Abstract
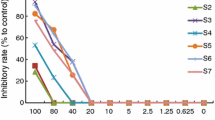
Heat stress (HS) may induce immunosuppression as well as inhibit the proliferation of lymphocytes. This study evaluated the effects on immune function of our prescription on splenic lymphocytes under HS as well as its compatibility. The effects of four herbal extracts from Agastache rugosa, Atractylodes lancea, Cortex Phellodendri, and Gypsum Fibrosum on heat treated splenic lymphocytes were investigated and the compatibility of the prescription was also explored by using the Taguchi method. This study revealed changes in proliferation by traditional Chinese medicines of splenic lymphocytes after HS. Proliferation in the HS group was significantly lower than the control group. Under HS, the effects of higher concentrations of Agastache rugosa (100 and 200 μg/mL), Atractylodes lancea (100 and 200 μg/mL), Cortex Phellodendri (50 and 100 μg/mL) and Gypsum Fibrosum (100 and 200 μg/mL) caused a significant increase on ConA/LPS-induced proliferation of lymphocytes than lower concentrations. We, therefore, conclude that the prescription of traditional Chinese medicines may recover splenic lymphocytes from the immunosuppression induced by HS. The Taguchi design, which allows rapid and high efficiency for the selection of the best conditions for our prescription on HS-treated splenic lymphocytes, demonstrated that Agastache rugosa (200 μg/mL), Atractylodes lancea (200 μg/mL), Cortex Phellodendri (100 μg/mL) and Gypsum Fibrosum (100 μg/mL) were the optimal conditions for the prescription. The validation experiment confirmed that our composition in optimum extraction conditions enhanced effects on ConA or LPS-stimulated lymphocytes under HS. The results showed that the Taguchi optimization approach is a suitable method for optimization of the composition of prescription.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beere, H. M. and Green, D. R., Stress management — heat shock protein-70 and the regulation of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol., 11, 6–10 (2001).
Blaszczyk, T., Krzyzanowska, J., and Lamer-Zarawska, E., Screening for antimycotic properties of 56 traditional Chinese drugs. Phytother. Res., 14, 210–212 (2000).
Cai, Y., Luo, Q., Sun, M., and Corke, H., Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci., 74, 2157–2184 (2004).
Che, Y. M., Mao, S. H., Jiao, W. L., and Fu, Z. Y., Susceptibilities of Mycoplasma hominis to herbs. Am. J. Chin. Med., 33, 191–196 (2005).
Chiba, S., Sakata, T., and Yoshimatsu, H., Chikuyou-sekkouto, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, modulates eating behavior and thermal response induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med., 35, 821–829 (2007).
Elvinger, F., Natzke, R. P., and Hansen, P. J., Interactions of heat stress and bovine somatotropin affecting physiology and immunology of lactating cows. J. Dairy Sci., 75, 449–462 (1992).
Hachicha, W., Kodjikian, L., and Fessi, H., Preparation of vancomycin microparticles: importance of preparation parameters. Int. J. Pharm., 324, 176–184 (2006).
Hou, X. L., Takahashi, K., Tanaka, K., Tougou, K., Qiu, F., Komatsu, K., Takahashi, K., and Azuma, J., Curcuma drugs and curcumin regulate the expression and function of Pgp in Caco-2 cells in completely opposite ways. Int. J. Pharm., 358, 224–229 (2008).
Hsu, C. H., Hwang, K. C., Chao, C. L., Chang, S. G., Ker, C. C., Chien, L. C., Ho, M. S., Lin, J. G., Chen, Y. M., and Chou, P., The lesson of supplementary treatment with Chinese medicine on severe laboratory-confirmed SARS patients. Am. J. Chin. Med., 34, 927–935 (2006).
Kamwanja, L. A., Chase, C. C. Jr., Gutierrez, J. A., Guerriero, V. Jr., Olson, T. A., Hammond, A. C., and Hansen, P. J., Responses of bovine lymphocytes to heat shock as modified by breed and antioxidant status. J. Anim. Sci., 72, 438–444 (1994).
Khajavi, M., Rahimi, S., Hassan, Z. M., Kamali, M. A., and Mousavi, T., Effect of feed restriction early in life on humoral and cellular immunity of two commercial broiler strains under heat stress conditions. Br. Poult. Sci., 44, 490–497 (2003).
Kim, T. H., Shin, J. H., Baek, H. H., and Lee, H. J., Volatile flavour compounds in suspension culture of Agastache rugosa Kuntze (Korean mint). J. Sci. Food Agric., 81, 569–575 (2001).
Kong, L. D., Yang, C., Ge, F., Wang, H. D., and Guo, Y. S., A Chinese herbal medicine Ermiao wan reduces serum uric acid level and inhibits liver xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol., 93, 325–330 (2004).
Lacetera, N., Bernabucci, U., Ronchi, B., Scalia, D., and Nardone, A., Moderate summer heat stress does not modify immunological parameters of Holstein dairy cows. Int. J. Biometeorol., 46, 33–37 (2002).
Liew, C. V., Gu, L., and Heng, P. W. S., The influence of operational variables on mean size and size distribution of spheroids produced by rotary spheronization using teardrop studs. Int. J. Pharm., 242, 345–348 (2002).
Liossis, S. N., Ding, X. Z., Kiang, J. G., and Tsokos, G. C., Overexpression of the heat shock protein 70 enhances the TCR/CD3- and Fas/Apo-1/CD95-mediated apoptotic cell death in Jurkat T cells. J. Immunol., 158, 5668–5675 (1997).
Mebius, R. E. and Kraal, G., Structure and function of the spleen. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 5, 606–616 (2005).
Miyamoto, Y., Ogawa, S., Miyajima, M., Matsui, M., Sato, H., Takayama, K., and Nagai, T., An application of the computer optimization technique to wet granulation process involving explosive growth of particles. Int. J. Pharm., 149, 25–36 (1997).
Morrow-Tesch, J. L., McGlone, J. J., and Salak-Johnson, J. L., Heat and social stress effects on pig immune measures. J. Anim. Sci., 72, 2599–2609 (1994).
Mosmann, T., Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods, 65, 55–63 (1983).
Mosser, D. D. and Martin, L. H., Induced thermo tolerance to apoptosis in a human T lymphocyte cell line. J. Cell. Physiol., 151, 561–570 (1992).
Nakai, Y., Kido, T., Hashimoto, K., Kase, Y., Sakakibara, I., Higuchi, M., and Sasaki, H., Effect of the rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea and its constituents on the delay of gastric emptying. J. Ethnopharmacol., 84, 51–55 (2003).
Nakayama, T., Suzuki, S., Kudo, H., Sassa, S., Nomura, M., and Sakamoto, S., Effects of three Chinese herbal medicines on plasma and liver lipids in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Ethnopharmacol., 109, 236–240 (2007).
Nanayakkara, G. R., Bartlett, A., Forbes, B., Marriott, C., Whitfield, P. J., and Brown, M. B., The effect of unsaturated fatty acids in benzyl alcohol on the percutaneous permeation of three model penetrants. Int. J. Pharm., 301, 129–139 (2005).
Narayan, A. R., Huang, Y. C., Zhang, Y. H., Li, X. M., and Frieri, M., Chinese herbal extract Glycyrrhiza uralensis (Gu), in the absence or presence of IL-1b, decreases nitrite production and proliferation of human type II alveolar epithelial cells (A549). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 117, S156 (2006).
National Commition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, Chinese Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing Chemical Industry Press, China, (2005).
Normile, D., Asian medicine. The new face of traditional Chinese medicine. Science, 299, 188–190 (2003).
Oh, H. M., Kang, Y. J., Lee, Y. S., Park, M. K., Kim, S. H., Kim, H. J., Seo, H. G., Lee, J. H., and Chang, K. C., Protein kinase G-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction by Agastache rugosa leaf extract protects RAW264.7 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced injury. J. Ethnopharmacol., 103, 229–235 (2006).
O’sullivan, S. T. and O’Connor, T. P., Immunosuppression following thermal injury: the pathogenesis of immunodysfunction. Br. J. Plast. Surg., 50, 615–623 (1997).
Sanders, V. M., Adrenergic receptors on T and B lymphocytes: Evidence, function, and clinical implications. Clin. Neurosci. Res., 6, 34–41 (2006).
Shah, R. B., Yang, Y., Khan, M. A., and Faustino, P. J., Molecular weight determination for colloidal iron by Taguchi optimized validated gel permeation chromatography. Int. J. Pharm., 353, 21–27 (2008).
Shephard, R. J. and Shek, P. N., Immune dysfunction as a factor in heat illness. Crit. Rev. Immunol., 19, 285–302 (1999).
Shin, S. and Kang, C. A., Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Agastache rugosa Kuntze and its synergism with ketoconazole. Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 36, 111–115 (2003).
Shouqin, Z., Junjie, Z., and Changzhen, W., Novel high pressure extraction technology. Int. J. Pharm., 278, 471–474 (2004).
Stone, K. D., Feldman, H. A., Huisman, C., Howlett, C., Jabara, H. H., and Bonilla, F. A., Analysis of in vitro lymphocyte proliferation as a screening tool for cellular immunodeficiency. Clin. Immunol., 131, 41–49 (2009).
Taguchi, G. and Konishi, S., Taguchi method, orthogonal arrays and linear graphs, Tools for Quality Engineering. American Supplier Institute. pp. 35–38, (1987).
Taguchi, I., Kiyohara, H., Matsumoto, T., and Yamada, H., Structure of oligosaccharide side chains of an intestinal immune system modulating arabinogalactan isolated from rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea DC. Carbohydr. Res., 339, 763–770 (2004).
Trout, J. M. and Mashaly, M. M., The effects of adrenocorticotropic hormone and heat stress on the distribution of lymphocyte populations in immature male chickens. Poult. Sci., 73, 1694–1698 (1994).
Ung, C. Y., Li, H., Cao, Z. W., Li, Y. X., and Chen, Y. Z., Are herb-pairs of traditional Chinese medicine distinguishable from others? Pattern analysis and artificial intelligence classification study of traditionally defined herbal properties. J. Ethnopharmacol., 111, 371–377 (2007).
Wang, K. H., Lin, R. D., Hsu, F. L., Huang, Y. H., Chang, H. C., Huang, C. Y., and Lee, M. H., Cosmetic applications of selected traditional Chinese herbal medicines. J. Ethnopharmacol., 106, 353–359 (2006).
Yang, S. H. and Yu, C. L., Antiinflammatory effects of Buzhong-yi-qi-tang in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. J. Ethnopharmacol., 115, 104–109 (2008).
Yokoyama, K., Shimada, Y., Hori, E., Sekiya, N., Goto, H., Sakakibara, I., Nishijo, H., and Terasawa, K., Protective effects of Choto-san and hooks and stems of Uncaria sinensis against delayed neuronal death after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil. Phytomedicine, 11, 478–489 (2004).
Yu, K. W., Kiyohara, H., Matsumoto, T., Yang, H. C., and Yamada, H., Structural characterization of intestinal immune system modulating new arabino-3,6-galactan from rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea DC. Carbohydr. Polym., 46, 147–156 (2001).
Zhang, H., Han, T., Sun, L. N., Huang, B. K., Chen, Y. F., Zheng, H. C., and Qin, L. P., Regulative effects of essential oil from Atractylodes lancea on delayed gastric emptying in stress-induced rats. Phytomedicine, 15, 602–611 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Joint first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Xy., Cheng, Gl., Liu, Fh. et al. Taguchi approach for anti-heat stress prescription compatibility in mice spleen lymphocytes In Vitro . Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1125–1133 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0710-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0710-2