Abstract
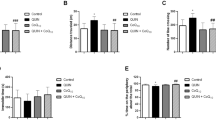
The effect that osteltamivir has on the metabolism of catecholamines and oxidative damage in the brains of young patients remains unclear. The purpose of this study was to measure the effects of oseltamivir, in the presence of oligoelements, on biogenic amines and select oxidative biomarkers in the brains of uninfected, young rats under normal conditions. The study was conducted using male Wistar rats intraperitoneally treated for three days with either a control dose of 0.9 % NaCl, oseltamivir (50 mg/kg), oligoelements (50 μL/rat), or oseltamivir (50 mg/kg) and oligoelements (50 μL/rat). The brain tissue extracted from the treated rats was used to determine the concentrations of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and dopamine, as well as the levels of GSH, lipid peroxidation, and ATPase activity. An increase in the concentration of adrenaline and noradrenaline and in the level of GSH in the group treated with oligoelements (p < 0.001) was observed, while the group treated with oseltamivir and oligoelements, the levels of dopamine increased (p < 0.001), and in the groups treated with oligoelements alone or combination with oseltamivir a decrease in lipid peroxidation was observed (p < 0.001). The results of this study suggest that the consumption of oseltamivir and oligoelements induce biphasic changes in the metabolism of catecholamines; thereby, inducing a protective mechanism against oxidative damage in the brains of young rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanis-Guzman, M. G. and Castro-Góngora, J. E., Mineral composition of milk produced in Monterrey, N. L. Mexico. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr., 42, 456–459 (1992).
Beckman, J. S., Beckman, T. W., Chen, J., Marshall, P. A., and Freeman, B. A., Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: Implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 87, 1620–1624 (1990).
Bediz, C. S., Baltaci, A. K., Mogulkoc, R., and Oztekin, E., Zinc supplementation ameliorates electromagnetic fieldinduced lipid peroxidation in the rat brain. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 208, 133–140 (2006).
Benuck, M., Banay-Schwartz, M., DeGuzman, T., and Lajtha, A., Effect of food deprivation on glutathione and amino acid levels in brain and liver of young and aged rats. Brain Res., 678, 259–264 (1995).
The Biochemical Pathways Charts. (BPC) Boehringer Mannheim Biochemica, Germany (1992).
Brase, D. A., Is intracellular sodium involved in the mechanism of tolerance to opioid drugs? Med. Hypotheses, 32, 161–167 (1990).
Calderón-Guzmán, D., Espitia-Vázquez, I., López-Domínguez, A., Hernández-García, E., Huerta-Gertrudis, B., Coballase-Urritia, E., Juárez-Olguín, H., and Garcia-Fernández, B., Effect of toluene and nutritional status on serotonin, lipid peroxidation levels and Na+/K+-ATPase in adult rat brain. Neurochem. Res., 30, 619–624 (2005).
Castilla-Serna, L. and Cravito, J., Estadística simplificada para la investigación en Ciencias de la Salud. Editorial Trillas. 1o Edición. México, D.F., (1991).
Chen, M. T., Yiin, S. J., Sheu, J. Y., and Huang, Y. L., Brain lipid peroxidation and changes of trace metals in rats following chronic manganese chloride exposure. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A, 65, 305–316 (2002).
Driver, A. S., Kodavanti, P. R., and Mundy, W. R., Age-related changes in reactive oxygen species production in rat brain homogenates. Neurotoxicol. Teratol., 22, 175–181 (2000).
Erikson, K. M., Dorman, D. C., Lash, L. H., and Aschner, M., Manganese inhalation by rhesus monkeys is associated with brain regional changes in biomarkers of neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci., 97, 459–466 (2007).
Fiske, C. H. and Subbarow, Y., The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. Biol. Chem., 66, 375–400 (1925).
Fuke, C., Ihama, Y., and Miyazaki, T., Analysis of oseltamivir active metabolite, oseltamivir carboxylate, in biological materials by HPLC-UV in a case of death following ingestion of Tamiflu. Leg. Med (Tokyo)., 10, 83–87 (2008).
Gülçin, I., Antioxidant activity of L-adrenaline: a structure-activity insight. Chem. Biol. Interact., 179, 71–80 (2009).
Gutteridge, J. M. and Halliwell, B., The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation in biological systems. Trends Biochem. Sci., 15, 129–135 (1990).
Henche-Morilla, A. L., Romero-Montero, C., and Llorente-Gonzalez, C., Levels of oligo-elements and trace elements in patients at the time of admission in intensive care units. Nutr. Hosp., 5, 338–344 (1990).
Hernández, R. J., A serotonin agonist-antagonist reversible effect on Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the developing rat brain. Dev. Neurosci., 5, 326–331 (1982).
Hissin, P. J. and Hilf, R., A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal. Biochem., 74, 214–226 (1976).
Izumi, Y., Tokuda, K., O’dell, K. A., Zorumski, C. F., and Narahashi, T., Neuroexcitatory actions of Tamiflu and its carboxylate metabolite. Neurosci. Lett., 426, 54–58 (2007).
Johanson, C. E., Permeability and vascularity of the developing brain: cerebellum vs cerebral cortex. Brain Res., 190, 3–16 (1980).
Ju, T. C., Chen, S. D, Liu, C. C., and Yang, D. I., Protective effects of S-nitrosoglutathione against amyloid beta-peptide neurotoxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 38, 938–949 (2005).
Kacergius, T., Ambrozaitis, A., Deng, Y., and Gravenstein, S., Neuraminidase inhibitors reduce nitric oxide production in influenza virus-infected and gamma interferonactivated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Pharmacol. Rep., 58, 924–930 (2006).
Madrigal, J. L., Kalinin, S., Richardson, J. C., and Feinstein, D. L., Neuroprotective actions of noradrenaline: effects on glutathione synthesis and activation of peroxisome pro liferator activated receptor delta. J. Neurochem., 103, 2092–2101 (2007).
Morimoto, K., Nakakariya, M., Shirasaza, Y., Kakinuma, C., Fujita, T., Tamai, I., and Ogihara, T., Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) efflux transport at the blood-brain barrier via P-Glycoprotein. Drug Metab. Dispos., 36, 6–9 (2008).
Muñoz, C. J., Montilla, P., Padillo, F. J., Bujalance, I., Muñoz, M. C., and Muntané, J., Role of serotonin in cerebral oxidative stress in rats. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars), 66, 1–6 (2006).
Neault, J. F., Benkiran, A., Malonga, H., and Tajmir-Riahi, H. A., The effects of anions on the solution structure of Na,K-ATPase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn., 19, 95–102 (2001).
Oshima, S., Nemoto, E., Kuramochi, M., Saitoh, Y., and Kobayashi, D., Penetration of oseltamivir and its active metabolite into the brain after lipopolysaccharide-induced inflamma- tion in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 61, 1397–1400 (2009).
Ozcelik, D. and Uzun, H., Copper intoxication; antioxidant defenses and oxidative damage in rat brain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 127, 45–52 (2009).
Pifl, C., Wolf, A., Rebernik, P., Reither, H., and Berger, M. L., Zinc regulates the dopamine transporter in a membrane potential and chloride dependent manner. Neuropharmacology, 56, 531–540 (2009).
Sigma-Aldrich/Supelco. HPLC applications drugs. Page 119 (2004).
Swapna, I., Sathya, K. V., and Murthy, C. R., Membrane alterations and fluidity changes in cerebral cortex during ammonia intoxication Neuro. Toxicology, 335, 700–704 (2005).
Thompson, W. W., Shay, D. K., Weintraub, E., Brammer, L., Cox, N., and Anderson, L. J., Mortality associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in the United States. JAMA, 289, 179–186 (2003).
Toovey, S., Rayner, C., Prinssen, E., Chu, T., Donner, B., and Thakrar, B., Assessment of neuropsychiatric adverse events in influenza patients treated with oseltamivir: a comprehensive review. Drug Saf., 31, 1097–1114 (2008).
Yoshino, T., Nisijima, K., Shioda, K., Yui, K., and Kato, S., Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) increases dopamine levels in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neurosci. Lett., 438, 67–69 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guzmán, D.C., García, E.H., Brizuela, N.O. et al. Effect of oseltamivir on catecholamines and select oxidative stress markers in the presence of oligoelements in the rat brain. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1671–1677 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1017-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1017-4