmacology 36: 377–380.
Vink, S., and P.F. Alewood. 2012. Targeting voltage-gated calcium channels: Developments in peptide and small-molecule inhibitors for the treatment of neuropathic pain. British Journal of Pharmacology 167: 970–989.
Wang, X.H., H.L. Wang, and X. Li. 2001. Studies on analgesic fractions in venom of Agkistrodon acutus. Chinese Journal of Biochemical Pharmaceutics 22: 198–199.
Wang, Y.P., Y.Q. Dai, and Y.B. Luo. 2012. Isolation and characterization of a kallikrein-like enzyme from Agkistrodon halys Pallas snake venom. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 92: 1497–1503.
Wei, E.T. 1981. Pharmacological aspects of shaking behavior produced by TRH, AG-3-5, and morphine withdrawal. Federation Proceedings 40: 1491–1496.
Xia, Q.C. 1997. Chemical research technology and development of protein. Beijing: Science Publishing House.
Zhang, K.G. 1999. Experimental method of drug dependence. Chinese Journal of Drug Dependence 8: 92–94.
Zhang, Y.N., W.T. Xu, B. Ma, K.L. Huang, M.W. Song, N. Zhang, and Y. Zhang. 2012. Isolation and characterization of a kallikrein-like enzyme from Agkistrodon halys pallas snake venom. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 92: 1497–1503.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff in the laboratory center of South China University of Technology for analyzing electrophoresis data. The financial support for this work from the NSFC (No. 81173646) is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Y., Li, M. & Chen, X. Purification and characterization of a novel antinociceptive peptide from venom of Agkistrodon halys Pallas. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 448–456 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0071-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0071-0