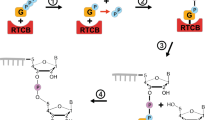
Abstract
The cellular pool of RNA is immensely diverse and complex. During their biosynthesis, RNA molecules undergo a vast number of co- and posttranscriptional processing and modification steps. A unique example of RNA processing is the non-conventional splicing of RNAs. This protein-catalysed splicing mechanism is an essential step during tRNA maturation and a main mode of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signalling. Here, I discuss the cellular roles and catalytic machinery of non-conventional splicing in eukaryotes.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Literatur
Popow J, Schleiffer A, Martinez J (2012) Diversity and roles of (t)RNA ligases. Cell Mol Life Sci 69: 2657–2670
Peebles CL, Ogden RC, Knapp G, Abelson J (1979) Splicing of yeast tRNA precursors: a two-stage reaction. Cell 18: 27–35
Lu Z, Filonov GS, Noto JJ et al. (2015) Metazoan tRNA introns generate stable circular RNAs in vivo. RNA 21: 1554–1565
Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334: 1081–1086
Peebles CL, Gegenheimer P, Abelson J (1983) Precise excision of intervening sequences from precursor tRNAs by a membrane-associated yeast endonuclease. Cell 32:525–536
Greer CL, Peebles CL, Gegenheimer P, Abelson J (1983) Mechanism of action of a yeast RNA ligase in tRNA splicing. Cell 32: 537–546
Sidrauski C, Cox JS, Walter P (1996) tRNA Ligase Is required for regulated mRNA splicing in the unfolded protein response. Cell 87: 405–413
Peschek J, Walter P (2019) tRNA ligase structure reveals kinetic competition between non-conventional mRNA splicing and mRNA decay. eLife 8: e44199
Popow J, Englert M, Weitzer S et al. (2011) HSPC117 is the essential subunit of a human tRNA splicing ligase complex. Science 331: 760–764
Peschek J, Acosta-Alvear D, Mendez AS, Walter P (2015) A conformational RNA zipper promotes intron ejection during non-conventional XBP1 mRNA splicing. EMBO reports 16:1688–1698
Hopper AK (2013) Transfer RNA post-transcriptional processing, turnover, and subcellular dynamics in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 194: 43–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding note
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Jirka Peschek 2002–2007 Biochemiestudium an der TU München. 2008–2012 Promotion bei Prof. Dr. J. Buchner an der TU München. 2013–2020 Postdoktorand bei Prof. Dr. P. Walter an der University of California, San Francisco, USA. Seit 2020 Emmy Noether-Nachwuchsgruppenleiter am Biochemie-Zentrum der Universität Heidelberg.
Rights and permissions
Dieser Artikel wird unter der Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International Lizenz veröffentlicht, welche die Nutzung, Vervielfältigung, Bearbeitung, Verbreitung und Wiedergabe in jeglichem Medium und Format erlaubt, sofern Sie den/die ursprünglichen Autor(en) und die Quelle ordnungsgemäß nennen, einen Link zur Creative Commons Lizenz beifügen und angeben, ob Änderungen vorgenommen wurden. Die in diesem Artikel enthaltenen Bilder und sonstiges Drittmaterial unterliegen ebenfalls der genannten Creative Commons Lizenz, sofern sich aus der Abbildungslegende nichts anderes ergibt. Sofern das betreffende Material nicht unter der genannten Creative Commons Lizenz steht und die betreffende Handlung nicht nach gesetzlichen Vorschriften erlaubt ist, ist für die oben aufgeführten Weiterverwendungen des Materials die Einwilligung des jeweiligen Rechteinhabers einzuholen. Weitere Details zur Lizenz entnehmen Sie bitte der Lizenzinformation auf http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/deed.de.
About this article
Cite this article
Peschek, J. Mechanismen des nicht konventionellen RNA-Spleißens. Biospektrum 27, 233–236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-021-1560-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-021-1560-1