Abstract
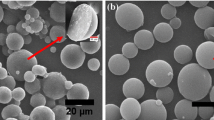
The aim of this study was to investigate whether hollow microspheres prepared from polymer blends of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) and ethyl cellulose (EC) could improve the vitro release behavior of the poorly water-soluble drug nifedipine. Hollow microspheres containing nifedipine were prepared by a solvent diffusion-evaporation method using various ratios of PVP and EC codissolved with drug in ethanol/ether (5:1, v/v). The hollow microspheres could float in release medium for more than 24 h, and floating capacities were not be influenced by mixing PVP. In vitro release profiles of hollow microspheres prepared using EC along showed an initial burst release to some extent, and the cumulative release percentage was less than 55% after 24 h. But, not only the slope but also the shape of the release curves was affected by using mixture of PVP and EC. What’s more important, when the ratio (PVP/EC) increased to 1.5:8.5, the cumulative release percentage could be increased to 95.8%. Furthermore, the release rate of microspheres showed a zero order approximate dynamic model and could be expressed by the following equation: Q=3.78t+8.52 (r=0.990). Consequently, hollow microspheres prepared using polymer blends of PVP and EC (1.5:8.5, w/w) could be suitable for floating-type controlled-release delivery systems for the oral administration of nifedipine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chowdary, K. P. R. and Girija Sankar, G., Eudragit microcapsules of nifedipine and its dispersions in HPMCMCC: Physicochemical characterization and drug release studies. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 23, 325–333 (1997).
El-Gibaly, I., Development and in vitro evaluation of novel floating chitosan microcapsules for oral use: comparison with non-floating chitosan microspheres. Int. J. Pharm., 249, 7–21 (2002).
Filipovic-Grcic, J., Becirevic-Lacan, M., Skalko, N., and Jalsenjak, I., Chitosan microspheres of nifedipine and nifedipine-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Int. J. Pharm., 135, 183–190 (1996).
Foster, T. S., Hamann, S. R., Richards, V. R., Bryant, P. J., Graves, D. A., and McAllister, R. G., Nifedipine kinetics and bioavailability after single intravenous and oral doses in normal subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 23, 161–170 (1983).
Joseph, N. J., Lakshmi, S., and Jayakrishnan, A., A floatingtype oral dosage form for piroxicam based on hollow polycarbonate microspheres: in vitro and in vivo evaluation in rabbits. J. Control. Release, 79, 71–79 (2002).
Lee, J. H., Park, T. G., and Choi, H. K., Development of oral drug delivery system using floating microspheres. J. Microencapsul., 16, 715–729 (1999).
Martin, A., Bustamante, P., and Chun, A. H. C., Physical Pharmacy (fourth ed.). B.I. Wavery Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, pp. 284–317, (1999).
Reddy, L. H. and Murtby, R. S., Floating dosage system in drug delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst., 19, 553–585 (2002).
Stithit, S., Chen, W., and Price, J. C., Development and characterization of buoyant theophylline microspheres with near zero order release kinetics. J. Microencapsul., 15, 725–737 (1998).
Soppimath, K. S., Kulkarni, A. R., and Aminabhavi, T. M., Development of hollow microspheres as floating controlled-release system for cardiovascular drugs: preparation and release characteristics. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 27, 507–515 (2001a).
Soppimath, K. S., Kulkarni, A. R., and Aminabhavi, T. M., Encapsulation of antihypertensive drugs in cellulose-based matrix microspheres: characterization and release kinetics of microspheres and tableted microspheres, J. Microencapsul., 18, 397–409 (2001b).
Sugimoto, I., Kuchiki, A., and Nakagawa, H., Stability of nifedipine-polyvinylpyrrolidone coprecipitate. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 29, 1715–1723 (1981).
Tateshita, K., Sugawara, S., Imai, T., and Otagiri, M., Preparation and evaluation of a controlled-release formulationof nifedipine using alginate gel beads. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 16, 420–424 (1993).
Thanoo, B. C., Sunny, M. C., and Jayakrishnan, A., Oral sustained-release drug delivery systems using polycarbonate microspheres capable of floating on the gastric fluid. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 45, 21–24 (1993).
Toyohiro, S., Hiromu Kondo, K., Hiroshi, N., Kazuhiro, S., and Masahiro, H., Time-release compression-coated core tablet containing nifedipine for chronopharmacotherapy. Int. J. Pharm., 280, 103–111 (2004).
Uekama, K., Ikegami, K., Wang, Z., Horiuchi, Y., and Hirayama, F., Inhibitory effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-cyclodextrin on crystal-growth of nifedipine during storage: superior dissolution and oral bioavailability compared with polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 44, 73–78 (1992).
Wei, Y. M. and Zhao, L., In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ranitidine hydrochloride loaded hollow microspheres in rabbits. Arch. Pharm. Res., 31, 1369–1377 (2008).
Yuan, Y., Li, S. M., and Mo, F. K., New process of floating drug delivery systems hollow microspheres. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ., 22, 235–240 (2005).
Yoo, H. S., Preparation of biodegradable polymeric hollow microspheres using o/o/w emulsion stabilized by Labrafil. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces, 52, 47–51 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Wei, Ym., Yu, Y. et al. Polymer blends used to prepare nifedipine loaded hollow microspheres for a floating-type oral drug delivery system: In vitro evaluation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 443–450 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0314-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0314-2