Abstract
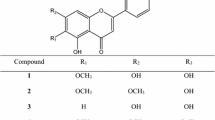
As part of our continuous search for compounds from natural sources that can treat diabetes and its diabetic complications, in the present work, we investigated the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and rat lens aldose reductase (RLAR) inhibitory activities of the roots of Aralia continentalis. The methanol extract showed a potent inhibitory activity against PTP1B and RLAR. Among the tested fractions, the n-hexane fraction exhibited the highest PTP1B inhibitory activity, while the EtOAc fraction showed highest RLAR inhibitory activity. Bioassayguided fractionation of the active n-hexane and EtOAc soluble fractions resulted in the isolation of the diterpenoids; ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-oic acid (continentalic acid, 1); ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid (kaurenoic acid, 2); ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-ol (3); 7-oxo-ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-oic acid (4); 16á-hydroxy-17-isovaleroyloxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (5); 17-hydroxy-entkaur-15-en-19-oic acid (6); 15á,16á-epoxy-17-hydroxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (7); 16á,17-dihydroxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (8); 8á-hydroxy-ent-pimara-15-en-19-ol (9); 4-epirulopezol (10) and 4â-hydroxy-19-nor-(−)-pimara-8(14),15-diene (11), from the n-hexane fraction, and 4-[formy-5-(methoxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl] butanoic acid (12); vanillic acid (13); 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (14); protocatechuic acid (15); nicotinic acid (16); aralia cerebroside (17); 5-O-feruloly quinic acid (18) from the EtOAc fraction. Of these, compounds 12∼14, 16 and 18 were isolated from A. continentalis for the first time. Compounds 1∼10 exhibited inhibitory potential against PTP1B, while compounds 12, 17, and 18 were found to be active against RLAR. Taken together, these results clearly demonstrate that the roots of A. continentalis displayed anti-diabetic and antidiabetic properties, which could be further explored to develop therapeutic and preventive agents for the treatment of diabetes and related complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, K. W., Medicinal Plants of Korea, Kyohak Publishing Co. Ltd., Seoul, p. 363, (2000)
Berger, B., Stenstrom, G., and Sundkvist, G., Incidence, prevalence and mortality of diabetes in a large population: a report from the Skaraborg diabetes registry. Diabetes Care, 22, 773–777 (1999).
Brownlee, M., Biology and molecular cell biology if diabetic complications. Nature, 414, 813–820 (2001).
Chin, Y. W., Lim, S. W., Kim, S. H., Shin, D. Y., Suh, Y. G., Kim, Y. B., Kim, Y. C., and Kim, J. W., Hepatoprotective pyrrole derivatives of Lycium chinense fruits. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 13, 79–81 (2003).
Chung, Y. S., Choi, Y. H., Lee, S. J., Choi, S. A., Lee, J. H., Kim, H., and Hong, E. K.. Water extract of Aralia elata prevents cataractogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol., 101, 49–54 (2005)
Cui, L., Na, M., Oh, H., Bae, E. Y., Jeong, D. G., Ryu, S. E., Kim, S., Kim, B. Y., Oh, W. K., and Ahn, J. S., Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from Morus root bark. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 16, 1426–1429 (2006).
Fowler, M. J., Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin. Diabetes, 26, 77–82 (2008).
Fujisawa, T., Ikegami, H., Inoue, K., Kawabata, Y., and Ogihara, T., Effect of two alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, voglibose and acarbose, on postprandial hyperglycemia correlates with subjective abdominal symptoms. Metabolism, 54, 387–390 (2005).
Hanefeld, M., The role of acarbose in the treatment of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complications, 12, 228–237 (1998).
Hayman, S. and Kinoshita, J. H., Isolation and properties of lens aldose reductase. J. Biol. Chem., 240, 877–882 (1965).
Hu, W., Huang, C., and Wang, M. H., Chemical composition, nutritional value, and antioxidant constituents of Kalopanax pictus leaves. Food Chem., 131, 449–455 (2012).
Hur, J. M., Park, J. C., and Hwang, Y. H., Aromatic acid and flavonoids from the leaves of Zanthoxylum piperium. Nat. Prod. Sci., 7, 23–26 (2001).
Jung, H. A., Lee, E. J., Kim, J. S., Kang, S. S., Lee, J. H., Min, B. S., and Choi, J. S., Cholinesterase and BACE1 inhibitory diterpenoids from Aralia cordata. Arch. Pharm. Res., 32, 1399–1408 (2009).
Kang, S. S., Chemistry and biological activity of the constitiuents from Aralia species. Ann. Rept. Nat. Prod. Sci., 5, 1–26 (1997).
Kang, S. S., Kim, J. S., Xu, Y. N., and Kim, Y. H., Isolation of a new cerebroside from the root bark of Aralia elate. J. Nat. Prod., 62, 1059–1062 (1999).
Kennedy, B. P., Role of protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B in diabetes and obesity. Biomed Pharmacother., 53, 466–470 (1999).
Kim, S., Na, M., Oh, H., Jang, J., Sohn, C. B., Kim, B. Y., Oh, W. K., and Ahn, J. S., PTP1B inhibitory activity of kaurane diterpenes isolated from Siegesbeckia glabrescens. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 21, 379–383 (2006).
Lee, H. S., Rat lens aldose reductase inhibitory activities of Coptis japonica root-derived isoquinoline alkaloids. J. Agric. Food Chem., 50, 7013–7016 (2002).
Lee, I. S., Jin, W. Y., Zhang, X. F., Hung, T, M., Song, K. S., Seong, Y. H., and Bae, K. H., Cytotoxic and COX-2 inhibitory constituents from the aerial parts of Aralia cordata. Arch. Pharm. Res., 29, 548–555 (2006).
Lee, W. T., Lineamenta Flora Koreae, Academy, Seoul, pp. 771–772, (1996).
Na, M., Oh, W. K., Kim, Y. H., Cai, X. F., Kim, S., Kim, B. Y., and Ahn, J. S., Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B by diterpenoids isolated from Acanthopanax koreanum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 16, 3061–3064 (2006).
Park, B. J. and Tomahiko, M., feruloly, caffeoyl, and flavonol glucosides from Equisetum hyemale. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 47, 363–365 (2011).
Perry, L. M., Medicinal Plants of East and Southeast Asia: Attributed Properties and Uses, The MIT press, Cambridge, p. 41, (1980).
Singh, S. K., Rai, P. K., Jaiswal, D., and Watal, G., Evidencebased critical evaluation of glycemic potential of Cynodon dactylon. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med., 5, 415–420 (2008).
Tahara, M., Okabe, T., Furihata, K., Tanaka, N., Yamaguchi, H., Nishimura, T., and Suzuki, H., Revised structure of resorthiomycin. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo), 44, 255 (1991).
Yu, Y., Gao, H., Tang, Z., Song, X., and Wu, L., Several phenolic acids from fruit of Capparis sainosa. Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines, 1, 1–4 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, H.J., Jung, H.A., Kang, S.S. et al. Inhibitory activity of Aralia continentalis roots on protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and rat lens aldose reductase. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 1771–1777 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1009-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1009-7