Abstract
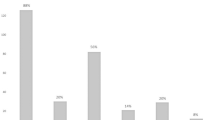
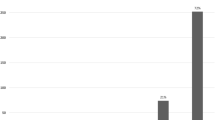
Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (LNF) is considered the surgical treatment of choice for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, persistent dysphagia (PD) occurs in up to 20% of patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the incidence of PD after LNF, the causes, and the methods of prevention and management. This study was a retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data. From April 1994 to November 2019, 868 patients underwent laparoscopic short-floppy Nissen fundoplication (LSFNF). A postoperative dysphagia score was obtained by using the “difficulty swallowing” question from the GERD-Health Related Quality of Life. The postoperative clinical outcomes were obtained from 822 to 868 patients (94.7%) after LSFNF. The mean follow-up period was 17.3 years (range 1–26). Only 12 patients (1.4%) with PD were treated. Seven patients (0.8%) required endoscopic dilatation. Too tight fundoplication was the most frequent cause of dysphagia. Dysphagia was resolved completely in all patients. Five patients (0.6%) required reoperation for prolonged dysphagia (three for a tight wrap and two for a tight esophageal hiatus) after failed dilatation attempts. All underwent laparoscopic conversion from Nissen procedure to Toupet with enlargement of hiatal opening in two. Dysphagia was resolved completely in all patients. Postoperative esophageal manometry was performed in all patients with PD. Pre- and postoperative manometric data were not significantly different between patients with moderate-severe PD, mild PD, and without dysphagia. PD is a common complication after LNF. The most frequent cause is too tight fundoplication. The LSFNF could prevent postoperative dysphagia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schietroma M, De Vita F, Carlei F, Leardi S, Pessia B, Sista F et al (2013) Laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication: 11-year follow-up. Surg Laparosc Endosc Tech 23:281–285
Schietroma M, Colozzi S, Romano L, Pessia B, Giuliani A, Vicentini V et al (2020) Short- and long-term results after laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication in elderly versus non-elderly patients. J Min Access Surg 16:256–263
El-Serag HB, Sonnenberg A (1999) Outcome of erosive reflux esophagitis after Nissen fundoplication. Am J Gastroenterol 94:1771–1776
Wills VL, Hunt DR (2001) Dysphagia after antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 88:486–499
Anvari M, Allen C (1998) Esophageal and lower esophageal sphincter pressure profiles 6 abd 24 month after laparoscopic fundoplication and their association with postoperative dysphagia. Surg Endosc 12:421–426
Schietroma M, Piccione F, Clementi M, Cecilia EM, Sista F, Pessia B, Carlei F, Guadagni S, Amicucci G (2017) Short- and long-term, 11-22 years, results after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in obese versus nonobese patients. J Obes 2017:7589408. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7589408
Dunnigton GL, DeMeester TR (1993) Outcome effect of adherence to operative principles of Nissen fundoplication by multiple surgeons. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Study Group. Am J Surg 166:654–7
Dalenback J, Lonroth H, Blomqvist A, Lundell L (1999) Improved functional outcome after laparoscopic fundoplication by complete gastric fundus mobilization. Gastroenterology 114:A1384
Wetscher GJ, Glaser K, Wieschemeyer T, Gadenstatter M (1997) Tailored antireflux surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease: effectiveness and risk of postoperative dysphagia. World J Surg 21:605–610
Granderath FA, Schweiger UM, Kamolz T, Pointner R (2005) Dysphagia after laparoscopic antireflux surgery: a problem of hiatal closure more than a problem of the wrap. Surg Endosc 19:1439–1446
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, Tapia FV, Harkabus MA (1996) Quality of life scale for gastroesphageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 183:217–224
Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gjawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJP et al (2015) The Chicago classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. International high resolution manometry working group. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27:160–74
Schietroma M, Giuliani M, Zoccali G, Carlei F, Bianchi Z, Amicucci G et al (2010) How does dexamethasone influence surgical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication? A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Updat Surg 62(1):47–54
Schietroma M, Carlei F, Cecilia EM, Piccione F, Sista F, De Vita F et al (2013) A Prospective randomized study of systemic inflammation and immune response after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication performed with standard and low-pressure pneumoperitoneum. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 23:189
Schietroma M, Colozzi S, Pessia B, Carlei F, Di Furia M, Amicucci G (2018) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: the effects of high-concentration supplemental perioperative oxygen on the inflammatory and immune response: a randomised controlled trial. J Minim Access Surg 14(3):221–229. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmas.JMAS_120_16
Bais JE, Bartelsman JF, Bonjer HJ, Cuesta MA, Go PM, Klinkenberg-Knol EC et al (2000) Laparoscopic or conventional Nissen fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: randomized clinical trial. Lancet 355:170–174
Laine S, Rantala A, Gullichsen R, Ovaska J (1997) Laparoscopic vs conventional Nissen fundoplication. A prospective randomized study. Surg Endosc 11:441–444
Ackroyd R, Watson DI, Majeed AW, Troy G, Treacy PJ, Stoddard CJ (2004) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic versus open fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 91:975–982
Richter JE (2013) Gastroesophageal reflux disease treatment: side effects and complications of fundoplication. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(5):465–471
Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Attwood S, Ell C, Fiocca R, Eklund S et al (2011) Laproscopic antireflux surgery vs esomeprazole treatment for chronic GERD: the LOTUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA 305(19):1969–1977
Hunter JG, Smith CD, Branum GD, Waring JP, Trus TL, Cornwall M et al (1999) Laparoscopic fundoplication failures: patterns of failure and response to fundoplication revision. Ann Surg 230:595–604
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Schweiger UM, Pasiut M, Haas CF, Wykypiel H Jr et al (2002) Is laparoscopic refundoplication feasible in patients with failed primary open antireflux surgery? Surg Endosc 16:381–385
Watson DI, Pike GK, Baigrie RJ, Mathew G, Devitt PG, Britten - Jones R et al (1997) Prospective double-blind randomized trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with division and without division of short gastric vessels. Ann Surg 226:642–52
Granderath FA, Schweiger UM, Kamolz Pasiut TM, Haas CF, Pointner R (2002) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery with routine mesh hiatoplasty in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg 6:347–353
Sato K, Awad ZT, Filipi CJ, Selima MA, Cummings JE, Fenton SJ et al (2002) Causes of long-term dysphagia after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. JSLS 6:35–40
De Meester TR, Stein HJ (1992) Minimizing the side effects of antireflux surgery. World J Surgery 16:335–336
Fibbe C, Layer P, Keller J, Strate U, Emmermann A, Zornig C (2001) Esophageal motility in reflux disease before and after fundoplication: a prospective, randomized, clinical, and manometric study. Gastroenterology 121:5–14
Gaudric M, Sabate JM, Artru P, Chaussade S, Couturier D (1999) Results of pneumatic dilatation in patients with dysphagia after antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 86:1088–1091
Skinner DB (1992) Surgical management after failed antireflux operations. World J Surg 16:359–363
Hunter JG, Smith CD, Branum GD, Waring JP, Trus TL, Cornwell M et al (1999) Laparoscopic fundoplication failures: patterns of failure and response to fundoplication revision. Ann Surg 230:595–606
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schietroma, M., Romano, L., Tomarelli, C. et al. Dysphagia After Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication: Incidence, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment. Indian J Surg 84, 792–798 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-021-02973-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-021-02973-1