Abstract
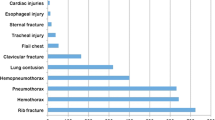
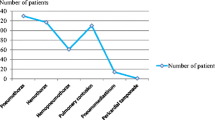
The aim of the study was to determine the frequency of different injuries caused by penetrating chest traumas, and also the cause and type of trauma and its accompanying injuries. This is a cross-sectional descriptive study, carried out on all patients referred to the emergency room of Shahid Bahonar Hospital, Kerman, from March 2000 to September 2008, due to penetrating chest trauma. The required information including age, sex, cause of trauma, type and site of injury, and accompanying injury was obtained and used to fill out a questionnaire and then was analyzed. 828 patients were included in the study; most of them were in the age range of 20–29. Of the patients, 97.6 % were males. The most frequent cause of trauma was stabbing, and the most frequent injuries following the trauma were pneumothorax and hemothorax. Orthopedic trauma was the most frequent accompanying injury. The most commonly used diagnostic method was plain chest radiography. In 93 % of the patients, the chest tube was placed and thoracotomy was performed for 97 % of the patients. Shahid Bahonar Hospital is a referral Trauma Centre and treats large number of chest trauma patients. Most patients need only chest tube placement as a definitive treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LoCicero J III, Mattox KL (1989) Epidemiology of chest trauma. Surg Clin North Am 69:15–19
Schwartz SI, Shier GT, Spencer FC. Principles of Surgery, 6th ed., 2003. Vol. l, pp. 672–684.
Adegboye VO, Ladipo JK, Brimmo IA et al (2002) Blunt chest trauma. Afr J Med Sci 31:315–320
Ceran S, Sunam GS, Aribas OK, Gormus N, Solak H (2002) Chest trauma in children. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 21:56–59
Liman ST, Kuzucu A, Tastepe AI, Ulasan GN, Topcu S (2003) Chest injury due to blunt trauma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 23:374–378
Karmy-Jones R, Jurkovich GJ (2004) Blunt chest trauma. Curr Probl Surg 41:211–380
Wicky S, Wintermark M, Schnyder P, Capasso P, Denys A (2000) Imaging of blunt chest trauma. Eur Radiol 10:1524–1538
Kulshrestha P, Munshi I, Wait R (2004) Profile of chest trauma in a level I trauma center. J Trauma 56:576–581
Rasmussen OV, Brynitz S, Struve-Christensen E (2005) Thoracic injuries. A review of 93 cases. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20:71–74
Shorr RM, Crittenden M, Indeck M, Hartunian SI, Rodriguez A (2004) Blunt thoracic trauma. Analysis of 515 patients. Ann Surg 206:200–205
Cakan A, Yuncu G, Olgaç G et al (2004) Thoracic trauma: analysis of 987 cases. Ulus Travma Derg 7:236–241
Demirhan R, Kucuk HF, Kargi AB, Altintas M, Kurt N, Gulmen M (2003) Evaluation of 572 cases of blunt and penetrating thoracic trauma. Ulus Travma Derg 7:231–235
Yalcinkaya I, Sayir F, Kurnaz M, Cobanoglu U (2005) Chest trauma: analysis of 126 cases. Ulus Travma Derg 6:288–291
Onat S, Ulku R, Avci A, Ates G, Ozcelik C (2011) Urgent thoracotomy for penetrating chest trauma: analysis of 158 patients of a single center. Injury 42:900–904
Clarke DL, Quazi MA, Reddy K, Thomson SR (2011) Emergency operation for penetrating thoracic trauma in a metropolitan surgical service in South Africa. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 142:563–568
Stewart RM, Myers JG, Dent DL et al (2003) Seven hundred fifty-three consecutive deaths in a level I trauma center: The argument for injury prevention. J Trauma 54:66–70
Mefire AC, Pagbe JJ, Fokou M, Nguimbous JF, Guifo ML, Bahebeck J (2010) Analysis of epidemiology, lesions, treatment and outcome of 354 consecutive cases of blunt and penetrating trauma to the chest in an African setting. Afr J Surg 48:90–93
Mollberg NM, Wise SR, De Hoyos AL, Lin FJ, Merlotti G (2012) Chest computed tomography for penetrating thoracic trauma after normal screening chest roentgenogram. Ann Thorac Surg 93:1830–1835
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Farzan Institute for Research and Technology for technical assistance.
Financial support
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghaei Afshar, M., Mangeli, F. & Nakhaei, A. Evaluation of Injuries Caused by Penetrating Chest Traumas in Patients Referred to the Emergency Room. Indian J Surg 77, 191–194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0757-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0757-4