Abstract
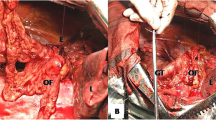
Bronchopleural fistula (BPF) is still a detrimental problem for thoracic surgeons that cause undesirable results in patients. The aim of this study is to evaluate the results of omentum transposition into the thoracic cavity which is used to treat the patients with BPF and empyema Between April 2008 and May 2018, 29 patients with postoperative BPF, two patients with empyema and one patient with tracheal rupture were treated by omentum transposition into the thoracic cavity to reinforce the bronchial stump and to obliterate the pleural space. Each procedure was performed using both thoracotomy and laparotomy, and the omentum was mobilized to the thoracic cavity by a transabdominal approach. The data of the patients’ were analyzed retrospectively. Total length of hospital stay was statistically higher in females (59 days) compared with males (38 days) (p = 0.04) and statistically lower in patients with lung cancer (34 days) compared with patients with benign diseases (57 days) (p = 0.016). There was a positive correlation between the age of patients, chest tube removal time, and the duration of hospital stay after omentopexy (r = 0.53, p = 0.002, r = 0.53, p = 0.01, respectively). The success rate was found to be 72% (n = 23) in the patients who underwent primary repair with omentopexy. Only 5 patients were discharged with a Heimlich valve. There was no complication associated with the omentum transposition except minimal temporary dyspeptic symptoms. Omentum transposition seems to be an invasive intervention for these patients. However, this research’s results reveal that BPF and empyema can be treated safely by omentum transposition.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greason KL et al (2003) Management of the irradiated bronchus after lobectomy for lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 76(1):180–185 discussion 185-6
Dziedzic D, Orlowski TM, Jakimiuk R (2000) Experimental study of the effects of different stapling devices in healing of the mechanically sutured bronchial stump. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 17(2):111–116
Salci H, Bayram AS, Ozyigit O, Gebitekin C, Gorgul OS (2007) Comparison of different bronchial closure techniques following pneumonectomy in dogs. J Vet Sci 8(4):393–399
Algar FJ, Alvarez A, Aranda JL, Salvatierra A, Baamonde C, López-Pujol FJ (2001) Prediction of early bronchopleural fistula after pneumonectomy: a multivariate analysis. Ann Thorac Surg 72(5):1662–1667
Hollaus PH, Setinek U, Lax F, Pridun NS (2003) Risk factors for bronchopleural fistula after pneumonectomy: stump size does matter. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 51(3):162–166
Toloza EM, Harpole DH Jr (2002) Intraoperative techniques to prevent air leaks. Chest Surg Clin N Am 12(3):489–505
Şanlı M, Işik AF, Tunçözgür B, Akar E, Elbeyli L (2008) Akciğer rezeksiyonlarından sonra oluşan bronkopulmoner fistüllerde konservatif yaklaşım. Gaziantep Tıp Dergisi 14:18–22
McManigle JE, Fletcher GL, Tenholder MF (1990) Bronchoscopy in the management of bronchopleural fistula. Chest 97(5):1235–1238
Hysi I, Rousse N, Claret A, Bellier J, Pinçon C, Wallet F, Akkad R, Porte H (2011) Open window thoracostomy and thoracoplasty to manage 90 postpneumonectomy empyemas. Ann Thorac Surg 92(5):1833–1839
Sakuraba M, Umezawa H, Miyamoto S, Fujiki M, Higashino T, Oshima A, Tsuboi M (2017) Reconstructive surgery for bronchopleural fistula and empyema: new application of free fascial patch graft combined with free flap. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 5(1):e1199
Taghavi S, Marta GM, Lang G, Seebacher G, Winkler G, Schmid K, Klepetko W (2005) Bronchial stump coverage with a pedicled pericardial flap: an effective method for prevention of postpneumonectomy bronchopleural fistula. Ann Thorac Surg 79(1):284–288
Shrager JB, Wain JC, Wright CD, Donahue DM, Vlahakes GJ, Moncure AC, Grillo HC, Mathisen DJ (2003) Omentum is highly effective in the management of complex cardiothoracic surgical problems. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 125(3):526–532
D’Andrilli A, Ibrahim M, Andreetti C, Ciccone AM, Venuta F, Rendina EA (2009) Transdiaphragmatic harvesting of the omentum through thoracotomy for bronchial stump reinforcement. Ann Thorac Surg 88(1):212–215
Bazzocchi R et al (2002) Bronchopleural fistula prevention after major pulmonary resection for primary lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 22(1):160
TOKAT AO, ÖZDEMİR N (2004) Rezeksiyon Sonrası Bronkoplevral Fistül Gelişimi ve Tedavi Yaklaşımları. Tüberküloz ve Toraks Dergisi 52(1):103–110
Ballore L et al (2008) Omentopexy associated with the use of Redon catheters in post-cardiac surgery mediastinitis with vascular prosthesis infection: immediate results in five patients. G Ital Cardiol (Rome) 9(11):759–762
Polat D, Rizalar R, Tander B, Yildiz L, Aritürk E, Bernay F (2004) Effects of splenohepatopexy and omentopexy in experimentally induced infrahepatic portal hypertension in rats. Pediatr Surg Int 20(6):434–438
Stamatis G, Freitag L, Wencker M, Greschuchna D (1994) Omentopexy and muscle transposition: two alternative methods in the treatment of pleural empyema and mediastinitis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 42(4):225–232
Hoshi E, Aoyama K, Yuki Y, Ooizumi H, Gotoh S, Fujishima T, Murai K, Washio M (1989) A case of omentopexy for bronchial fistula and pyothorax following the right completion pneumonectomy with combined resection of pericardium, diaphragm and chest wall. Kyobu Geka 42(13):1114–1117
Agnol G, Vieira A, Oliveira R, Figueroa P (2017) Surgical approaches for bronchopleural fistula. Shanghai Chest:1(3)
Shinohara S et al (2016) Benefits of using omental pedicle flap over muscle flap for closure of open window thoracotomy. J Thorac Dis 8(7):1697–1703
Levashev YN, Akopov AL, Mosin IV (1999) The possibilities of greater omentum usage in thoracic surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 15(4):465–468
Chichevatov D, Gorshenev A (2005) Omentoplasty in treatment of early bronchopleural fistulas after pneumonectomy. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 13(3):211–216
Cardillo G, Carbone L, Carleo F, Galluccio G, di Martino M, Giunti R, Lucantoni G, Battistoni P, Batzella S, dello Iacono R, Petrella L, Dusmet M (2015) The rationale for treatment of postresectional bronchopleural fistula: analysis of 52 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 100(1):251–257
Jiang F, Huang J, You Q, Yuan F, Yin R, Xu L (2013) Surgical treatment for bronchopleural fistula with omentum covering after pulmonary resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer 4(3):249–253
Wright CD, Wain JC, Grillo HC, Moncure AC, Macaluso SM, Mathisen DJ (1997) Pulmonary lobectomy patient care pathway: a model to control cost and maintain quality. Ann Thorac Surg 64(2):299–302
Çobanoğlu U, Melek M, Edirne Y, Mergan D (2011) Removal of chest tubes: a prospective randomized study. Turk J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 19(4):593–597
Duan M, Chen G, Wang T, Zhang Y, Dong J, Li Z, Sui T (1999) One-stage pedicled omentum majus transplantation into thoracic cavity for treatment of chronic persistent empyema with or without bronchopleural fistula. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 16(6):636–638
Boudaya MS, Smadhi H, Zribi H, Mohamed J, Ammar J, Mestiri T, Kilani T (2013) Conservative management of postoperative bronchopleural fistulas. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 146(3):575–579
Chawla RK, Madan A, Bhardwaj PK, Chawla K (2012) Bronchoscopic management of bronchopleural fistula with intrabronchial instillation of glue (N-butyl cyanoacrylate). Lung India 29(1):11–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Gaziantep University, and the ethics approval number was 04.04.2016-102. Informed consent for study participation was obtained from all patients.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulusan, A., Benli, M.Y., Ekici, M.A. et al. Omentum Transposition as a Solution for Bronchopleural Fistula and Empyema. Indian J Surg 82, 74–80 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-019-02028-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-019-02028-6