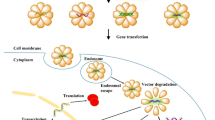
Abstract
The genetic materials for systemic administration meet a number of huddles before they reach the nucleus of the target cells, such as enzymatic degradation in the bloodstream, extravascularization around the target tissue, endocytosis by the target cells, and endosomal escape of the genes. Therefore, there have been tremendous needs of effective gene carriers that can deliver the genetic materials to the target site. Of numerous approaches, recent studies have demonstrated that the lipid-based emulsion systems have the high potential as non-viral gene carriers: 1 lipid emulsions are biocompatible because their major constituents are composed of the non-toxic oils and amphiphilic lipids; 2 the cationic lipid emulsions can form nano-sized complexes with negatively charged DNAs, through which the genetic materials can be protected from the enzymatic degradation in the body fluids; 3 The emulsion/DNA complexes are shown to be stable in the bloodstream since their surfaces are rarely recognized by the immune-related cells and serum proteins; and 4 the surfaces of the emulsion complexes are readily modified by varying the lipid composition. In this review, highlighted are the recent advances in the emulsion-based gene carriers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, T. M., Hansen, C., Martin, F., Redemann, C., and Yau-Young, A., Liposomes containing synthetic lipid derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) show prolonged circulation half-lives in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1066, 29–36 (1991).
Audouy, S. A., de Leij, L. F., Hoekstra, D., and Molema, G., In vivo characteristics of cationic liposomes as delivery vectors for gene therapy. Pharm. Res., 19, 1599–1605 (2002).
Bottega, R. and Epand, R. M., Inhibition of protein kinase C by cationic amphiphiles. Biochemistry, 31, 9025–9030 (1992).
Choi, B. Y., Chung, J. W., Park, J. H., Kim, K. H., Kim, Y. I., Koh, Y. H., Kwon, J. W., Lee, K. H., Choi, H. J., Kim, T. W., Kim, Y. J., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., and Jeong, S. Y., Gene delivery to the rat liver using cationic lipid emulsion/DNA complex: comparison between intraarterial, intraportal and intravenous administration. Korean J. Radiol., 3, 194–198 (2002).
Chung, H., Kim, T. W., Kwon, M., Kwon, I. C., and Jeong, S. Y., Oil components modulate physical characteristics and function of the natural oil emulsions as drug or gene delivery system. J. Control. Release, 71, 339–350 (2001).
Davis, S. S. and Hansrani, P., The influence of emulsifying agents on the phargocytosis of lipid emulsions by marcrophates. Int. J. Pharm., 23, 69–77 (1985).
Duvaz- N. D., Heyes, J., and Springer, C. J., Structure-activity relationship in cationic lipid mediated gene transfection. Curr. Med. Chem., 10, 1022–1261 (2003).
Felgner, J. H., Kumar, R., Sridhar, C. N., Wheeler, C. J., Tsai, Y. J., Border, R., Ramsey, P., Martin, M., and Felgner, P. L., Enhanced gene delivery and mechanism studies with a novel series of cationic lipid formulations. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 2550–2561 (1994).
Felgner, P. L., Gadek, T. R., Holm, M., Roman, R., Chan, H. W., Wenz, M., Northrop, J. P., Ringold, G. M., and Danielsen, M., Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 84, 7413–7417 (1987).
Fukushima, S., Kishimoto, S., Takeuchi, Y., and Fukushima, M., Preparation and evaluation of o/w type emulsions containing antitumor prostaglandin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 45, 65–75 (2000).
Gao, H. and Hui, K. M., Synthesis of a novel series of cationic lipids that can act as efficient gene delivery vehicles through systematic heterocyclic substitution of cholesterol derivatives. Gene Ther., 8, 855–863 (2001).
Gao, X. and Huang, L., A novel cationic liposome reagent for efficient transfection of mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 179, 280–285 (1991).
Harris, J. M., Martin, N. E., and Modi, M., Pegylation: a novel process for modifying pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 40, 539–551 (2001).
Harvie, P., Wong, F. M., and Bally, M. B., Characterization of lipid DNA interactions. I. Destabilization of bound lipids and DNA dissociation. Biophys. J., 75, 1040–1051 (1998).
Hashida, M., Kawakami, S., and Yamashita, F., Lipid carrier systems for targeted drug and gene delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo), 53, 871–880 (2005).
Hong, K., Zheng, W., Baker, A., and Papahadjopoulos, D., Stabilization of cationic liposome-plasmid DNA complexes by polyamines and poly(ethylene glycol)-phospholipid conjugates for efficient in vivo gene delivery. FEBS Lett., 400, 233–237 (1997).
Ilies, M. A., Seitz, W. A., Johnson, B. H., Ezell, E. L., Miller, A. L., Thompson, E. B., and Balaban, A. T., Lipophilic pyrylium salts in the synthesis of efficient pyridinium-based cationic lipids, gemini surfactants, and lipophilic oligomers for gene delivery. J. Med. Chem., 49, 3872–3887 (2006).
Ishida, E., Managit, C., Kawakami, S., Nishikawa, M., Yamashita, F., and Hashida, M., Biodistribution characteristics of galactosylated emulsions and incorporated probucol for hepatocyte-selective targeting of lipophilic drugs in mice. Pharm. Res., 21, 932–939 (2004).
Jumaa, M. and Müller, B. W., The effect of oil components and homogenization conditions on the physicochemical properties and stability of parenteral fat emulsions. Int. J. Pharm., 163, 81–89 (1998).
Karmali, P. P. and Chaudhuri, A., Cationic liposomes as non-viral carriers of gene medicines: resolved issues, open questions, and future promises. Med. Res. Rev., 27, 696–722 (2007).
Kim, T. W., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., Sung, H. C., and Jeong, S. Y., Optimization of lipid composition in cationic emulsion as in vitro and in vivo transfection agents. Pharm. Res., 18, 54–60 (2001).
Kim, T. W., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., Sung, H. C., Shin, B. C., and Jeong, S. Y., Airway gene transfer using cationic emulsion as a mucosal gene carrier. J. Gene Med., 7, 749–758 (2005).
Kim, T. W., Kim, Y. J., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., Sung, H. C., and Jeong, S. Y., The role of non-ionic surfactants on cationic lipid mediated gene transfer. J. Control. Release, 82, 455–465 (2002).
Kim, Y. J., Kim, T. W., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., Sung, H. C., and Jeong, S. Y., The effects of serum on the stability and the transfection activity of the cationic lipid emulsion with various oils. Int. J. Pharm., 252, 241–252 (2003).
Klibanov, A. L., Maruyama, K., Torchilin, V. P., and Huang, L. Amphipathic polyethyleneglycols effectively prolong the circulation time of liposomes. FEBS Lett., 268, 235–237 (1990).
Koltover, I., Salditt, T., Radler, J. O., and Safinya, C. R., An inverted hexagonal phase of cationic liposome-DNA complexes related to DNA release and delivery. Science, 281, 78–81 (1998).
Kurihara, A., Shibayama, Y., Mizota, A., Yasuno, A., Ikeda, M., and Hisaoka, M., Pharmacokinetics of highly lipophilic antitumor agent palmitoyl rhizoxin incorporated in lipid emulsions in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 19, 252–258 (1996).
Lee, J. H., Lee, H. B., and Andrade, J. D., Blood compatibility of polyethylene oxide surfaces. Prog. Polym. Sci., 20, 1043–1079 (1995).
Litzinger, D. C., Brown, J. M., Wala, I., Kaufman, S. A., Van, G. Y., Farrell, C. L., and Collins, D., Fate of cationic liposomes and their complex with oligonucleotide in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1281, 139–149 (1996).
Liu, D., Hu, J., Qiao, W., Li, Z., Zhan, S., and Cheng, L., Synthesis and characterization of a series of carbamate-linked cationic lipids for gene delivery. Lipids, 40, 839–848 (2005a).
Liu, D., Hu, J., Qiao, W., Li, Z., Zhang, S., and Cheng, L., Synthesis of carbamate-linked lipids for gene delivery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 15, 3147–3150 (2005b).
Liu, D., Ren, T., and Gao, X., Cationic transfection lipids. Curr. Med. Chem., 10, 1307–1315 (2003).
Liu, F. Yang, J., Huang, L., and Liu, D., New cationic lipid formulations for gene transfer. Pharm. Res., 13, 1856–1860 (1996).
Liu, F. and Liu, D., Long-circulating emulsions (oil-inwater) as carriers for lipophilic drugs. Pharm. Res., 12, 1060–1064 (1995).
Liu, F., Qi, H., Huang, L., and Liu, D., Factors controlling the efficiency of cationic lipid-mediated transfection in vivo via intravenous administration. Gene Ther., 4, 517–523 (1997).
Mahato, R. I., Anwer, K., Tagliaferri, F., Meaney, C., Leonard, P., Wadhwa, M. S., Logan, M., French, M., and Rolland, A., Biodistribution and gene expression of lipid/plasmid complexes after systemic administration. Hum. Gene Ther., 9, 2083–2099 (1998).
Pinnaduwage, P., Schmitt, L., and Huang, L., Use of a quaternary ammonium detergent in liposome mediated DNA transfection of mouse L-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 985, 33–37 (1989).
Rao, N. M. and Gopal, V., Cell biological and biophysical aspects of lipid-mediated gene delivery. Biosci. Rep., 26, 301–324 (2006).
Simoes, S., Slepushkin, V., Pires, P., Gaspar, R., de Lima, M. P., and Duzgunes, N., Mechanisms of gene transfer mediated by lipoplexes associated with targeting ligands or pH-sensitive peptides. Gene Ther., 6, 1798–1807 (1999).
Solodin, I., Brown, C. S., Bruno, M. S., Chow, C. Y., Jang, E. H., Debs, R. J., and Heath, T. D., A novel series of amphiphilic imidazolinium compounds for in vitro and in vivo gene delivery. Biochemistry, 34, 13537–13544 (1995).
Song, Y. K. and Liu, D., Free liposomes enhance the transfection activity of DNA/lipid complexes in vivo by intravenous administration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1372, 141–150 (1998).
Song, Y. K., Liu, F., Chu, S., and Liu, D., Characterization of cationic liposome-mediated gene transfer in vivo by intravenous administration. Hum. Gene Ther., 8, 1585–1594 (1997).
Takino, T., Nakajima, C., Takakura, Y., Sezaki, H., and Hashida, M., Controlled biodistribution of highly lipophilic drugs with various parenteral formulation. J. Drug Target., 1, 117–124 (1993).
Tamilvanan, S., Oil-in-water lipid emulsions: implications for parenteral and ocular delivering systems. Prog. Lipid Res., 43, 489–533 (2004).
Tang, F. and Hughes, J. A., Synthesis of a single-tailed cationic lipid and investigation of its transfection. J. Control. Release, 62, 345–358 (1999).
Torchilin, V. P., Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 4, 145–160 (2005).
van der Woude, I., Wagenaar, A., Meekel, A. A., ter Beest, M. B., Ruiters, M. H., Engberts, J. B., and Hoekstra, D., Novel pyridinium surfactants for efficient, nontoxic in vitro gene delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 94, 1160–1165 (1997).
Wang, J., Guo, X., Xu, Y., Barron, L., and Szoka, F. C., Jr., Synthesis and characterization of long chain alkyl acyl carnitine esters. Potentially biodegradable cationic lipids for use in gene delivery. J. Med. Chem., 41, 2207–2215 (1998).
Woodle, M. C. and Lasic, D. D., Sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1113, 171–199 (1992).
Yeeprae, W., Kawakami, S., Higuchi, Y., Yamashita, F., and Hashida, M., Biodistribution characteristics of mannosylated and fucosylated O/W emulsions in mice. J. Drug Target., 13, 479–487 (2005).
Yoo, H. S., Kwon, S. M., Kim, Y. J., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., Kim, J., and Jeong, S. Y., Cationic lipid emulsions containing heavy oils for the transfection of adherent cells. J. Control. Release, 98, 179–188 (2004).
Zuidam, N. J. and Barenholz, Y., Electrostatic and structural properties of complexes involving plasmid DNA and cationic lipids commonly used for gene delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1368, 115–128 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, H.Y., Park, J.H., Kim, K. et al. Lipid-based emulsion system as non-viral gene carriers. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 639–646 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1500-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1500-y