Abstract
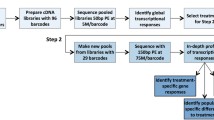
Gene expression studies have become valuable tools to identify the complex mode of action of toxic or carcinogenic substances. In our group we established a quantitative high-throughput RT-qPCR technique using Fluidigm dynamic arrays on the BioMark™ System to analyze the expression level of 95 genes in 96 samples in parallel. By creating a special gene set comprising critical genes of the DNA damage response system the impact on genomic stability can be investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Fischer B, Neumann D, Piberger A et al. (2015) Use of high-throughput RT-qPCR to assess modulations of gene expression profiles related to genomic stability and inter - actions by cadmium. Arch Toxicol, doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1621-7
Harper JW, Elledge SJ (2007) The DNA damage response: ten years after. Mol Cell 28:739–745
Zhou BB, Elledge SJ (2000) The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature 408:433–439
Spurgeon SL, Jones RC, Ramakrishnan R (2008) High throughput gene expression measurement with real time PCR in a microfluidic dynamic array. PLoS One 3:e1662
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, B.M., Hartwig, A. Aufklärung toxischer Wirkmechanismen mittels Hochdurchsatz-RT-qPCR. Biospektrum 22, 499–500 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-016-0718-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-016-0718-8