Abstract
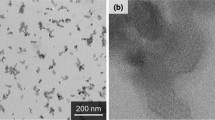
Platinum nanoparticles (PNPs) are potentially useful for sensing, catalysis, and other applications in the biological and medical sciences. However, toxicity data on the PNPs are very limited. In this study, we prepared PNPs using K2PtCl6, (21 nm in phosphate buffered saline) and tested inflammatory responses in mice after a single intratracheal instillation. The concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, TNF-α, and IL-6), TH0 cytokine (IL-2), TH1-type cytokine (IL-12), and TH2-type cytokines (IL-4 and IL-5) were increased in broncho-alveolar lavage fluid by PNPs. It was found that the induciton of TH2-type cytokines were higher than TH1-type cytokine on day 28 after instillation. TGF-β was also significantly increased in broncho-alveolar lavage fluid during the experimental period. IgE level in serum was increased with the increase of B cells distribution. Intracellular level of glutathione (GSH) was diminished by treatment of PNPs. When the distribution of T cell subtype (CD4+/CD8+) was analyzed, the ratio was decreased. Gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases was found to be significantly increased on day 1. By histopathological examination, cell infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils was observed in lung tissue during the experimental period. Based on these findings, it is suggested that the exposure to PNPs may induce inflammatory responses in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, P. J., Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 8, 183–192 (2008).
Cheng, H., Xi, C., Meng, X., Hao, Y., Yu, Y., and Zhao, F., Polyethylene glycol-stabilized platinum nanoparticles: the efficient and recyclable catalysts for selective hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene to o-chloroaniline. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 336, 675–678 (2009).
Cho, W. S., Choi, M., Han, B. S., Cho, M., Oh, J., Park, K., Kim, S. J., Kim, S. H., and Jeong, J., Inflammatory mediators induced by intratracheal instillation of ultrafine amorphous silica particles. Toxicol. Lett., 175, 24–33 (2007).
Cho, W. S., Cho, M., Jeong, J., Choi, M., Cho, H. Y., Han, B. S., Kim, S. H., Kim, H. O., Lim, Y. T., Chung, B. H., and Jeong, J., Acute toxicity and pharmacokinetics of 13 nmsized PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 236, 16–24 (2009).
Chung, K. F., Inflammatory mediators in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy, 4, 619–625 (2005).
Gao, J., Liang, G., Cheung, J. S., Pan, Y., Kuang, Y., Zhao, F., Zhang, B., Zhang, X., Wu, E. X., and Xu, B., Multifunctional yolk-shell nanoparticles: A potential MRI contrast and anticancer agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 130, 11828–11833 (2008).
Goodman, C. M., McCusker, C. D., Yilmaz, T., and Rotello, V. M., Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjug. Chem., 15, 897–900 (2004).
Haider, S. and Knöfler, M., Human tumour necrosis factor: physiological and pathological roles in placenta and endometrium. Placenta, 30, 111–123 (2009).
Hamasaki, T., Kashiwagi, T., Imada, T., Nakamichi, N., Aramaki, S., Toh, K., Morisawa, S., Shimakoshi, H., Hisaeda, Y., and Shirahata, S., Kinetic analysis of superoxide anion radical-scavenging and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities of platinum nanoparticles. Langmuir, 24, 7354–7364 (2008).
Johansson, N., Ahonen, M., and Kähäri, V. M., Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion. Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 57, 5–15 (2000).
Kim, J., Takahashi, M., Shimizu, T., Shirasawa, T., Kajita, M., Kanayama, A., and Miyamoto, Y., Effects of a potent antioxidant, platinum nanoparticle, on the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev., 129, 322–331 (2008).
Komanicky, V., Iddir, H., Chang, K. C., Menzel, A., Karapetrov, G., Hennessy, D., Zapol, P., and You, H., Shape-dependent activity of platinum array catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131, 5732–5733 (2009).
Larsen, A., Kolind, K., Pedersen, D. S., Doering, P., Pedersen, M. O., Danscher, G., Penkowa, M., and Stoltenberg, M., Gold ions bio-released from metallic gold particles reduce inflammation and apoptosis and increase the regenerative responses in focal brain injury. Histochem. Cell Biol., 130, 681–692 (2008).
Lawrence, D. A., Transforming growth factor-beta: a general review. Eur. Cytokine Netw., 7, 363–374 (1996).
Manosroi, A., Saraphanchotiwitthaya, A., and Manosroi, J., In vitro immunomodulatory effect of Pouteria cambodiana (Pierre ex Dubard) Baehni extract. J. Ethnopharmacol., 101, 90–94 (2005).
Onizawa, S., Aoshiba, K., Kajita, M., Miyamoto, Y., and Nagai, A., Platinum nanoparticle antioxidants inhibit pulmonary inflammation in mice exposed to cigarette smoke. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther., 22, 340–349 (2009).
Pan, Y., Neuss, S., Leifert, A., Fischler, M., Wen, F., Simon, U., Schmid, G., Brandau, W., and Jahnen-Dechent, W., Size-dependent cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. Small, 3, 1941–1949 (2007).
Park, E. J., Choi, J., Park, Y. K., and Park, K., Oxidative stress induced by cerium oxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicology, 245, 90–100 (2008).
Park, E. J., Yoon, J., Choi, K., Yi, J., and Park, K., Induction of chronic inflammation in mice treated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles by intratracheal instillation. Toxicology, 260, 37–46 (2009).
Rahman, I. and MacNee, W., Regulation of redox glutathione levels and gene transcription in lung inflammation: therapeutic approaches. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 28, 1405–1420 (2000).
Rahman, I., Biswas, S. K., Jimenez, L. A., Torres, M., and Forman, H. J., Glutathione, stress responses, and redox signaling in lung inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal., 7, 42–59 (2005).
Schmid, M., Zimmermann, S., Krug, H. F., and Sures, B., Influence of platinum, palladium and rhodium as compared with cadmium, nickel and chromium on cell viability and oxidative stress in human bronchial epithelial cells. Environ. Int., 33, 385–390 (2007).
Tedesco, S., Doyle, H., Redmond, G., and Sheehan, D., Gold nanoparticles and oxidative stress in Mytilus edulis. Mar. Environ. Res., 66, 131–133 (2008).
Teranishi, T., Hosoe, M., Tanaka, T., and Miyake, M. B., Size control of monodispersed Pt nanoparticles and their 2D organization by electrophoretic deposition., J. Phys. Chem. B., 103, 3818–3827 (1999).
Theron, A. J., Ramafi, G. J., Feldman, C., Grimmer, H., Visser, S. S., and Anderson, R., Effects of platinum and palladium ions on the production and reactivity of neutrophilderived reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 36, 1408–1417 (2004).
Tsuji, J. S., Maynard, A. D., Howard, P. C., James, J. T., Lam, C. W., Warheit, D. B., and Santamaria, A. B., Research strategies for safety evaluation of nanomaterials, part IV: risk assessment of nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci., 89, 42–50 (2006).
Tsai, C. Y., Shiau, A. L., Chen, S. Y., Chen, Y. H., Cheng, P. C., Chang, M. Y., Chen, D. H., Chou, C. H., Wang, C. R., and Wu, C. L., Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in rats by nanogold. Arthritis Rheum., 56, 544–554 (2007).
Vendrame, M., Gemma, C., Pennypacker, K. R., Bickford, P. C., Davis Sanberg, C., Sanberg, P. R., and Willing, A. E., Cord blood rescues stroke-induced changes in splenocyte phenotype and function. Exp. Neurol., 199, 191–200 (2006).
Wan, R., Mo, Y., Zhang, X., Chien, S., Tollerud, D. J., and Zhang, Q., Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 are induced differently by metal nanoparticles in human monocytes: The role of oxidative stress and protein tyrosine kinase activation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 233, 276–285 (2008).
Wang, X., Liu, F., Andavan, G. T., Jing, X., Singh, K., Yazdanpanah, V. R., Bruque, N., Pandey, R. R., Lake, R., Ozkan, M., Wang, K. L., and Ozkan, C. S., Carbon nanotube-DNA nanoarchitectures and electronic functionality. Small, 2, 1356–1365 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, EJ., Kim, H., Kim, Y. et al. Intratracheal instillation of platinum nanoparticles may induce inflammatory responses in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 727–735 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0512-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0512-y