Abstract
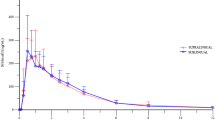
To develop sildenafil lactate, a salt form of sildenafil with improved solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble sildenafil base, this salt form was prepared using a spray dryer. Its solubility and pharmacokinetics in rabbits were evaluated compared with sildenafil base and sildenafil citrate. Sildenafil lactate improved the solubility of sildenafil in various solvents including distilled water compared with sildenafil citrate. It provided higher AUC and Cmax and, shorter t1/2 values than did the other materials, indicating that it improved the oral bioavailability of sildenafil in rabbits. Our results suggest that sildenafil lactate would be useful to deliver sildenafil in a pattern that allows fast absorption and late metabolism. Furthermore, the plasma concentration at 0.25 h in sildenafil lactate was similar to the Cmax value at Tmax (0.5 h) in sildenafil citrate. Thus, sildenafil lactate might provide a faster onset of action and immediate erection compared with sildenafil citrate, the conventional drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amidon, G. L., Lennernas, H., Shah, V. P., and Crison, J. R., A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutics durg classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res., 12, 413–420 (1995).
Boolell, M., Gepi-Attee, S., Gingell, J. C., and Allen, M. J., Sildenafil, a novel effective oral therapy for male erectile dysfunction. Br. J. Urol., 184, 63–72 (1996).
Choi, H. G., Oh, Y. K., and Kim, C. K., In situ gelling and mucoadhesive liquid suppository containing acetaminophen: enhanced bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm., 165, 23–32 (1998).
Choi, H. G., Lee, B. J., Yong, C. S., Rhee, J. D., Han, J. H., Lee, M. K., Park, K. M., and Kim, C. K., Terfenadine-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex with the anti-histaminic activity enhancement. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 27, 857–862 (2007).
Eardly, I., Ellis, P., Boolell, M., and Wulff, M., Onset and duration of action of sildenafil citrate treatment of erectile dysfunction. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 53, 61S–65S (2002).
Elshafeey, A. H., Bendas, E. R., and Mohamed, O. H., Intranasal microemulsion of sildenafil citrate: in vitro evaluation and in vivo pharmacokinetic study in rabbits. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10, 361–367 (2009).
Gibaldi, M. and Perrier, D., Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed. Marcel-Dekker, New York, (1982).
Gratz, S. R., Flurer, C. L., and Wolnik, K. A., Analysis of undeclared synthetic phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in dietary supplements and herbal matrices by LC-ESI-MS and LC-UV. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 36, 525–533 (2004).
Gupta, M., Kovar, A., and Meibohm, B., The clinical pharmacokinetics of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 45, 987–1003 (2005).
Li, D. X., Oh, Y. K., Lim, S. J., Kim, J. O., Yang, H. J., Sung, J. H., Yong, C. S., and Choi, H. G., Novel gelatin microcapsule with bioavailability enhancement of ibuprofen using spray drying technique. Int. J. Pharm., 355, 277–284 (2008).
Quintero, A., Caldera, A., Milano, B., Odreman, I., Hurtado, A., Manzanares, L., and Villamizar, J., Validation of an HPLC method for sildenafil citrate analysis in human plasma samples. Pharmazie, 64, 796–799 (2009).
Shin, H. S., Bae, S. K., and Lee, M. G., Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after intravenous and oral administration in rats: hepatic and intestinal first-pass effects. Int. J. Pharm., 320, 64–70 (2006).
Society of Toxicology (SOT), Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals in Toxicology (2008): www.toxicology.org/AI/FA/guidingprinciples.pdf.
Wang, Y., Chow, M. S., and Zuo, Z., Mechanistic analysis of pH-dependent solubility and trans-membrane permeability of amphoteric compounds: application to sildenafil. Int. J. Pharm., 352, 217–224 (2008).
Yong, C. S., Yang, C. H., Rhee, J. D., Lee, B. J., Kim, D. C., Kim, D. D., Kim, C. K., Choi, J. S., and Choi, H. G., Enhanced rectal bioavailability of ibuprofen in rats by poloxamer 188 and menthol. Int. J. Pharm., 269, 169–176 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, SY., Seo, YG., Kim, G.K. et al. Comparison of the solubility and pharmacokinetics of sildenafil salts. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 451–454 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0313-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0313-y