Abstract
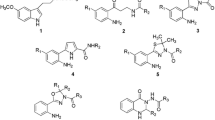
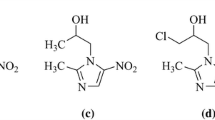
The reaction of substituted benzylhalides, or of halomethyl derivatives of thiophene or furane, with thiourea or its derivatives yielded the respective isothioureas as hydrohalide salts. The products (a total of 17, including 16 novel compounds) were tested for activity against five Gram-positive and nine Gram-negative bacterial strains, six yeast species and two protozoan species. The most active against Gram-positive bacteria were S-(2,4-dinitrobenzyl)isothiourea hydrochloride (MIC range for four out of five strains tested: 12.5–25 μg/mL) and S-(2,3,4,5,6-pentabromobenzyl)isothiourea hydrobromide (MIC range: 12.5–50 μg/mL). The lowest MICs of novel isothioureas for yeast and Gram-negative bacteria ranged between 50 and 100 μg/mL. Nine novel isothioureas showed appreciable genotoxicity in the Bacillus subtilis ‘rec-assay’ test, the most potent being S-2-(5-nitrofuran-2-ylmethyl)isothiourea and S-(2-nitrobenzyl) isothiourea. At 10 μM concentration, S-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)isothiourea hydrochloride and S-(2,3,4,5,6-pentabromobenzyl)isothiourea hydrobromide inhibited Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent (non-inducible) nitric oxide synthase activity in normal rat brain homogenates stronger (p < 0.05) than the reference drug 7-nitroindazole (by 78, 76 and 60%, respectively); ten other new isothiourea derivatives significantly inhibited the activity to a lower extent (by 28–60%). These results extend the list of promising isothioureas with substantial activity in vitro and suggest that an in-depth study of toxicity, antimicrobial properties in vivo and nitric oxide synthase isoform selectivity of selected novel compounds is warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu, B. R. and Griffith, O. W., Design of isoform-selective inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2, 491–500 (1998).
Barocelli, E., Ballabeni, V., Ghizzardi, P., Cattanuzza, F., Bertoni, S., Lagrasta, C. A. M., and Impiccatore, M., The selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase prevents instestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Nitric Oxide, 14, 212–218 (2006).
Blattner, F. R., Plunkett, G. 3rd, Bloch, C. A., Perna, N. T., Burland, V., Riley, M., Collado-Vides, J., Glasner, J. D., Rode, C. K., Mayhew, G. F., Gregor, J., Davis, N. W., Kirkpatrick, H. A., Goeden, M. A., Rose, D. J., Mau, B., and Shao, Y., The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science, 277, 1453–1462 (1997).
Castano, T., Encinas, A., Perez, C., Castro, A., Campilo, N. E., and Gil, C., Design, synthesis, and evaluation of potential inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 16, 6193–6206 (2008).
Cedillo-Rivera, R. and Munoz, O., In vitro susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to albendazole, mebendazole and other chemotherapeutic agents. J. Med. Microbiol., 37, 221–224 (1992).
Cedillo-Rivera, R., Tapia-Contreras, A., Torres, J., and Munoz, O., In vitro susceptibility of Entamoeba histolytica to fluoroquinolones, nitrofurans and other antiamebic agents. Arch. Med. Res., 28 (Spec. iss.), 295–297 (1997).
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. Approved standard — ninth edition. CLSI document M2-A9, Wayne, PA, USA (2006a).
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard — seventh edition. CLSI document M7-A7, Wayne, PA, USA (2006b).
del Campo, R., Criado, J. J., Gheorghe, R., Gonzalez, F. J., Hermosa, M. R., Sanz, F., Mazano, J. L., Monte, E., and Rodriguez-Fernandez, E., N-benzoyl-N′-alkylthioureas and their complexes with Ni(II), Co(III) and Pt(II) — crystal structure of 3-benzoyl-1-butyl-1-methyl-thiourea: activity against fungi and yeast. J. Inorg. Biochem., 98, 1307–1314 (2004).
Eissa, A. A. and Moneer, A. A., Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of novel tetrahydrobenzothienopyrimidines. Arch. Pharm. Res., 27, 885–892 (2004).
Garvey, E. P., Oplinger, J. A., Tanoury, G. J., Sherman, P. A., Fowler, M., Marshall, S., Harmon, M. F., Paith, J. E., and Furfine, E. S., Potent and selective inhibition of human nitric oxide synthases. Inhibition by non-amino acid isothioureas. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 26669–26676 (1994).
Handy, R. L., Wallace, P., and Moore, P. K., Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase by isothioureas: cardiovascular and antinociceptive effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 55, 179–184 (1996).
Ijuin, R., Umezawa, N., Nagai, S., and Higuchi, T., Evaluation of 3-substituted arginine analogs as selective inhibitors of human nitric oxide synthase isozymes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 15, 2881–2885 (2005).
Iwai, N., Ebata, T., Nagura, H., Kitazume, T., Nagai, K., and Wachi, M., Structure-activity relationship of S-benzylisothiourea derivatives to induce spherical cells in Escherichia coli. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 68, 2265–2269 (2004).
Iwai, N., Nagai, K., and Wachi, M., Novel S-benzylisothiourea compound that induces spherical cells in Escherichia coli probably by acting on a rod-shape-determining protein(s) other than penicillin-binding protein 2. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 66, 2658–2662 (2002).
Jesko, H. A., Chalimoniuk, M., and Strosznajder, J. B., Activation of constitutive nitric oxide synthase(s) and absence of inducible isoform in aged rat brain. Neurochem. Int., 42, 315–322 (2003).
Jin, G. H., Lee, D. Y., Cheon, Y. J., Gim, H. J., Kim D. H., Kim, H. D., Ryu, J. H., and Jeon, R., Synthesis of phenylisothiourea derivatives as inhibitors of NO production in LPS activated macrophages. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 19, 3088–3092 (2009).
Kada, T., Hirano, K., and Shirasu, Y., Bacillus subtilis recassay test. In de Sevres, F. E. and Hollaender, A. (Eds.). Chemical Mutagens, vol. 6, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 149, (1980).
Kaminska, B., Ellert-Miklaszewska, A., Oberbek, A., Wisniewski, P., Kaza, B., Makowska, M., Bretner, M., and Kazimierczuk, Z., Efficacy and mechanism of anti-tumor action of new potential CK2 inhibitors toward glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Oncol., 35, 1091–1100 (2009).
Kang, I. J., Wang, L. W., Lee, C. C., Lee, Y. C., Chao, Y. S., Hsu, T. A., and Chern, J. H., Design, synthesis, and anti-HCV activity of thiourea compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 19, 1950–1955 (2009).
Khan, S. A., Singh, N., and Saleem, K., Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antibacterial activity of thiourea and urea derivatives of steroids. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 43, 2272–2277 (2008).
Li, H. Q., Lv, P. C., Yan, T., and Zhu, H. L., Urea derivatives as anticancer agents. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem., 9, 471–480 (2009a).
Li, J., Tan, Z., Tang, S., Hewlett, I., Pang, R., He, M., He, S., Tian, B., Chen, K., and Yang, M., Discovery of dual inhibitors targeting both HIV-1 capsid and human cyclophilin A to inhibit the assembly and uncoating of the viral capsid. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 17, 3177–3188 (2009b).
Nicholson, A., Perry, J. D., James, A. L., Stanforth, S. P., De Soyza, A., and Gould, K., Antimicrobial activity of novel S-(benzyl) isothiourea derivatives against multiply resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia complex from patients with cystic fibrosis undergoing lung transplant assessment. J. Heart Lung Transplant., 28, S160 (2009).
Paesano, N., Marzocco, S., Vicidomini, C., Saturnino, C., Autore, G., De Martino, G., and Sbardella, G., Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-benzyl-1-methyl- and 1-methyl-3-phenyl-isothioureas as potential inhibitors of iNOS. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 15, 539–543 (2005).
Paquay, J. B., Hoen, P. A., Voss, H. P., Bast, A., Timmerman, H., and Haenen, G. R., Nitric oxide synthase inhibition by dimaprit and dimaprit analogues. Br. J. Pharmacol., 127, 331–334 (1999).
Perlovich, G. L., Proshin, A. N., Volkova, T. V., Kurkov, S. V., Grigoriev, V. V., Petrova, L. N., and Bachurin, S. O., Novel isothiourea derivatives as potent neuroprotectors and cognition enhancers: synthesis, biological and physicochemical properties. J. Med. Chem., 52, 1845–1852 (2009).
Rodriguez-Fernandez, E., Mazano, J. L., Benito, J. J., Hermosa, M. R., Monte, E., and Criado, J. J., Thiourea, triazole and thiadiazine compounds and their metal complexes as antifungal agents. J. Inorg. Biochem., 99, 1558–1572 (2005).
Sadaie, Y. and Kada, T., Recombination-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol., 125, 489–500 (1976).
Salerno, L., Sorrenti, V., Di Giacomo, C., Romeo, G., and Siracusa, M. A., Progress in the development of selective nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des., 8, 177–200 (2002).
Shearer, B. G., Lee, S., Oplinger, J. A., Frick, L. W., Garvey, E. P., and Furfine, E. S., Substituted N-phenylisothioureas: potent inhibitors of human nitric oxide synthase with neuronal isoform selectivity. J. Med. Chem., 40, 1901–1905 (1997).
Shirota, F. N., Stevens-Johnk, J. M., DeMaster, E. G., and Nagasawa H. T., Novel prodrugs of cyanamide that inhibit aldehyde dehydrogenase in vivo. J. Med. Chem., 40, 1870–1875 (1997).
Southan, G. J., Szabo, C., and Thiemermann, C., Isothioureas: potent inhibitors of nitric oxide synthases with variable isoform selectivity. Br. J. Pharmacol., 114, 510–516 (1995).
Szabo, C., Southan, G. J., and Thiemermann, C., Beneficial effects and improved survival in rodent models of septic shock with S-methylisothiourea sulfate, a potent and selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 91, 12472–12476 (1994).
Tait, A., Di Bella, M., Bondi, M., Quaglio, G., and Fabio, U., Carbamimidothioic acid phenylmethyl ester salts and their N, N′-tetramethyl derivatives as possible antimicrobial agents. Farmaco, 45, 617–630 (1990).
Tait, A., Giovannini, M. G., Di Bella, M., Bondi, M., and Quaglio, G.P., S-Aryl(tetramethyl)isothiouronium salts as possible antimicrobial agents, IV. Farmaco, 44, 1129–1140 (1989).
Thoma, G., Streiff, M. B., Kovarik, J., Glickman, F., Wagner, T., Beerli, C., and Zerwes, H. G., Orally bioavailable isothioureas block function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in vitro and in vivo. J. Med. Chem., 51, 7915–7920 (2008).
Wang, Y., Lawson, J. A., and Jaeschke, H., Differential effect of 2-aminoethyl-isothiourea, an inhibitor of the inducible nitric oxide synthase, on microvascular blood flow and organ injury in models of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and endotoxemia. Shock, 10, 20–25 (1998).
Xu, Y. G., Zhang, J. X., Hua, W. Y., and Zhu, D. Y., Synthesis and nNOS inhibitory activity of benzenealkyl isothiourea compounds. Yao Xue Xue Bao, 38, 586–591 (2003).
Zhang, H. B., Zhang, Y. A., Wu, G. Z., Zhou, J. P., Huang, W. L., and Hu, X. W., Synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfonylurea and thiourea derivatives substituted with benzenesulfonamide groups as potential hypoglycemic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 19, 1740–1744 (2009).
Zhong, Z., Xing, R., Liu, S., Wang, L., Cai, S., and Li, P., Synthesis of acyl thiourea derivatives of chitosan and their antimicrobial activities in vitro. Carbohydr. Res., 343, 566–570 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazimierczuk, Z., Chalimoniuk, M., Laudy, A.E. et al. Synthesis and antimicrobial and nitric oxide synthase inhibitory activities of novel isothiourea derivatives. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 821–830 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0604-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0604-8