Abstract
Background and Methods
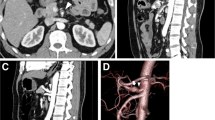
Median arcuate ligament syndrome (MALS) is caused by extrinsic compression of the celiac artery. It is characterized clinically by postprandial abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss, mimicking chronic mesenteric ischemia. Patients often undergo exhaustive but unremarkable diagnostic workup. Diagnosis is based on a combination of Doppler or angiographic studies of the celiac artery and clinical presentation. We report our 11-year experience (2008–19) of laparoscopic treatment of MALS. The objectives of this study were to review our technical experience and describe the long-term surgical outcomes.
Results
Out of 17 patients treated for MALS, 14 were female and with a median age of 36 years. All of them presented with abdominal pain. The length of symptoms on presentation was 10 months. Duplex ultrasonography indicated celiac trunk stenosis in each case, with an elevated peak velocity flow in the celiac trunk of 431 (± 80) cm/s. All underwent successful laparoscopic treatment with only one conversion to open. The operating time was 117 min (70–122) and intraoperative blood loss was < 50 ml in all but one converted to open. Length of stay was 3 to 6 days, with no postoperative complications or mortality. Median follow-up was 109.5 months (78–113.5). At this point, all patients remained symptom-free with only one patient who complained of occasional pain, not requiring any analgesics.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic management of MALS is a safe and effective approach to achieve long-term improvement of symptoms after surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipshutz B (1917) A composite study of the coeliac axis artery. Ann Surg 65(2):159–169
Harjola PT (1963) A rare obstruction of the coeliac artery. Report of a case. Ann Chir Gynaecol Fenn 52:547–555
Dunbar JD, Molnar W, Beman FF, Marable SA (1965) Compression of the celiac trunk and abdominal angina: preliminary report of 15 cases. Am J Roentgenol 95(3):731–744
Kim EN, Lamb K, Relles D, Moudgill N, DiMuzio PJ, Eisenberg JA (2016) Median arcuate ligament syndrome—review of this rare disease. JAMA surgery 151(5):471–477
Ramakrishnan P, Deuri B, Keerthi MSS, Naidu SB, Subbaiah R, Raj P, Palanisamy S, Chinnusamy P (2016) Laparoscopic division of median arcuate ligament for the celiac axis compression syndrome—two case reports with review of literature. Indian Journal of Surgery 78(2):163–165
Park CM, Chung JW, Kim HB, Shin SJ, Park JH (2001) Celiac axis stenosis: incidence and etiologies in asymptomatic individuals. Korean J Radiol 2(1):8–13
Sultan S, Hynes N, Elsafty N, Tawfick W (2013) Eight years experience in the management of median arcuate ligament syndrome by decompression, celiac ganglion sympathectomy, and selective revascularization. Vasc Endovasc Surg 47(8):614–619
San Norberto EM, Romero A, Fidalgo-Domingos LA, García-Saiz I, Taylor J, Vaquero C (2019) Laparoscopic treatment of median arcuate ligament syndrome: a systematic review. International angiology: a journal of the International Union of Angiology 38(6):474–483
Szilagyi DE, Rian RL, Elliott JP, Smith RF (1972) The celiac artery compression syndrome: does it exist? Surgery 72(6):849–863
Bech FR (1997) Celiac artery compression syndromes. Surg Clin N Am 77(2):409–424
Loukas M, Pinyard J, Vaid S, Kinsella C, Tariq A, Tubbs RS (2007) Clinical anatomy of celiac artery compression syndrome: a review. Clinical Anatomy: The Official Journal of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists and the British Association of Clinical Anatomists 20(6):612–617
Duffy AJ, Panait L, Eisenberg D, Bell RL, Roberts KE, Sumpio B (2009) Management of median arcuate ligament syndrome: a new paradigm. Ann Vasc Surg 23(6):778–784
Reuter SR, Bernstein EF (1973) The anatomic basis for respiratory variation in median arcuate ligament compression of the celiac artery. Surgery 73(3):381–385
Brandt LJ, Boley SJ (1978) Celiac axis compression syndrome. Am J Dig Dis 23(7):633–640
Cusati DA, Noel AA, Gloviczki P, et al. (2006). Median arcuate ligament syndrome: a 20-year experience of surgical treatment. Presented at: 60th annual meeting of the Society for Vascular Surgery; Philadelphia, PA
Gloviczki P, Duncan AA (2007) Treatment of celiac artery compression syndrome: does it really exist? Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther 19(3):259–263
Ozel A, Toksoy G, Ozdogan O, Mahmutoglu AS, Karpat Z (2012) Ultrasonographic diagnosis of median arcuate ligament syndrome: a report of two cases. Medical ultrasonography 14(2):154–157
Reilly LM, Ammar AD, Stoney RJ, Ehrenfeld WK (1985) Late results following operative repair for celiac artery compression syndrome. J Vasc Surg 2(1):79–91
Takach TJ, Livesay JJ, Reul JG, Cooley DA (1996) Celiac compression syndrome: tailored therapy based on intraoperative findings. J Am Coll Surg 183(6):606–610
Delis KT, Gloviczki P, Altuwaijri M, McKusick MA (2007) Median arcuate ligament syndrome: open celiac artery reconstruction and ligament division after endovascular failure. J Vasc Surg 46(4):799–802
Grotemeyer D, Duran M, Iskandar F, Blondin D, Nguyen K, Sandmann W (2009) Median arcuate ligament syndrome: vascular surgical therapy and follow-up of 18 patients. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 394(6):1085–1092
Roseborough GS (2009) Laparoscopic management of celiac artery compression syndrome. J Vasc Surg 50(1):124–133
Wang X, Impeduglia T, Dubin Z, Dardik H (2008) Celiac revascularization as a requisite for treating the median arcuate ligament syndrome. Ann Vasc Surg 22(4):571–574
Guttman OT, Rosenblatt MA, Mims T (2008) Median arcuate ligament syndrome—a novel treatment using an intrathecal morphine pump to relieve intractable visceral pain. Pain Practice 8(2):133–137
Salem D, Delibasic M (2017) Endovascular approach to treat median Arcuate ligament compressing syndrome. Vascular Disease Management 14(2):E37–E45
Garriboli, L., Miccoli, T., Damoli, I., Rossini, R., Sartori, C. A., Ruffo, G., & Jannello, A. M. (2020). Hybrid laparoscopic and endovascular treatment for median Arcuate ligament syndrome: case report and review of literature. Annals of Vascular Surgery 63:457.e7-457.e11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Institutional ethics committee approval was obtained prior to data collection.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rege, S.A., Singh, A. & Dalvi, A.N. Chronic Non-specific Upper Abdominal Pain of Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome: Laparoscopic Treatment. Indian J Surg 83, 237–243 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02355-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02355-z