Abstract
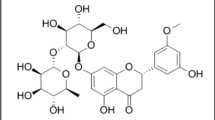
Two stable high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods were developed that could quantitatively analyze 10 major marker compounds of Artemisia capillaris Thunb and could also distinguish among ‘Injinho’ and ‘Myeon-injin’ and ‘Haninjin’ — A. capillaris collected in autumn, A. capillaris collected in spring and A. iwayomogi, which can be misused as ‘Injinho’ in Korean herbal drug markets. The first HPLC method was a reversed-phase chromatography using a C18 column with an isocratic solvent system of phosphoric acid (0.05%) and acetonitrile at the flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, ultraviolet (UV) detection wavelength at 254 nm and column temperature at 40°C. Calibration and quantitation were made by using acetaminophen as an internal standard (I.S-A) and chlorogenic acid (1) was determined within 20 min. The second HPLC method was a reversed-phase chromatography using a C18 column with a gradient solvent system of phosphate buffer (0.015 M, pH 6) and acetonitrile at the flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, UV detection wavelength at 254 nm and column temperature at 40°C. Calibration and quantitation were made by using ethylparaben as an internal standard (I.S-B) and 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (2), 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (3), 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (4), hyperoside (5), isoquercitrin (6), isorhamnetin 3-O-robinobioside (7), isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside (8), isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside (9) and scoparone (10) were determined within 60 min. Pattern recognition analysis of data from the 60 samples classified them clearly into three groups. These assay methods could be applied for QA/QC of A. capillaris and Artemisia iwayomogi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cha, J. D., Jeong, M. R., Jeong, S. I., Moon, S. E., Kim, J. Y., Kil, B. S., and Song, Y. H., Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Artemisia scoparia and A. capillaris. Planta Med., 71, 186–190 (2005).
Cha, J. D., Moon, S. E., Kim, H. Y., Lee, J. C., and Lee, K. Y., The essential oil isolated from Artemisia capillaris prevents LPS-induced production of NO and PGE2 by inhibiting MAPK-mediated pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Immunol. Invest., 38, 483–497 (2009a).
Cha, J. D., Moon, S. E., Kim, H. Y., Cha, I. H., and Lee, K. Y., Essential oil of Artemisia capillaris induces apoptosis in KB cells via mitochondrial stress and caspase activation mediated by MAPK-stimulated signaling pathway. J. Food Sci., 74, T75–T81 (2009b).
Choi, J. H., Kim, D. W., Yun, N., Choi, J. S., Islam, M. N., Kim, Y. S., and Lee, S. M., Protective effects of hyperoside against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in mice. J. Nat. Prod., 74, 1055–1060 (2011).
Chu, C. Y., Tseng, T. H., Hwang, J. M., Chou, F. P., and Wang, C. J., Protective effects of capillarisin on tert-butylhydroperoxide- induced oxidative damage in rat primary hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol., 73, 263–268 (1999).
Guo, F. Q., Liang, Y. Z., Xu, C. J., Li, X. N., and Huang, L. F., Analyzing of the volatile chemical constituents in Artemisia capillaris herba by GC-MS and correlative chemometric resolution methods. J Pharm Biomed Anal., 35, 469–478 (2004).
Hong, J. H., Lee, J. W., Park, J. H., and Lee, I. S., Antioxidative and cytoprotective effects of Artemisia capillaris fractions. Biofactors, 31, 43–53 (2007).
Hong, J. H. and Lee, I. S., Effects of Artemisia capillaris ethyl acetate fraction on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Chem. Biol. Interact., 179, 88–93 (2009a).
Hong, J. H. and Lee, I. S., Cytoprotective effect of Artemisia capillaris fractions on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in V79 cells. Biofactors, 35, 380–388 (2009b).
Hu, Y. Q., Tan, R. X., Chu, M. Y., and Zhou, J., Apoptosis in human hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721 induced by watersoluble macromolecular components of Artemisia capillaris Thunberg. Jpn. J. Cancer Res., 91, 113–117 (2000).
Okuno, I., Uchida, K., Kadowaki, M., and Akahori, A., Choleretic effect of Artemisia capillaris extract in rats. Jpn. J. pharmacol., 31, 835–838 (1981).
Okuno, I., Uchida, K., Nakamura, M., and Sakurawi, K., Studies on choleretic constituents in Artemisia capillaris Thunb. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 36, 769–775 (1988).
Jang, S. I., Kim, Y. J., Lee, W. Y., Kwak, K. C., Baek, S. H., Kwak, G. B., Yun, Y. G., Kwon, T. O., Chung, H. T., and Chai, K. Y., Scoparone from Artemisia capillaris inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells upon stimulation cells by interferon-gamma plus LPS. Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 203–208 (2005).
Jang, S. I., Kim, Y. J., Kim, H. J., Lee, J. C., Kim, H. Y., Kim, Y. C., Yun, Y. G., Yu, H. H., and You, Y. O., Scoparone inhibits PMA-induced IL-8 and MCP-1 production through suppression of NF-κB activation in U937 cells. Life Sci., 78, 2937–2943 (2006).
Jung, H. A., Lee, H. J., Kim, Y. A., Park, K. E., Ahn, J. W., Lee, B. J., Moon, S. G., and Seo, Y. W., Antioxidant activity of Artemisia capillaris Thunberg. Food Sci. Biotechnol., 13, 328–331 (2004).
Kim, Y. S., Bahn, K. N., Hah, C. K., Gang, H. I., and Ha, Y. L., Inhibition of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced mouse skin carcinogenesis by Artemisia capillaris. J. Food Sci., 73, T16–T20 (2008).
Kim, S. W., Kim, H. W., Woo, M. H., Lee, J. H., Choi, J. S., and Min, B. S., Quantitative determination of bioactive compounds in some Artemisia capillaris by high-performance liquid chromatography. Nat. Prod. Sci., 16, 233–238 (2010).
Kimura, Y., Okuda, H., Okuda, T., Hatano, T., Agata, I., and Arichi, S., Studies on the activities of tannins and related compounds from medicinal plants and drugs. VII. Effects of extracts of leaves of Artemisia species, and caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid on lipid metabolic injury in rats fed peroxidized oil. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 2028–2034 (1985).
Kwon, O. S., Choi, J. S., Islam, M. N., Kim, Y. S., and Kim, H. P., Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and skin inflammation by the aerial parts of Artemisia capillaris and its constituents. Arch. Pharm. Res., 34, 1561–1569 (2011).
Park, H. J., Nugroho, A., Lee, J., Kim, J. D., Kim, W. B., Lee, K. R., and Choi, J. S., HPLC analysis of caffeoylqunic acids in the extract of Cacalia firma and peroxynitrite scavenging effect. Kor. J. Pharmacogn., 40, 365–369 (2009).
Sheu, S. J., Chieh, C. L., and Weng, W. C., Capillary electrophoretic determination of the constituents of Artemisiae Capillaris Herba. J. Chromatogr. A, 911, 285–293 (2001).
Tien, Y. C., Liao, J. C., Chiu, C. S., Huang, T. H., Huang, C. Y., Chang, W. T., and Peng, W. H., Esculetin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-mediated hepatic apoptosis in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 12, 4053–4067 (2011).
Wang, H. L., Zou, H. F., Ni, J. Y., Kong, L., Gao, S., and Guo, B. C., Fractionation and analysis of Artemisia capillaris Thunb. by affinity chromatography with human serum albumin as stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A, 870, 501–510 (2000).
Yang, C. C., Lee, M. R., Hsu, S. L., and Chang, C. M. J., Supercritical fluids extraction of capillarisin from Artemisia capillaris and its inhibition of in vitro growth of hepatoma cells. J. Supercrit. Fluid, 42, 96–103 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, K.M., Li, Y., Kim, B. et al. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis for quantitation of marker compounds of Artemisia capillaris thunb.. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 2153–2162 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1213-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1213-5