Abstract
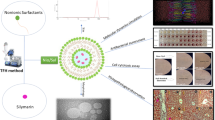
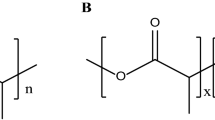
Hydrogels are widely used in drug delivery systems because they can control the release and thereby enhance the efficiency of locally delivered bioactive molecules such as therapeutic drugs, proteins, or genes. For gene delivery, localized release of plasmid DNA or polymer/DNA complexes can transfect cells and produce sustained protein production. We tested the galactosylated chitosan-graft-polyethylenimine (GC-g-PEI)/DNA complexes-loaded poly(organophosphazene) thermosensitive biodegradable hydrogel as a hepatocyte targeting gene delivery system. The poly(organophosphazene) hydrogel loaded with GC-g-PEI/DNA complexes showed low cytotoxicity and higher transfection efficiency than PEI/DNA complexes, as well as good hepatocyte specificity in vitro and in vivo. Our results indicate that poly(organophosphazene) hydrogels loaded with GC-g-PEI/DNA complexes may be a safe and efficient hepatocyte targeting gene delivery system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Laporte, L. and Shea, L. D., Matrices and scaffolds for DNA delivery in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 59, 292–307 (2007).
Greish, Y. E., Bender, J. D., Lakshmi, S., Brown, P. W., Allcock, H. R., and Laurencin, C. T., Low temperature formation of hydroxyapatite-poly(alkyl oxybenzoate)phosphazene composites for biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 26, 1–9 (2005).
Holmes, T. C., de Lacalle, S., Su, X., Liu, G., Rich, A., and Zhang, S., Extensive neurite outgrowth and active synapse formation on self-assembling peptide scaffolds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 97, 6728–6733 (2000).
Jiang, H. L., Kim, Y. K., Arote, R., Nah, J. W., Cho, M. H., Choi, Y. J., Akaike, T.m and Cho, C. S.m Chitosan-graftpolyethylenimine as a gene carrier. J. Control. Release, 117, 273–280 (2007a).
Jiang, H. L., Kwon, J. T., Kim, Y. K., Kim, E. M., Arote, R., Jeong, H. J., Nah, J. W., Choi, Y. J., Akaike, T., Cho, M. H., and Cho, C. S., Galactosylated chitosan-graft-polyethylenimine as a gene carrier for hepatocyte targeting. Gene Ther., 14, 1389–1398 (2007b).
Jiang, H. L., Kwon, J. T., Kim, E. M., Kim, Y. K., Arote, R., Jere, D., Jeong, H. J., Jang, M. K., Nah, J. W., Xu, C. X., Park, I. K., Cho, M. H., and Cho, C. S., Galactosylated poly(ethylene glycol)-chitosan-graft-polyethylenimine as a gene carrier for hepatocyte-targeting. J. Control. Release, 131, 150–157 (2008).
Kang, G. D., Cheon, S. H., Khang, G., and Song, S. C., Thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) hydrogels for a controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 63, 340–346 (2006).
Kasper, F. K., Seidlits, S. K., Tang, A., Crowther, R. S., Carney, D. H., Barry, M. A., and Mikos, A. G., In vitro release of plasmid DNA from oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) hydrogels. J. Control. Release, 104, 521–539 (2005).
Klouda, L. and Mikos, A. G., Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 68, 34–45 (2008).
Kushibiki, T. and Tabata, Y., A new gene delivery system based on controlled release technology. Curr. Drug Deliv., 1, 153–163 (2004).
Lee, B. H., Lee, Y. M., Sohn Y. S., and Song, S. C., A thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) gel. Macromolecules, 35, 3876–3879 (2002).
Lee, B. H. and Song, S. C., Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) gels. Macromolecules, 37, 4533–4537 (2004).
Lei, Y. and Segura, T., DNA delivery from matrix metalloproteinase degradable poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels to mouse cloned mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials, 30, 254–265 (2009).
Li, Z., Ning, W., Wang, J., Choi, A., Lee, P. Y., Tyagi, P., and Huang, L., Controlled gene delivery system based on thermosensitive biodegradable hydrogel. Pharm. Res., 20, 884–888 (2003).
Luten, J., van Steenis, J. H., van Someren, R., Kemmink, J., Schuurmans-Nieuwenbroek, N. M., Koning, G. A., Crommelin, D. J., van Nostrum, C. F., and Hennink, W. E., Water-soluble biodegradable cationic polyphosphazenes for gene delivery. J. Control. Release, 89, 483–497 (2003).
Nukavarapu, S. P., Kumbar, S. G., Brown, J. L., Krogman, N. R., Weikel, A. L., Hindenlang, M. D., Nair, L. S., Allcock, H. R., and Laurencin, C. T., Polyphosphazene/nano-hydroxyapatite composite microsphere scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules, 9, 1818–1825 (2008).
Park, K. H. and Song, S. C., A thermo-sensitive poly(organophosphazene) hydrogel used as an extracellular matrix for artificial pancreas. J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed., 16, 1421–1431 (2005).
Park, T. G., Jeong, J. H., and Kim, S. W., Current status of polymeric gene delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 58, 467–486 (2006).
Petka, W. A., Harden, J. L., McGrath, K. P., Wirtz, D., and Tirrell, D. A., Reversible hydrogels from self-assembling artificial proteins. Science, 281, 389–392 (1998).
Scherer, F., Schillinger, U., Putz, U., Stemberger, A., and Plank, C., Nonviral vector loaded collagen sponges for sustained gene delivery in vitro and in vivo. J. Gene Med., 4, 634–643 (2002).
Segura, T., Volk, M. J., and Shea, L. D., Substrate-mediated DNA delivery: role of the cationic polymer structure and extent of modification. J. Control. Release, 93, 69–84 (2003).
Shea, L. D., Smiley, E., Bonadio, J., and Mooney, D. J., DNA delivery from polymer matrices for tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol., 17, 551–554 (1999).
Wieland, J. A., Houchin-Ray, T. L., and Shea, L. D., Nonviral vector delivery from PEG-hyaluronic acid hydrogels. J. Control. Release, 120, 233–241 (2007).
Yang, Y., Xu, Z., Jiang, J., Gao, Y., Gu, W., Chen, L., Tang, X., and Li, Y., Poly(imidazole/DMAEA)phosphazene/DNA self-assembled nanoparticles for gene delivery: synthesis and in vitro transfection. J. Control. Release, 127, 273–279 (2008).
Zhang, J. X., Yan, M. Q., Li, X. H., Qiu, L. Y., Li, X. D., Li, X. J., Jin, Y., and Zhu, K. J., Local delivery of indomethacin to arthritis-bearing rats through polymeric micelles based on amphiphilic polyphosphazenes. Pharm. Res., 24, 1944–1953 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, HL., Kim, YK., Lee, SM. et al. Galactosylated chitosan-g-PEI/DNA complexes-loaded poly(organophosphazene) hydrogel as a hepatocyte targeting gene delivery system. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 551–556 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0409-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0409-9