Abstract
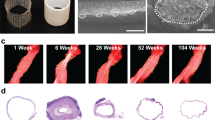
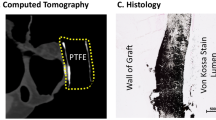
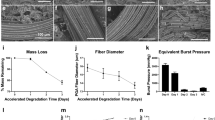
Patients who undergo implantation of a tissue-engineered vascular graft (TEVG) for congenital cardiac anomalies are monitored with echocardiography, followed by magnetic resonance imaging or angiography when indicated. While these methods provide data regarding the lumen, minimal information regarding neotissue formation is obtained. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) has previously been used in a variety of conditions to evaluate the vessel wall. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the utility of IVUS for evaluation of TEVGs in our ovine model. Eight sheep underwent implantation of TEVGs either unseeded or seeded with bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells. Angiography, IVUS, and histology were directly compared. Endothelium, tunica media, and graft were identifiable on IVUS and histology at multiple time points. There was strong agreement between IVUS and angiography for evaluation of luminal diameter. IVUS offers a valuable tool to evaluate the changes within TEVGs, and clinical translation of this application is warranted.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- °C:
-
Degrees Celsius
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha smooth muscle actin
- CaVC:
-
Caudal vena cava
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- IF:
-
Immunofluorescence
- IVUS:
-
Intravascular ultrasound
- GMP:
-
Good Manufacturing Practice
- kg:
-
Kilogram
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- mg:
-
Milligram
- mm:
-
Millimeter
- μm:
-
Micrometer
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- PCLA:
-
Polycaprolactone and polylactic acid
- PGA:
-
Polyglycolic acid
- TEVG:
-
Tissue-engineered vascular graft
- vWF:
-
von Willebrand factor
References
Hoffman, J. I., & Kaplan, S. (2002). The incidence of congenital heart disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 39(12), 1890–1900.
Simeone, R. M., Oster, M. E., Cassell, C. H., Armour, B. S., Gray, D. T., & Honein, M. A. (2014). Pediatric inpatient hospital resource use for congenital heart defects. Birth Defects Research. Part A, Clinical and Molecular Teratology, 100(12), 934–943. doi:10.1002/bdra.23262.
Russo, C. A, Elixhauser, A. (2006). Hospitalizations for Birth Defects, 2004: Statistical Brief #24. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Rockville (MD).
Shin’oka, T., Matsumura, G., Hibino, N., Naito, Y., Watanabe, M., Konuma, T., Sakamoto, T., Nagatsu, M., & Kurosawa, H. (2005). Midterm clinical result of tissue-engineered vascular autografts seeded with autologous bone marrow cells. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 129(6), 1330–1338. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2004.12.047.
Hibino, N., McGillicuddy, E., Matsumura, G., Ichihara, Y., Naito, Y., Breuer, C., & Shinoka, T. (2010). Late-term results of tissue-engineered vascular grafts in humans. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 139(2), 431–436. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.09.057. 436 e431-432.
Pedra, C. A. C., Fleishman, C., Pedra, S. F., & Cheatham, J. P. (2011). New imaging modalities in the catheterization laboratory. Current Opinion in Cardiology, 26(2), 86–93. doi:10.1097/HCO.0b013e3283437fb4.
Diethrich, E. B., Irshad, K., & Reid, D. B. (2006). Virtual histology and color flow intravascular ultrasound in peripheral interventions. Seminars in Vascular Surgery, 19(3), 155–162. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2006.06.001.
Lee, J. T., Fang, T. D., & White, R. A. (2006). Applications of intravascular ultrasound in the treatment of peripheral occlusive disease. Seminars in Vascular Surgery, 19(3), 139–144. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2006.06.004.
Pearce, B. J., & Jordan, W. D., Jr. (2009). Using IVUS during EVAR and TEVAR: improving patient outcomes. Seminars in Vascular Surgery, 22(3), 172–180. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2009.07.009.
Wallace, G. A., Starnes, B. W., Hatsukami, T. S., Sobel, M., Singh, N., & Tran, N. T. (2015). Intravascular ultrasound is a critical tool for accurate endograft sizing in the management of blunt thoracic aortic injury. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 61(3), 630–635. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.10.014.
Marrocco, C. J., Jaber, R., White, R. A., Walot, I., DeVirgilio, C., Donayre, C. E., & Kopchok, G. (2012). Intravascular ultrasound. Seminars in Vascular Surgery, 25(3), 144–152. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2012.07.006.
Park, S. J., Kang, S. J., Virmani, R., Nakano, M., & Ueda, Y. (2012). In-stent neoatherosclerosis: a final common pathway of late stent failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 59(23), 2051–2057. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.10.909.
Gogas, B. D., Farooq, V., Serruys, P. W., & Garcia-Garcia, H. M. (2011). Assessment of coronary atherosclerosis by IVUS and IVUS-based imaging modalities: progression and regression studies, tissue composition and beyond. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 27(2), 225–237. doi:10.1007/s10554-010-9791-0.
Nasu, K., Tsuchikane, E., Katoh, O., Vince, D. G., Margolis, P. M., Virmani, R., Surmely, J. F., Ehara, M., Kinoshita, Y., Fujita, H., Kimura, M., Asakura, K., Asakura, Y., Matsubara, T., Terashima, M., & Suzuki, T. (2008). Impact of intramural thrombus in coronary arteries on the accuracy of tissue characterization by in vivo intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. American Journal of Cardiology, 101(8), 1079–1083. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.064.
Nair, A., Margolis, M. P., Kuban, B. D., & Vince, D. G. (2007). Automated coronary plaque characterisation with intravascular ultrasound backscatter: ex vivo validation. EuroIntervention, 3(1), 113–120.
Nair, A., Kuban, B. D., Tuzcu, E. M., Schoenhagen, P., Nissen, S. E., & Vince, D. G. (2002). Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation, 106(17), 2200–2206.
Garcia-Garcia, H. M., Gogas, B. D., Serruys, P. W., & Bruining, N. (2011). IVUS-based imaging modalities for tissue characterization: similarities and differences. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 27(2), 215–224. doi:10.1007/s10554-010-9789-7.
Madssen, E., Moholdt, T., Videm, V., Wisloff, U., Hegbom, K., & Wiseth, R. (2014). Coronary atheroma regression and plaque characteristics assessed by grayscale and radiofrequency intravascular ultrasound after aerobic exercise. The American Journal of Cardiology, 114(10), 1504–1511. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.08.012.
Virmani, R., Kolodgie, F. D., Burke, A. P., Farb, A., & Schwartz, S. M. (2000). Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 20(5), 1262–1275.
Stone, G. W., Maehara, A., Lansky, A. J., de Bruyne, B., Cristea, E., Mintz, G. S., Mehran, R., McPherson, J., Farhat, N., Marso, S. P., Parise, H., Templin, B., White, R., Zhang, Z., Serruys, P. W., & Investigators, P. (2011). A prospective natural-history study of coronary atherosclerosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 364(3), 226–235. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1002358.
Fatakdawala, H., Gorpas, D., Bishop, J. W., Bec, J., Ma, D., Southard, J. A., Margulies, K. B., & Marcu, L. (2015). Fluorescence lifetime imaging combined with conventional intravascular ultrasound for enhanced assessment of atherosclerotic plaques: an ex vivo study in human coronary arteries. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 8(4), 253–263. doi:10.1007/s12265-015-9627-3.
Ishii, M., Kato, H., Kawano, T., Akagi, T., Maeno, Y., Sugimura, T., Hashino, K., & Takagishi, T. (1995). Evaluation of pulmonary artery histopathologic findings in congenital heart disease: an in vitro study using intravascular ultrasound imaging. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 26(1), 272–276.
Xu, J., Shiota, T., Omoto, R., Zhou, X., Kyo, S., Ishii, M., Rice, M. J., & Sahn, D. J. (1997). Intravascular ultrasound assessment of regional aortic wall stiffness, distensibility, and compliance in patients with coarctation of the aorta. American Heart Journal, 134(1), 93–98.
Day, R. W., & Tani, L. Y. (1997). Pulmonary intravascular ultrasound in infants and children with congenital heart disease. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Diagnosis, 41(4), 395–398.
Berger, R. M., Cromme-Dijkhuis, A. H., Hop, W. C., Kruit, M. N., & Hess, J. (2002). Pulmonary arterial wall distensibility assessed by intravascular ultrasound in children with congenital heart disease: an indicator for pulmonary vascular disease? Chest, 122(2), 549–557.
Veeram Reddy, S. R., Welch, T. R., Wang, J., Richardson, J. A., Forbess, J. M., Riegel, M., & Nugent, A. W. (2015). A novel design biodegradable stent for use in congenital heart disease: mid-term results in rabbit descending aorta. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 85(4), 629–639. doi:10.1002/ccd.25648.
Hibino, N., Nalbandian, A., Devine, L., Martinez, R. S., McGillicuddy, E., Yi, T., Karandish, S., Ortolano, G. A., Shin’oka, T., Snyder, E., & Breuer, C. K. (2011). Comparison of human bone marrow mononuclear cell isolation methods for creating tissue-engineered vascular grafts: novel filter system versus traditional density centrifugation method. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods, 17(10), 993–998. doi:10.1089/ten.TEC.2011.0110.
Hibino, N., Yi, T., Duncan, D. R., Rathore, A., Dean, E., Naito, Y., Dardik, A., Kyriakides, T., Madri, J., Pober, J. S., Shinoka, T., & Breuer, C. K. (2011). A critical role for macrophages in neovessel formation and the development of stenosis in tissue-engineered vascular grafts. FASEB Journal, 25(12), 4253–4263. doi:10.1096/fj.11-186585.
Khosravi, R., Miller, K. S., Best, C. A., Shih, Y. C., Lee, Y. U., Yi, T., Shinoka, T., Breuer, C. K., & Humphrey, J. D. (2015). Biomechanical diversity despite mechanobiological stability in tissue engineered vascular grafts 2 years post-implantation. Tissue Engineering Part A, 21(9–10), 1529–1538. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2014.0524.
van Ditzhuijzen, N. S., van den Heuvel, M., Sorop, O., van Duin, R. W., Krabbendam-Peters, I., van Haeren, R., Ligthart, J. M., Witberg, K. T., Duncker, D. J., Regar, E., van Beusekom, H. M., & van der Giessen, W. J. (2011). Invasive coronary imaging in animal models of atherosclerosis. Netherlands Heart Journal, 19(10), 442–446. doi:10.1007/s12471-011-0187-0.
Acknowledgements
The Comparative Mouse Phenotyping and Pathology Shared Resource, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, and the Comprehensive Cancer Center at the Ohio State University performed tissue embedding, sectioning, and H&E staining. The Morphology Core at Nationwide Children’s Hospital performed Masson’s Trichrome staining. Assistance with biostatistical analysis was provided by Yongjie Miao of the Biostatistics Core from the Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital. We would like to acknowledge the contributions of our animal care staff, veterinary staff, and interventional cardiology team, without whom the work performed would not be possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Sources of Funding
Funding for this study was provided by NIH R01 HL128847 as well as internal sources from Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, OH to C.K.B. and T.S. The work presented was also supported by T32 OD010429-13 to ESC and T32AI106704 to EAO. The Comparative Mouse Phenotyping and Pathology Shared Resource is supported in part by grant P30 CA016058.
Disclosures
Support for graft production for this study was provided by Gunze Limited. Christopher Breuer, MD is also on the scientific advisory board for Cook Biomedical and is the founder of Lyst Therapeutics. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest.
Human Subjects/Animal Subjects Statement
No human studies were carried out by the authors for this article. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed and approved by the appropriate institutional committees.
Additional information
Associate Editor Adrian Chester oversaw the review of this article
Victoria K. Pepper and Elizabeth S. Clark are shared first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pepper, V.K., Clark, E.S., Best, C.A. et al. Intravascular Ultrasound Characterization of a Tissue-Engineered Vascular Graft in an Ovine Model. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 10, 128–138 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-016-9725-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-016-9725-x