Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether the kainate (KA) receptor subunit GluR6 is involved in the acute inflammatory pain.
Methods
Formalin was injected into the mucosa of rectum in Sprague-Dawley rats to induce visceral pain. The antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) of GluR6 were injected once per day for 3 d before formalin injection, after which GluR6 protein level was examined by immunoblotting method. The change of visceral pain was also investigated.
Results
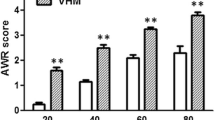
The expression of GluR6 in the spinal cord of rats increased after the formalin injection. Moreover, pre-treatment of GluR6 antisense ODNs could suppress GluR6 expression in the spinal cord of rats and decrease the scores of visceral pain at 45 min following formalin injection.
Conclusion
Kainate receptor subunit GluR6 plays an important role in the visceral pain induced by injection of formalin into the wall of rectum. GluR6 may serve as a potential target for the treatment of acute inflammatory visceral pain.
摘要
目的
探讨海藻氨酸受体亚单位GluR6在急性内脏炎性痛中的作用。
方法
在SD大鼠直肠粘膜下注射福尔马林建立内脏痛模型。 鞘内注射GluR6 反义寡核苷酸, 通过行为学评分观察注射后大鼠疼痛行为学的变化, 并用免疫印迹法检测GluR6蛋白的表达变化。
结果
直肠内注射福尔马林后大鼠脊髓GluR6表达升高。 鞘内注射GluR6反义寡核苷酸后, 在福尔马林注射后45min时, GluR6蛋白表达降低, 大鼠疼痛行为学评分显著降低。
结论
GluR6在福尔马林致大鼠直肠炎性痛中可能起重要作用, 这为临床治疗内脏痛提供了新思路。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Procacci P, Zoppi M, Maresca M. Clinical approach to visceral sensation. Brain Res 1986, 67: 21–28.
Cervero F, Laird J MA. Visceral pain. Lancet 1999, 353: 2145–2148.
Lerma J. Kainate receptor physiology. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2006, 6: 89–97.
Seeburg PH. The molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Neurosci 1993, 16: 359–365.
Hollmann M, Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 1994, 17: 31–108.
Pei DS, Guan QH, Sun YF, Zhang QX, Xu TL, Zhang GY. Neuroprotective effects of GluR6 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides on transient brain ischemia/reperfusion-induced neuronal death in rat hippocampal CA1 region. J Neurosci Res 2005, 82: 642–649.
Wu HW, Li HF, Guo J. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediate diphosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases through Src family tyrosine kinasesand Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in rat hippocampus after cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Bull 2007, 23: 107–112.
Lu Y, Sun YN, Wu X, Sun Q, Liu FY, Xing GG, et al. Role of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate(AMPA) receptor subunit GluR1 in spinal dorsal horn in inflammatory nociception and neuropathic nociception in rat. Brain Res 2008, 1200: 19–26.
Nakanishi S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science 1992, 58: 597–603.
Lu CR, Willcockson HH, Phend KD, Lucifora S, Darstein M, Valtschanoff JG, et al. Ionotropic glutamate receptors are ex pressed in GABAergic terminals in the rat superficial dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol 2005, 486: 169–178.
Carlton SM, Coggeshall RE. Inflammation-induced changes in peripheral glutamate receptor populations. Brain Res 1999, 20: 63–70.
Youn DH, Randic M. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the spinal substantia gelatinosa of mice deficient in the kainate receptor GluR5 and/or GluR6 subunit. J Physiol 2004, 553: 683–698.
Guo W, Zou S, Tal M, Ren K. Activation of spinal kainate receptors after inflammation:behavioral hyperalgesia and subunit gene expression. Eur J Pharmacol 2002, 452: 309–318.
Cao JL, He JH, Ding HL, Zeng YM. Activation of the spinal ERK signaling pathway contributes naloxone-precipitated withdrawal in morphine-dependent rats. Pain 2005, 118: 336–349.
Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav 1976, 7: 1032–1036.
Miampamba M, Chéry-Croze S, Gorry F, Berger F, Chayvialle JA. Inflammation of the colonic wall induced by formalin as a model of acute visceral pain. Pain 1994, 57: 327–334.
Laird JMA, Souslova V, Wood JN, Cervero F. Deficits in visceral pain and referred hyperalgesia in Nav1.8 (SNS/PN3)-null mice. J Neurosci 2002, 22: 8352–8356.
Wu LJ, Ko SW, Zhuo M. Kainate receptors and pain: from dorsal root ganglion to the anterior cingulate cortex. Curr Pharm Des 2007, 13: 1597–1605.
Lu CR, Willcockson HH, Phend KD, Lucifora S, Darstein M, Valtschanoff JG, et al. Ionotropic glutamate receptors are expressed in GABAergic terminals in the rat superficial dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol 2005, 486: 169–178.
Li P, Wilding TJ, Kim SJ, Calejesan AA, Huettner JE, Zhuo M. Kainate-receptor-mediated sensory synaptic transmission in mammalian spinal cord. Nature 1999, 397: 161–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, WG., Zhang, LC., Peng, ZD. et al. Intrathecal injection of GluR6 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides alleviates acute inflammatory pain of rectum in rats. Neurosci. Bull. 25, 319–323 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-0326-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-0326-4