Abstract
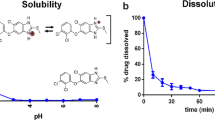
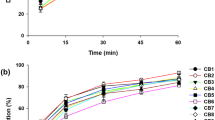
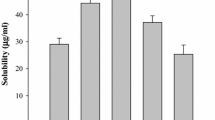
To develop a novel itraconazole-loaded solid dispersion without crystalline change with improved bioavailability, various itraconazole-loaded solid dispersions were prepared with water, polyvinylpyrroline, poloxamer and citric acid. The effect of carriers on aqueous solubility of itraconazole was investigated. Their physicochemical properties were investigated using SEM, DSC, and powder X-ray diffraction. The dissolution, bioavailability in rats and stability of solid dispersions were evaluated. Unlike conventional solid dispersion system, the itraconazole-loaded solid dispersion with relatively rough surface did not change crystalline form of drug. Our DSC and powder X-ray diffraction results suggested that this solid dispersion was formed by attaching hydrophilic carriers to the surface of drug without crystal change, resulting in conversion of the hydrophobic drug to hydrophilic form. The itraconazole-loaded solid dispersion at the weight ratio of itraconazole/polyvinylpyrroline/poloxamer of 10/2/0.5 gave maximum drug solubility of about 20 μg/mL. It did not change the crystalline form of drug for at least 6 months, indicating that it was physically stable. It gave higher AUC, Cmax and Tmax compared to itraconazole powder and similar values to the commercial product, suggesting that it was bioequivalent to commercial product in rats. Thus, it would be useful to deliver a poorly water-soluble itraconazole without crystalline change with improved bioavailability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amidon, G. L., Lennernas, H., Shah, V. P., and Crison, J. R., A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutics durg classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res., 12, 413–420 (1995).
Bogaerts, M. A., Maertens, J., Van der Geest, R., Bosly, A., Michaux, J. L., Van Hoof, A., Cleeren, M., Woestenborghs, R., and De Beule, K., Pharmacokinetics and safety of a 7-day administration of intravenous itraconazole followed by a 14-day administration of itraconazole oral solution in patients with hematologic malignancy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 45, 981–985 (2001).
Buchanan, C. M., Buchanan, N. L., Edgar, K. J., Klein, S., Little, J. L., Ramsey, M. G., Ruble, K. M., Wacher, V. J., and Wempe, M. F., Pharmacokinetics of itraconazole after intravenous and oral dosing of itraconazole-cyclodextrin formulations. J. Pharm. Sci., 96, 3100–3116 (2007).
Chiou, W. L. and Riegelman, S., Pharmaceutical application of solid dispersion systems. J. Pharm. Sci., 60, 1281–1302 (1971).
Choi, H. G., Oh, Y. K., and Kim, C. K., In-situ gelling and mucoadhesive liquid suppository containing acetaminophen: enhanced bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm., 165, 23–32 (1998).
Choi, H. G., Lee, B. J., Yong, C. S., Rhee, J. D., Han, J. H., Lee, M. K., Park, K. M., and Kim, C. K., Terfenadine-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex with the anti-histaminic activity enhancement. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 27, 857–862 (2001).
Craig, D. Q. M., The mechanism of drug release from solid dispersion in water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm., 231, 131–144 (2002).
Doherty, C. and York, P., Mechanisms of dissolution of frusemide/PVP solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm., 34, 197–205 (1987).
Holvoet, C., Vander Heyden, Y., and Plaizier-Vercammen, J., Influence of preparation method on itraconazole oral solutions using cyclodextrins as complexing agents. Pharmazie, 62, 510–514 (2007).
Hong, J. Y., Kim, J. K., Song, Y. K., Park, J. S., and Kim, C. K., A new self-emulsifying formulation of itraconazole with improved dissolution and oral absorption. J. Control. Release, 110, 332–338 (2006).
Jung, J. Y., Yoo, S. D., Lee, S. H., Kim, K. H., Yoon, D. S., and Lee, K. H., Enhanced solubility and dissolution rate of itraconazole by a solid dispersion technique. Int. J. Pharm., 187, 209–218 (1999).
Kachrimanis, K., Nikolakakis, I., and Malamataris, S., Spherical crystal agglomeration of ibuprofen by the solvent-change technique in presence of methacrylic polymers. J. Pharm. Sci., 89, 250–259 (2000).
Khan, G. M. and Jiabi, Z., Preparation, characterization, and dissolution studies of ibuprofen solid dispersions using polyethylene glycol (PEG), talc, and PEG-talc as dispersion carriers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 24, 455–462 (1998).
Kipp, J. E., The role of solid nanoparticle technology in the parenteral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm., 284, 109–122 (2004).
Lee, S. W., Kim, M. H., and Kim, C. K., Encapsulation of ethanol by spray drying technique: effects of sodium lauryl sulfate. Int. J. Pharm., 187, 193–198 (1999).
Leuner, C. and Dressman, J., Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 50, 47–60 (2000).
Li, D. X., Oh, Y. K., Lim, S. J., Kim, J. O., Yang, H. J., Sung, J. H., Yong, C. S., and Choi, H. G., Novel gelatin microcapsule with bioavailability enhancement of ibuprofen using spray drying technique. Int. J. Pharm., 355, 277–284 (2008).
Miller, D. A., McConville, J. T., Yang, W., Williams, R. O. 3rd, and McGinity, J. W., Hot-melt extrusion for enhanced delivery of drug particles. J. Pharm. Sci., 96, 361–376 (2007).
Newa, M., Bhandari, K. H., Li, D. X., Kwon, T. H., Kim, J. A., Yoo, B. K., Woo, J. S., Lyoo, W. S., Yong, C. S., and Choi, H. G., Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of ibuprofen binary solid dispersions with poloxamer 188. Int. J. Pharm., 343, 228–237 (2007).
Newa, M., Bhandari, K. H., Li, D. X., Kim, J. O., Yoo, D. S., Kim, J. A., Yoo, B. K., Woo, J. S., Lyoo, W. S., Yong, C. S., and Choi, H. G., Preparation and evaluation of immediate release ibuprofen solid dispersions using polyethylene glycol 4000. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 939–945 (2008).
Okimoto, K., Miyake, M., Ibuki, R., Yasumura, M., Ohnishi, N., and Nakai, T., Dissolution mechanism and rate of solid dispersion particles of nilvadipine with hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose. Int. J. Pharm., 159, 85–93 (1997).
Overhoff, K. A., Moreno. A., Miller, D. A., Johnston, K. P., and Williams III, R. O., Solid dispersions of itraconazole and enteric polymers made by ultra-rapid freezing. Int. J. Pharm., 336, 122–132 (2007).
Society of Toxicology (SOT), Guilding Priciples in the Use of Animals in Toxicology, www.toxicology.org/AI/FA/guidingprinciples.pdf. (2008).
Sung, M. H., Kim, J. S., Kim, W. S., and Hirasawa, I., Modification of crystal growth mechanism of yttrium oxalate in metastable solution. J. Cryst. Growth, 235, 529–540 (2002).
Taylor, L. S. and Zografi, G., Spectroscopic characterization interactions between PVP and indomethacin in amorphous molecular dispersions. Pharm. Res., 14, 1691–1698 (1997).
Vandecruys, R., Peeters, J., Verreck, G., and Brewster, M. E., Use of a screening method to determine excipients which optimize the extent and stability of supersaturated drug solutions and application of this system to solid formulation design. Int. J. Pharm., 342, 168–175 (2007).
Venkateswarlu, V. and Manjunath, K., Preparation, characterization and in vitro release kinetics of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Control. Release, 95, 627–638 (2004).
Walser, S., Hruby, R., Hesse, E., Heinzl, H., and Mascher, H., Preliminary toxicokinetic study with different crystal forms of S (+)-ibuprofen (dexibuprofen) and R,S-ibuprofen in rats. Arzneimittelforschung, 47, 750–754 (1997).
Wempe, M. F., Wacher, V. J., Ruble, K. M., Ramsey, M. G., Edgar, K. J., Buchanan, N. L., and Buchanan, C. M., Pharmacokinetics of raloxifene in male Wistar-Hannover rats: influence of complexation with hydroxybutenyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm., 346, 25–37 (2008).
Willems, L., Van Der Geest, R., and De Beule, K., Itraconazole oral solution and intravenous formulations: A review of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther., 26, 159–169 (2001).
Yamashita, K., Nakate, T., Okimoto, K., Ohike, A., Tokunaga, Y., Ibuki, R., Higaki, K., and Kimura, T., Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus. Int. J. Pharm., 267, 79–91 (2003).
Yi, Y., Yoon, H. J., Kim, B. O., Shim, M., Kim, S. O., Hwang, S. J., and Seo, M. H., A mixed polymeric micellar formulation of itraconazole: Characteristics, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. J. Control. Release, 117, 59–67 (2007).
Yong, C. S., Yang, C. H., Rhee, J. D., Lee, B. J., Kim, D. C., Kim, D. D., Kim, C. K., Choi, J. S., and Choi, H. G., Enhanced rectal bioavailability of ibuprofen in rats by poloxamer 188 and menthol. Int. J. Pharm., 269, 169–176 (2004).
Yong, C. S., Li, D. X., Oh, D. H., Kim, J. A., Yoo, B. K., Woo, J. S., Rhee, J. D., and Choi, H. G., Retarded dissolution of ibuprofen in gelatin microcapsule by cross-linking with glutaradehyde. Arch. Pharm. Res., 29, 520–524 (2006).
Yoo, S. D., Lee, S. H., Kang, E., Jun, H., Jung, J. Y., Park, J. W., and Lee, K. H., Bioavailability of itraconazole in rats and rabbits after administration of tablets containing solid dispersion particles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 26, 27–34 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, YJ., Xuan, J.J., Oh, D.H. et al. Development of novel itraconazole-loaded solid dispersion without crystalline change with improved bioavailability. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1217–1225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0812-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0812-2