Abstract
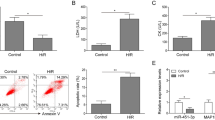
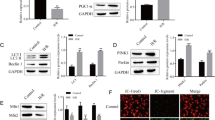
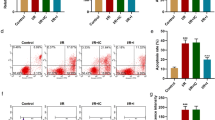
We investigated the potential role of miR-490-3p in ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury. We first determined the expression of miR-490-3p and autophagy-related 4B cysteine (ATG4B) in IR. Then, to explore whether miR-490-3p would affect autophagy, apoptosis, and IR injury, we evaluated apoptosis, autophagy, and infarct size via gain- and loss-of-function experiments. Furthermore, we used adenovirus to enhance or inhibit the expression of ATG4B, and then measured autophagy, apoptosis, and IR injury. miR-490-3p was downregulated in the hearts during the process of IR, while ATG4B was upregulated. The inhibition of miR-490-3p or overexpression of ATG4B could promote the expression of LC3II, increase the autolysosomes, inhibit the expression of p62, and reduce infarct size. On all accounts, the inhibition of miR-490-3p could promote autophagy to reduce myocardial IR injury by upregulating ATG4B, a finding that provides new insights for the protective mechanism of autophagy in IR.

Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eltzschig, H. K., & Eckle, T. (2011). Ischemia and reperfusion—from mechanism to translation. Nature Medicine, 17(11), 1391–1401.
Rosero, O., Onody, P., Kovacs, T., Molnar, D., Fulop, A., Lotz, G., et al. (2017). Postconditioning: “toll-erating” mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion injury? Surgery, 161(4), 1004–1015.
Yellon, D. M., & Hausenloy, D. J. (2007). Myocardial reperfusion injury. The New England Journal of Medicine, 357(11), 1121–1135.
Fan, Z. X., & Yang, J. (2015). The role of microRNAs in regulating myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Saudi Medical Journal, 36(7), 787–793.
Sciarretta, S., Volpe, M., & Sadoshima, J. (2014). Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in cardiac physiology and disease. Circulation Research, 114(3), 549–564.
Petrovski, G., Das, S., Juhasz, B., Kertesz, A., Tosaki, A., & Das, D. K. (2011). Cardioprotection by endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 14(11), 2191–2200.
Ma, X., Godar, R. J., Liu, H., & Diwan, A. (2012). Enhancing lysosome biogenesis attenuates BNIP3-induced cardiomyocyte death. Autophagy., 8(3), 297–309.
Jiang, M., Liu, K., Luo, J., & Dong, Z. (2010). Autophagy is a renoprotective mechanism during in vitro hypoxia and in vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury. The American Journal of Pathology, 176(3), 1181–1192.
Zhou, L., Zang, G., Zhang, G., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Johnston, N., et al. (2013). MicroRNA and mRNA signatures in ischemia reperfusion injury in heart transplantation. PLoS One, 8(11), e79805.
Small, E. M., & Olson, E. N. (2011). Pervasive roles of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature, 469(7330), 336–342.
Yang, M., Kong, D. Y., & Chen, J. C. (2019). Inhibition of miR-148b ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234, 17757–17766.
Yang, Z., & Klionsky, D. J. (2009). An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 335, 1–32.
Wang, I. K., Sun, K. T., Tsai, T. H., Chen, C. W., Chang, S. S., Yu, T. M., et al. (2015). MiR-20a-5p mediates hypoxia-induced autophagy by targeting ATG16L1 in ischemic kidney injury. Life Sciences, 136, 133–141.
Li, Z., Wang, G., Feng, D., Zu, G., Li, Y., Shi, X., et al. (2018). Targeting the miR-665-3p-ATG4B-autophagy axis relieves inflammation and apoptosis in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death & Disease, 9(5), 483.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408.
Hamacher-Brady, A., Brady, N. R., Logue, S. E., Sayen, M. R., Jinno, M., Kirshenbaum, L. A., Gottlieb, R. A., & Gustafsson, A. B. (2007). Response to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury involves Bnip3 and autophagy. Cell Death and Differentiation, 14(1), 146–157.
Zhang, C. X., Cheng, Y., Liu, D. Z., Liu, M., Cui, H., Zhang, B. L., Mei, Q. B., & Zhou, S. Y. (2019). Mitochondria-targeted cyclosporin A delivery system to treat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury of rats. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 17(1), 18.
Skytte Rasmussen, M., Mouilleron, S., Kumar Shrestha, B., Wirth, M., Lee, R., Bowitz Larsen, K., et al. (2017). ATG4B contains a C-terminal LIR motif important for binding and efficient cleavage of mammalian orthologs of yeast Atg8. Autophagy, 13(5), 834–853.
Kabeya, Y., Mizushima, N., Yamamoto, A., Oshitani-Okamoto, S., Ohsumi, Y., & Yoshimori, T. (2004). LC3, GABARAP and GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II formation. Journal of Cell Science, 117(Pt 13), 2805–2812.
Satoo, K., Noda, N. N., Kumeta, H., Fujioka, Y., Mizushima, N., Ohsumi, Y., et al. (2009). The structure of Atg4B-LC3 complex reveals the mechanism of LC3 processing and delipidation during autophagy. The EMBO Journal, 28(9), 1341–1350.
Zheng, W., Men, H., Li, J., Xing, Y., Wu, B., Wang, Z., et al. (2016). Global microRNA expression profiling of mouse livers following ischemia-reperfusion injury at different stages. PLoS One, 11(2), e0148677.
Wojciechowska, A., Braniewska, A., & Kozar-Kaminska, K. (2017). MicroRNA in cardiovascular biology and disease. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 26(5), 865–874.
Guclu, A., Kocak, C., Kocak, F. E., Akcilar, R., Dodurga, Y., Akcilar, A., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-125b as a new potential biomarker on diagnosis of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. The Journal of Surgical Research, 207, 241–248.
Yang, Z., Wilkie-Grantham, R. P., Yanagi, T., Shu, C. W., Matsuzawa, S., & Reed, J. C. (2015). ATG4B (Autophagin-1) phosphorylation modulates autophagy. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290(44), 26549–26561.
Wu, Y., Dai, X., Ni, Z., Yan, X., He, F., & Lian, J. (2017). The downregulation of ATG4B mediated by microRNA-34a/34c-5p suppresses rapamycin-induced autophagy. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 20(10), 1125–1130.
Wang, Z. C., Huang, F. Z., Xu, H. B., Sun, J. C., & Wang, C. F. (2019). MicroRNA-137 inhibits autophagy and chemosensitizes pancreatic cancer cells by targeting ATG5. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 111, 63–71.
Huang, J., Pan, W., Ou, D., Dai, W., Lin, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2015). LC3B, a protein that serves as an autophagic marker, modulates angiotensin II-induced myocardial hypertrophy. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 66(6), 576–583.
Agrotis, A., Pengo, N., Burden, J. J., & Ketteler, R. (2019). Redundancy of human ATG4 protease isoforms in autophagy and LC3/GABARAP processing revealed in cells. Autophagy, 15(6), 976–997.
Xiao, J., Zhu, X., He, B., Zhang, Y., Kang, B., Wang, Z., et al. (2011). MiR-204 regulates cardiomyocyte autophagy induced by ischemia-reperfusion through LC3-II. Journal of Biomedical Science, 18, 35.
Islam, M. A., Sooro, M. A. & Zhang, P. (2018). Autophagic regulation of p62 is critical for cancer therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5),
McAlindon, E., Bucciarelli-Ducci, C., Suleiman, M. S., & Baumbach, A. (2015). Infarct size reduction in acute myocardial infarction. Heart, 101(2), 155–160.
Tang, Y., Zhong, Z., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., & Chang, Z. (2019). MicroRNA-497 inhibition mitigates myocardial infarction via enhancing wingless/integrated signal pathway in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120(8), 13403–13412.
Acknowledgments
We would like to offer our sincere appreciation to the reviewers for their critical comments on this article.
Availability of Data and Materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yufu Wu and Qing Mao designed the study. Xiulin Liang collated the data. Yufu Wu, Qing Mao, and Xiulin Liang contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Statement
The protocol of animal experiments was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanjing Lishui People’s Hospital, Zhongda Hospital Lishui Branch, Southeast University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Associate Editor Joost Sluijter oversaw the review of this article
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Mao, Q. & Liang, X. Targeting the MicroRNA-490-3p-ATG4B-Autophagy Axis Relieves Myocardial Injury in Ischemia Reperfusion. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 14, 173–183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-020-09972-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-020-09972-9