Abstract
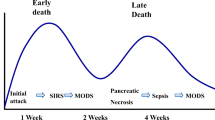
Surgery for acute pancreatitis has undergone significant changes over the last 3 decades. A better understanding of the pathophysiology has contributed to this, but the greatest driver for change has been the rise of less invasive interventions in the fields of laparoscopy, endoscopy and radiology. Surgery has a very limited role in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. The most common indication for intervention in acute pancreatitis is for the treatment of complications and most notably the treatment of infected walled off necrosis. Here, the step-up approach has become established, with prior drainage (either endoscopic or percutaneous) followed by delay for maturing of the wall and then debridement by endoscopic or minimally invasive surgical methods. Open surgery is only indicated when this approach fails. Other indications for surgery in acute pancreatitis are for the treatment of acute compartment syndrome, non-occlusive intestinal ischaemia and necrosis, enterocutaneous fistulae, vascular complications and pseudocyst. Surgery also has a role in the prevention of recurrent acute pancreatitis by cholecystectomy. Despite the more restricted role, surgeons have an important contribution to make in the multidisciplinary care of patients with complicated acute pancreatitis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Windsor JA, Petrov MS (2013) Acute pancreatitis re-classified. Gut 62:4–5
Radenkovic DV, Bajec D, Ivancevic N, Bumbasirevic V, Milic N, Jeremic V et al (2010) Decompressive laparotomy with temporary abdominal closure versus percutaneous puncture with placement of abdominal catheter in patients with abdominal compartment syndrome during acute pancreatitis: background and design of multicenter, randomised, controlled study. BMC Surg 10:22
Bhandari V, Jaipuria J, Singh M, Chawla AS (2013) Intra-abdominal pressure in the early phase of severe acute pancreatitis: canary in a coal mine? Results from a rigorous validation protocol. Gut Liver 7(6):731–738
Keskinen P, Leppaniemi A, Pettila V, Piilonen A, Kemppainen E, Hynninen M (2007) Intra-abdominal pressure in severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Surg 2:2
Aitken EL, Gough V, Jones A, Macdonald A (2014) Observational study of intraabdominal pressure monitoring in acute pancreatitis. Surgery 155(5):910–918
Deitch EA (2010) Gut lymph and lymphatics: a source of factors leading to organ injury and dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1207(S1):E103–E111
Fanous MYZ, Phillips AJ, Windsor JA (2007) Mesenteric lymph: the bridge to future management of critical illness. J Pancreas 8(4):374–399
Cheathem ML, Malbrain ML, Kirkpatrick A, Sugrue M, Parr M et al (2007) Results from the international conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome II. Recommendations. Intensive Care Med 33:951–962
Valle RGL, Godoy FL (2014) Neostigmine for acute colonic pseudo-obstruction: a meta-analysis. Annals Med Surg 3:60–64
Loveday BPT, Srinivasa S, Vather R, Mittal A, Petrov MS, Phillips ARJ, Windsor JA (2010) High quantity and variable quality of guidelines for acute pancreatitis: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 105:1466–1476
Trikudanathan G, Vege SS (2014) Current concepts of the role of abdominal compartment syndrome in acute pancreatitis :An opportunity or merely an epiphenomenon. Pancreatology 14(4):238–243
Mentula P, Hienonen P, Kemppainen E, Puolakkainen P, Leppäniemi A et al (2010) Surgical decompression for abdominal compartment syndrome in severe acute pancreatitis. Arch Surg 145(8):764–769
Melis M, Fichera A, Ferguson MK (2006) Bowel necrosis associated with early jejunal tube feeding: a complication of postoperative enteral nutrition. Arch Surg 141(7):701–704
Marvin RG, McKinley BA, McQuiggan M, Cocanour CS, Moore FA (2000) Non occlusive bowel necrosis occurring in critically Ill trauma patients receiving enteral nutrition manifests no reliable clinical signs for early detection. Am J Surg 179(1):7–12
Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Buskens E, Boermeester MA, van Goor H, Dutch Acute Pancreatitis Study Group (2008) Probiotic prophylaxis in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 371(9613):651–659
Watts GT (1963) Total pancreatectomy for fulminant pancreatitis. Lancet 2(7304):384
Alexandre JH, Guerri MT (1981) Role of total pancreatectomy in the treatment of necrotizing pancreatitis. World J Surg 5:369–377
Kivilaakso E, Fraki O, Nikki P et al (1981) Resection of the pancreas for acute fulminant pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 152:493–498
Aldridge MC, Ornstein M, Glazer G et al (1985) Pancreatic resection for severe acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 72:796–800
Mier J, Leon EL, Castillo A et al (1997) Early versus late necrosectomy in severe necrotizing pancreatitis. Am J Surg 173:71–75
Branum G, Galloway J, Hirchowitz W et al (1998) Pancreatic necrosis: results of necrosectomy, packing, and ultimate closure over drains. Ann Surg 227:870–877
Rau B, Bothe A, Beger HG (2005) Surgical treatment of necrtotising pancreatitis by necrosectomy and closed lavage: changing patient characteristics and outcome in a 19 year, single centre series. Surgery 138(1):28–39
Windsor JA (2007) Minimally invasive pancreatic necrosectomy. Br J Surg 94(2):132–133
Loveday BP, Petrov MS, Connor S, Pancreas Network of New Zealand et al (2011) A comprehensive classification of invasive procedures for treating the local complications of acute pancreatitis based on visualization, route and purpose. Pancreatology 11(4):406–413
van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, Hofker HS, Boermeester MA, Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group et al (2010) A step-up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 362(16):1491–1502
Van Branschot S, Bakker OJ, Besselink MG, Fockens P, Gooszen HG, Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group et al (2012) Treatment of necrotizing pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(11):1190–1201
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines (2013) IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 13(4 Suppl 2):e1–15
Van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Horvath KD et al (2007) Videoscopic assisted retroperitoneal debridement in infected necrotizing pancreatitis. HPB 9(2):156–159
Carter CR, McKay CJ, Imrie CW (2000) Percutaneous necrosectomy and sinus tract endoscopy in the management of infected pancreatic necrosis: an initial experience. Ann Surg 232(2):175–180
Windsor JA (2011) Infected pancreatic necrosis: drain first, but do it better. HPB (Oxford) 13(6):367–368
Werner J, Feuerbach S, Uhl W, Büchler MW (2005) Management of Acute pancreatitis: from surgery to interventional intensive care. Gut 54(3):426–436
Tsiotos GG, Smith CD, Sarr MG (1995) Incidence and management of pancreatic and enteric fistulas after surgical management of severe necrotizing pancreatitis. Arch Surg 130(1):48–52
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group et al (2013) Classification of acute pancreatitis.- 2012: revision of Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 62(1):102–111
Cheruvu CV, Clarke MG, Prentice M, Eyre-Brook IA (2003) Conservative treatment as an option in the management of pancreatic pseudocyst. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 85:313–316
Draganov PV (2009) Pancreatic pseudocyst. World J Gastroenterol 15(1):38–47
Nealon WH, Walser E (2002) Main pancreatic ductal anatomy can direct choice of modality for treating pancreatic pseudocysts (surgery versus percutaneous drainage). Ann Surg 235(6):751–758
Itoi T, Reddy N, Yasuda I (2013) New fully-covered self expandable metals stent for endoscopic ultrasonography-guided intervention in infectious walled-off pancreatic necrosis (with video). J Hepatobiliary Pancreati Sci 20:403–406
Varadarajulu S, Rana SS, Bhasin DK (2013) Endoscopic therapy for pancreatic duct leaks and disruptions. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 23(4):863–892
Tann M, Maglinte D, Howard TJ, Sherman S, Fogel E, Madura JA, Lehman GA (2003) Disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome: imaging findings and therapeutic implications in 26 surgically corrected patients. Abdom Imaging 27(4):577–582
Tse F, Yuan Y (2012) Early routine endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography strategy versus early conservative management strategy in acute gallstone pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5, CD009779. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009779.pub2
Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS, American College of Gastroenterology (2013) American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 108(9):1400–1415, 1416
Van Baal MC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, Van Santvoort HC, Schaapherder AF, Nieuwenhuijs VB et al (2012) Timing of cholecystectomy after mild biliary pancreatitis: a systematic review. Ann Surg 255:860–866
Sanjay P, Yeeting S, Whigham C, Judson H, Polignano FM, Tait IS (2007) Endoscopic sphincterotomy and interval cholecystectomy are reasonable alternatives to index cholecystectomy in severe acute gallstone pancreatitis (GSP). Surg Endosc 22(8):1832–1837
Bakker OJ, van Santvoort HC, Hagenaars JC, Besselink MG, Bollen TL, Gooszen HG, Schaapherder AF, Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group (2011) Timing of cholecystectomy after mild biliary pancreatitis. Br J Surg 98(10):1446–1454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navadgi, S., Pandanaboyana, S. & Windsor, J.A. Surgery for Acute Pancreatitis. Indian J Surg 77, 446–452 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-015-1357-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-015-1357-x