Abstract
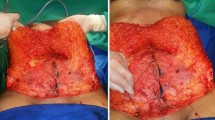
Abdominoplasties are among the most widely requested surgical procedures, and, since the umbilicus is an important component of abdominal harmony, achieving an esthetic and natural umbilicus is one of the primary goals of the operation. The aim of this study is to present the results of a neo-umbilicus recreation to provide a deeper and desirable appearance, and also its simplifying effect for a laparoscopic hernia repair when needed. This is a single-center case-series scientific study which is presenting a total of 26 female patients who underwent classical abdominoplasty and neo-umbilicus recreation surgery with modified concomitant defatting suture and fat injection technique. Of the 26 cases, two patients (7.7%) developed seroma, whereas one patient had hypertrophic scar tissue. We did not observe any major complications, and none of the patients required revision or resuturing. Eight of the cases (30.8%) with multiparous pregnancies underwent a laparoscopic umbilical hernia repair. The patients regained their abdominal cutaneous sensitivity at the postoperative 8 ± 6 months. The neo-umbilici were free of visible scars in all individuals, none of the patients had a postoperative malposition, and all patients reported high satisfaction rates. The average follow-up was 18 months, ranging from 9–26 months. The technique described here provides efficient and satisfactory esthetic results that are acknowledged by the patients in the short and long term. The technique is also safe for concomitant hernia repair.
Level of Evidence III.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Raw data for the dataset presented herein are not publicly available to preserve individuals’ privacy under the European General Data Protection Regulation. However, will be presented as per the editor request.
References
da Silva Júnior VV, de Sousa FRS (2017) Improvement on the neo-umbilicoplasty technique and review of the literature. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41(3):600–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0847-6
Mendes FH, Donnabella A, Fagotti Moreira AR (2019) Fleur-de-lis abdominoplasty and neo-umbilicus. Clin Plast Surg 46(1):49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2018.08.007
Aherrera AS, Pincus DJ, Vernadakis AJ, Pandya SN (2015) Evaluation of abdominal cutaneous sensibility following abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 135(3):526e–532e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000000969
Sisti A, Huayllani MT, Boczar D, Restrepo DJ, Cinotto G, Lu X, Cuomo R, Grimaldi L, Nisi G, Forte AJ (2021) Umbilical reconstruction techniques: a literature review. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(3):1078–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01989-4
Joseph WJ, Sinno S, Brownstone ND, Mirrer J, Thanik VD (2016) Creating the perfect umbilicus: a systematic review of recent literature. Aesthetic Plast Surg 40(3):372–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0633-x
Pallua N, Markowicz MP, Grosse F, Walter S (2010) Aesthetically pleasant umbilicoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 64(6):722–725. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181ba5770
Visconti G, Visconti E, Bonomo L, Salgarello M (2015) Concepts in navel aesthetic: a comprehensive surface anatomy analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 39(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0434-z
Tobler WD, Nicholas KN, Cruz C (2019) Spare parts neoumbilicoplasty. Arch Plast Surg 46(4):371–374. https://doi.org/10.5999/aps.2018.00794
Dubou R, Ousterhout DK (1978) Placement of the umbilicus in an abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 61:291–293
Yu D, Novicoff WM, Gampper TJ (2016) The average size and position of the umbilicus in young men and women. Ann Plast Surg 76(3):346–348. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000000478
Abhyankar SV, Rajguru AG, Patil PA (2006) Anatomical localization of the umbilicus: an Indian study. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1153–1157
Rohrich RJ, Sorokin ES, Brown SA et al (2003) Is the umbilicus truly midline? Clinical and medicolegal implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:259–263
Lee SJ, Garg S, Lee HP (2014) Computer-aided analysis of the “beautiful” umbilicus. Aesthet Surg J 34(5):748–756. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X14533565
Bilgen F, Duman Y, Ural A et al (2020) Determining anatomical position of the umbilicus in Turkish population. Indian J Surg 82:899–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02239-2
Wan D, Hubbard BA, Byrd HS (2019) Achieving aesthetic results in the umbilical float mini-abdominoplasty: patient selection and surgical technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 143(3):722–732. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005387
Shipkov HD, Mojallal A, Braye F (2017) Simultaneous abdominoplasty and umbilical hernia repair via laparoscopy: a preliminary report. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 59(2):222–227. https://doi.org/10.1515/folmed-2017-0026
McKnight CL, Fowler JL, Cobb WS et al (2012) Concomitant sublay mesh repair of umbilical hernia and abdominoplasty Concomitant sublay mesh repair of umbilical hernia and abdominoplasty. Can J Plast Surg 20(4):258–60
Tremp M, Wang W, Oranges CM, Schaefer DJ, Wang W, Kalbermatten DF (2017) Evaluation of the neo-umbilicus cutaneous sensitivity following abdominoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41(6):1382–1388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0951-7
Novais CS, Carvalho J, Valença-Filipe R, Rebelo M, Peres H, Costa-Ferreira A (2020) Abdominoplasty with Scarpa fascia preservation: randomized controlled trial with assessment of scar quality and cutaneous sensibility. Plast Reconstr Surg 146(2):156e–164e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000007024
Rangaswamy M (2008) Lipoabdominoplasty: a versatile and safe technique for abdominal contouring. Indian J Plast Surg 41(Suppl):S48-55
Alvarez E, Alvarez D, Caldeira A (2021) Non-scarring minimal ıncision neo-omphaloplasty in abdominoplasty: the Alvarez technique.A new proposal. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 9(11):e3956. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000003956
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, all the patients had signed the informed consent.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MOV 37294 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MOV 66267 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MOV 21353 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kandulu, H. Creating a Neo-umbilicus in Abdominoplasty. Indian J Surg 85, 1434–1440 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-023-03876-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-023-03876-z