Abstract
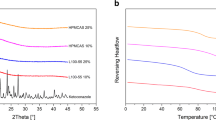
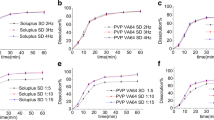
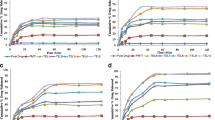
Solid dispersions of artemether (ARM), a poorly soluble drug, were prepared using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVPK25, MW 25000) and polyethyleneglycol (PEG4000, MW 4000) as excipients. These dispersions were studied by physical mixture, freeze-drying, and melting methods. They were characterized by X-ray diffraction pattern, fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry, differential scanning calorimetery, and dissolution studies. X-ray diffraction pattern revealed the complete crystalline nature of artemether, whereas physical mixtures, melt mixtures (MM), and freeze-dried solid dispersions (FDSD) of ARM-PVP and ARM-PEG showed reduced peak intensities with increased PVP/PEG content. PEG showed lower decreases in intensity than PVP preparations. Differential scanning calorimetery also confirmed this finding by showing either a small or absent endotherm. Red shifts in O-H stretching vibrations of ARM were higher in the MM of ARM-PVP than its FDSD as exhibited by fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. The carbonyl peak of PEG was blue shifted in MM and FDSD, whereas the C=O peak of PVP was red shifted in FDSD and MM, indicating different H-bonding by PEG and PVP with ARM. The rate of dissolution (phosphate buffer at pH 4.5) was improved up to 4-fold in MM and FDSD compared to artemether, and up to 50% compared to physical mixtures. The preparation of solid dispersions influenced the rate of dissolution at various drug-carrier ratios, i.e., the dissolution order of 1:1–1:4 ratio was MM > FDSD; FDSD > MM at 1:6–1:8 ratios of both ARM-PVP and ARM-PEG; and FDSD of ARM-PEG > FDSD of ARM-PVP > MM of ARM-PEG > MM of ARM-PVP at a 1:10 ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja, N., Katare, O. P., and Singh, B., Studies on dissolution enhancement and mathematical modeling of drug release of a poorly water-soluble drug using water-soluble carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 65, 26–38 (2007).
Ansari, M. T. and Sunderland, V. B., Solid dispersions of dihydroartemisinin in polyvinylpyrrolidone. Arch. Pharm. Res., 31, 390–398 (2008).
Anshuman, A. Mahadik, A. K. R., and Paradkar, A., Stability study of amorphous Valdecoxib. Int. J. Pharm., 282, 151–162 (2004).
Betageri, G. V. and Makarla, K. R., Enhancement of dissolution of glyburide by solid dispersion and lyophilization techniques. Int. J. Pharm., 126, 155–160 (1995).
Bhadra, D., Bhadra, S., and Jain, N. K., Pegylated Lysine based copolymeric dendritic micelles for solubilization and delivery of artemether. J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci., 8, 467–482 (2005).
Chawla, G. and Bansal. A., Improved dissolution of a poorly water soluble drug in solid dispersions with polymeric and non-polymeric hydrophilic additives. Acta Pharm., 58, 257–274 (2008).
Damian, F., Blaton, N., Naesens, L., Balzarini, J., Kinget, P., Augustijns, P., and van den Mooter, G., Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of the antiviral agent UC-781 with polyethylene glycol 6000 and Gelucire 44/14. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 10, 311–322 (2000).
Dittgen, M., Graiser, T., Kaufmann, G., Gerecke, H., Osterwald, H., and Oettel, M., Hot spin mixing: A new technology to manufacture solid dispersions-Part 2: dienogest. Pharmazie, 50, 50–51 (1995A).
Dittgen, M., Fricke, S., Gerecke, H., and Osterwald, H., Hot spin mixing: a new technology to manufacture solid dispersions-Part 3: progesterone. Pharmazie, 50, 507–508 (1995B)
Dittgen, M., Fricke, S., Gerecke, H., and Osterwald, H., Hot spin mixing: A new technology to manufacture solid dispersions-Part 1: testosterone. Pharmazie, 50, 225–226 (1995C).
El-Badry, E. and Fathy, M., Enhancement of the dissolution and permeation rates of meloxicam by formation of its freeze-dried solid dispersions in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 32, 141–150 (2006).
Elizabeth, A., Mcgready, R., Proux, S., and Nosten, F., Malaria. Travel Med. Inf. Disea., 342, 1–15 (2005).
Emara, L. H., Badr, R. M., and Elbary, A. A., Improving the dissolution and bioavailability of nifedipine using solid dispersions and solubilizers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 28, 795–807 (2002).
Erdemi, H. and Bozkurt, A., Synthesis and characterization of poly (vinylpyrrolidone-co-vinylphosphoric acid) copolymers. Eur. Polym. J., 40, 1925–1929 (2004).
Forster, J., Hempenstall, J., and Rades, T., Characterization of glass solutions of poorly water-soluble drug produced by melt extrusion with hydrophilic amorphous polymers. J. Pharm. Phamacol., 53, 303–315 (2001).
Gu, J., Chen, K., Jiang, H., and Ji. R., A DFT study of Artemisinin and 1,2,4-trioxane. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem., 459, 103–111 (1999).
Guyot, M., Fawaz, F., Bildet, J., Bonini, F., and Lagueny, A. M., Physicochemical characterization and dissolution of norfloxacin/cyclodextrins inclusion compounds and PEG solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm., 123, 53–63 (1995).
Heo, M. Y., Piao, Z. Z., Kim, T. W., Cao, Q. R., Kim, A., and Lee, B. J., Effect of solubilizing and microemulsifying excipients in polyethylene glycol 6000 solid dispersion on enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of ketoconazole. Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 604–611 (2005).
Horter, D. and Dressman, J. B., Influence of physicochemical properties on dissolution of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Drug Del. Rev., 46, 75–87 (2001).
Hulsmann, S., Backensfeld, T., Keitel, S., and Bodmeier, R., Melt-extrusion — an alternative method for enhancing the dissolution rate of 17-â-estradiol hemihydrate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 49, 237–242 (2000).
Ilarduya, T. M., C. D., Martin, C., Goni, M. M., and Martinez-Oharriz, M. C., Solubilization and Interaction of Sulindac with PVP K30 in the solid state and in aqueous solution. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 24, 295–300 (1998).
Karavas, E., Georgarakis, E., Sigalas, M., Avgoustakis, K., and Bikiaris, D., Investigation of the release mechanism of a sparingly soluble drug from solid dispersions in hydrophilic carrier based on physical state of the drug, particle size distribution and drug-polymer interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 66, 334–347 (2007).
Khougaz, K. and Clas, S. D., Crystallization inhibition in solid dispersions of MK-0591 and polyvinylpyrrolidone polymers. J. Pharm. Sci., 89, 1325–1334 (2000).
Lefèvre, G., Bindschedler, M., Ezzet, F., Schaeffer, N., Meyer, I., and Thomsen, M., Pharmacokinetic interaction trial between co-artemether and mefloquine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 10, 141–151 (2000).
Lin, Y. E. and Wilken, L. O., Some effects of a modified lyophilization procedure on dissolution and other properties of digoxin powders and tablets. M. S. Thesis. Auburn University, AL, pp. 63, (1980).
Martinez-Oharriz, M. C., Rodriguez-Espinosa, C., Martin, C., Goni, M. M., Tros-Illarduya, M. C., and Sanchez, M., Solid dispersions of diflunisal-PVP: Polymorphic and amorphous states of the drug. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 28, 717–725 (2002).
Miyazaki, T., Yoshioka, S., Aso, Y., and Kojima, S., Ability of polyvinylpyrrolidone and polyacrylic acid to inhibit the crystallization of amorphous acetaminophen. J. Pharm. Sci., 93, 2710–2717 (2004).
Mooter, G. V. D., Wuyts, M., Blaton, N., Busson, R., Grobet, P., August, P., and Kinget, R., Physical stabilization of amorphous ketoconazole in solid dispersions with Polyvinylpyrrolidone K25. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 12, 261–269 (2001).
Narang, A. S. and Srivastava, A. K., Evaluation of solid dispersions of Clofazimine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 28, 1001–1013 (2002).
Rawlinson, C. F., Williams, A. C., Timmins, P., and Grimsey, I., Polymer-mediated disruption of drug crystallinity. Int. J. Pharm., 336, 42–48 (2007).
Sekiguchi, K. and Obi, N., Studies on absorption of eutectic mixtures. 1. A comparison of the behavior of eutectic mixtures of sulfathiazole and that of ordinary thiazole in man. Chem. Pharm. Bullet., 9, 866–872 (1961).
Sethabouppha, B., Puttipipatkhachorn, S., Tozuka, Y., and Yamamoto, K., Amorphization of dihydroartemisinin by co-grinding with additives. Presented at the First Asian Particle Technology Symposium (APT2000), Bangkok, Thailand, 13–15, December, 2000.
Silverstein, R. M., Bassler, G. C., and Morril, T. C., Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. Wiley, New York, pp.91–131, (1991).
Te Wierik, G. H., Eissens, A. C., Besemer, A. C., and Lerk, C. F., Preparation, characterization, and pharmaceutical application of linear dextrins. II: Complexation and dispersion of drugs with amylodextrin by freeze-drying and kneading. Pharm. Res., 10, 1280–1284 (1993).
Trapani, G., Franco, M., Latrofa, A., Pantaleo, M. R., Provanzano, M. R., Sanna, E., Maciocco, E., and Liso, G., Physicochemical characterization and in vivo properties of zolpidem in solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol 4000 and 6000. Int. J. Pharm., 184, 121–130 (1999).
Van Drooge, D. J., Hinrichs, W. L. J., Wegman, K. A. M., Visser, M. R., Eissens, A. C., and Frijlink, H. W., Solid dispersions based on inulin for the stabilisation and formulation of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 21, 511–518 (2004).
Vivekanandhan, S., Venkateswarlu, M., and Satyanarayana, N., Effect of different ethylene glycol precursors on the Pechini process for the synthesis of nano-crytalline LiNi0.5Co0.5VO4 powders. Mater. Chem. Phys., 91, 54–59 (2005).
Wang, L., Cui, F. D., Hayase, T., and Sunada, H., Preparation and evaluation of solid dispersions for nitrendipinecarbopol and nitrendipine-HPMCP systems using a twin screw extruder. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 53, 1240–1245 (2005).
White, N., Antimalarial drug resistance and combination chemotherapy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 354, 739–749 (1999).
White, N. J., Nosten, F., Looareesuwan, S. et al., Averting a malaria disaster. Lancet, 353, 1965–1967 (1999).
WHO, Antimalarial Drug Combination Therapy. Report of a WHO Technical Consultation. (WHO/CDS/RBM/2001.35). WHO, Geneva (2001).
WHO, The use of artemisinin & its derivatives as antimalarial drugs world health organization. WHO/MAL/98/1086 Geneva, Malaria Unit Division of Control of Tropical Diseases (1998).
WHO, Application for inclusion of artemether/lumefantrine dispersible tablets 20mg/120 mg in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for Children. WHO 17th Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Geneva, March (2009).
Zajc, N. and Srcic, S., Binary melting phase diagrams of nifedipine-PEG 4000 and nifedipine-mannitol systems. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 77, 571–280 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, M.T., Karim, S., Ranjha, N.M. et al. Physicochemical characterization of artemether solid dispersions with hydrophilic carriers by freeze dried and melt methods. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 901–910 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0613-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0613-7