Abstract
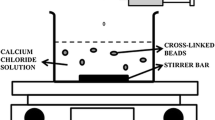
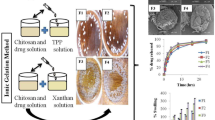
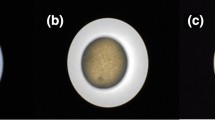
This work focused on the development of mucoadhesive and floating chitosan-coated alginate beads as a gastroretensive delivery vehicle for amoxicillin, towards the effective eradication of Helicobacter pylori, a major causative agent of peptic ulcers. Alginate was used as the core bead core polymer and chitosan as the mucoadhesive polymer coating. Amoxicillin-loaded alginate beads coated with 0.5% (w/v) chitosan (ALG/0.5%CHI) exhibited excellent floating ability, high encapsulation efficiency, high drug loading capacity, and a strong in vitro mucoadhesion to the gastric mucosal layer. In vitro, amoxicillin was released faster in simulated gastric fluid (pH 1.2, HCl) than in simulated intestinal fluid (phosphate buffer, pH 7.4). ALG/0.5%CHI could be prepared with a > 90% drug encapsulation efficiency and exhibited more than 90% muco-adhesiveness, 100% floating ability, and achieved sustained release of amoxicillin for over six hours in SGF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, F. P. and Almeida, A. J., Cross-linked alginategelatine beads: a new matrix for controlled release of pindolol. J. Control. Release, 97, 431–439 (2004).
Anal, A. K. and Stevens, W. F., Chitosan-alginate multilayer beads for controlled release of ampicillin. Int. J. Pharm., 290, 45–54 (2005).
Atherton, J. C., Cockayne, A., Balsitis, M., Kirk, G. E., Hawley, C. J., and Spiller, R. C., Detection of the intragastric sites at which Helicobacter pylori evades treatment with amoxicillin and cimetidine. Gut, 36, 670–674 (1995).
Axon, A. T., The role of acid inhibition in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand. J. Gastroenterol., 29, 16–23 (1994).
Bodmeier, R. and Wang, J., Microencapsulation of drugs with aqueous colloidal polymer dispersions., J. Pharm. Sci., 82, 191–194 (1993).
Buzas, G. M. and Szekely, E., Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer patients. Orv. Hetil., 140, 121–124 (1999).
Chun, M., Sah, H., and Choi, H., Preparation of mucoadhesive microspheres containing antimicrobial agents for eradication of H. pylori. Int. J. Pharm., 297, 172–179 (2005).
Cooreman, M. P., Krausgrill, P., and Hengels, K. J., Local gastric and serum amoxicillin concentrations after different oral application forms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 37, 1506–1509 (1993).
Du, Y., Dong, Z., and Wang, Q., Alginate/gelatin blend films and their properties for drug controlled release. J. Membr. Sci., 280, 37–44 (2006).
Erah, P. O., Goddard, A. F., Barrett, D. A., Shaw, P. N., and Spiller, C., The stability of amoxicillin, clarithromycin and metronidazole in gastric juice: relevance to the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 39, 5–12 (1997).
Giacomo, F., Mariano, L., Silvana, M., Domenico, S., and Gaetano, G., Amoxicillin-loaded polyethylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles:influence PEG coating on the particle size, drug release rate and phagocytic uptake. Biomaterials, 22, 2857–2865 (2001).
He, P., Stanley, S. D., and Illum, L., In vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of chitosan microspheres. Int. J. Pharm., 166, 75–88 (1998).
Hilton, A. K. and Deasy, P. B., In vitro and in vivo evaluation of an oral sustained-release floating dosage form of amoxicillin trihydrate. Int. J. Pharm., 86, 79–88 (1992).
Huguet, M. L., Neufeld, R. J., and Dellacherie, E., Calciumalginate beads coated with polycationic polymer: comparison of chitosan and DEAE-dextran. Process Biochemistry, 31, 347–353 (1996).
Kawabami, E., Ogata, S. K., and Portorreal, A. C., Triple therapy with clarithromycin, amoxicillin and omeprazole for Helicobacter pylori eradication in children and adolescents. Arq. Gastroenterol., 38, 203–206 (2001).
Kulkarni, A. R., Soppimath, K. S., Aminabhavi, T. M., Dave, A. M., and Metha, M. H., Glutaraldehyde cross-linked sodium alginate beads containing liquid pesticide for soil application. J. Control. Release., 63, 1121–1124 (2000).
Lin, C. K., Hsu, P. I., and Lai, K. H., One-week quadruple therapy is an effective salvage regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection in patients after failure of standard triple therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol., 34, 547–551 (2002).
Liu, P. and Krishnan, T. R., Alginate-pectin-poly-L-lysine particulate as a potential controlled release formulation. J. Pharm. Phamacol., 51, 141–149 (1999).
Liu, Z., Lu, W., Qian, L., Zhang, X., Zeng, P., and Pan, J., In vitro and in vivo studies on mucoadhesive microspheres of amoxicillin. J. Control. Release., 102, 135–144 (2005).
Nagahara, N., Akiyma, Y., Nakao, M., Tada, M., Kitano, M., and Ogawa, Y., Mucoadhesive microspheres containing amoxicillin for clearance of Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 42, 2492–2494 (1998).
Orienti, I., Cerchiara, T., Luppi, B., Bigucci, F., Zuccari, G., and Zecchi, V., Influence of different chitosan salts on the release of sodium diclofenac in colon-specific delivery. Int. J. Pharm., 238, 51–59 (2002).
Rajinikanth, S. and Mishra, B., Floating in situ gelling system for stomach site-specific delivery of clarithromycin to eradicate H. pylori. J. Control. Release., 125, 33–41 (2008).
Ranga, R. K. V. and Buri, P., A novel situ method to test polymer and coated microspheres for bioadhesion. Int. J. Pharm., 52, 265–270 (1989).
Reich, G., Walther, S., and Stather, F., The influence of the age of cattle and pigskin on the yield and the guality of the gelatines obtained after the acid conditioning process. In Investigation of Collagen and Gelatine IV. Deutsche Lederinstitut, Frieberg/SA., 18, 15–23 (1962).
Remunan-Lopez, C., Portero, A., Lemos, M., Vila-Jato, J. L., Nuñez, M. J., Riveiro, P., Lpez, J. M., Piso, M., and Alonso, M. J., Chitosan microspheres for the specific delivery of amoxycillin to the gastric cavity. S. T. P. Pharma. Sci., 10, 69–76 (2000).
Sahasathian, T., Kerdcholpetch, T., Chanweroch, A., Praphairaksit, N., Suwonjandee, N., and Muangsin, N., Sustained release of amoxicillin from chitosan tablets. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, 526–531 (2007).
Sezer, A. D. and Akbûga, J., Controlled release of piroxicam from chitosan beads. Int. J. Pharm., 121, 113–116 (1995).
Shu, X. Z. and Zhu, K. J., A novel approach to prepare tripolyphosphate/chitosan complex beads for controlled release drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm., 201, 51–58 (2000).
Tokumura, T. and Machida, Y., UV absorption method should not be applied for determining amoxicillin in acidic dissolution test medium. Int. J. Pharm., 228, 1–4 (2001).
Tønnesen, H. H. and Karlsen, J., Alginate in drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 28, 621–630 (2002).
Torre, M. L., Giunchedi, P., Maggi, L., Stefli, R., Ochoa Machiste, E., and Conte, U., Formulation and characterization of calcium alginate beads containing ampicillin. Pharm. Dev. Technol., 3, 193–198 (1998).
Wang, J., Tauchi, Y., Deguchi, Y., Morimoto, K., Tabata, Y., and Ikada, Y., Positively charged gelatin microspheres as gastric mucoadhesive drug delivery system for eradication of H. pylori. Drug Deliv., 7, 237–243 (2000).
Wang, K. and He, Z., Alginate-konjac glucomannan-chitosan beads as controlled release matrix. Int. J. Pharm., 244, 117–126 (2002).
Ward, A. G. and Courts, A., The Science and Technology of Gelatin. Academic Press, New York, (1997).
Whitehead, L., Collett, J. H., and Fell, J. T., Amoxicillin release from a floating dosage form based on alginates. Int. J. Pharm., 210, 45–49 (2002).
Xiao, C. B., Liu, H. J., Lu, Y. S., and Zhang, L. N., Blend films from sodium alginate and gelatin solutions. J. Macromol. Sci.-Pure Appl Chem., 38, 317–328 (2001).
Yao, F., Chen, W., Wang, H., Liu, H., Yoa, K., Sun, P., and Lin, H., A study on cytocompatible poly(chitosan-g-L-lactic acid). Polymer, 44, 6435–6441 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahasathian, T., Praphairaksit, N. & Muangsin, N. Mucoadhesive and floating chitosan-coated alginate beads for the controlled gastric release of amoxicillin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 889–899 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0612-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0612-8