Abstract
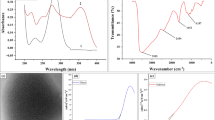
In the present study, an aptamer-based fluorescent assay was developed to detect fipronil in liquid eggs, using a carboxyfluorescein (FAM)-labeled aptamer (FAM aptamer) and partially complementary DNA labeled with carboxytetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA cDNA). The fipronil amount in analytical samples was determined by measuring FAM fluorescence at 522 nm. In the absence of fipronil, FAM fluorescence is effectively quenched by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) phenomenon generated by the hybridized structure of the FAM aptamer and TAMRA cDNA. In contrast, in the presence of fipronil, FAM fluorescence is gradually recovered in a fipronil concentration-dependent manner because the FAM aptamer has a stronger affinity for fipronil than for TAMRA cDNA. The proposed analytical method for fipronil involves a simple one-step procedure of mixing the sample solution without any washing step, and the results can be obtained in approximately 30 min. Under optimized conditions, the developed assay showed a linear response to fipronil in the egg sample in the range of 25-300 ppb with a detection limit of 53.8 ppb (0.068 mg/kg) and recovery rates in the range of 94.7-114.4%. Additionally, the assay selectivity for fipronil was investigated against eight pesticides, and it showed good specificity for fipronil. Compared with conventional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), the proposed method provides a simple, easy, and fast method to detect fipronil in egg samples without requiring bulky and expensive instruments and complicated and laborious processes. We believe this detection method could be a promising platform for fipronil detection in real food samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomlin, C. D. S. (2006) The Pesticide Manual: A World Compendium. 14th ed., pp. 462–464. British Crop Protection Council, Hampshire, UK.
Li, P. and G. Akk (2008) The insecticide fipronil and its metabolite fipronil sulphone inhibit the rat a1β2γ2L GABAA receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 155: 783–794.
Tingle, C. C., J. A. Rother, C. F. Dewhurst, S. Lauer, and W. J. King (2003) Fipronil: environmental fate, ecotoxicology, and human health concerns. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 176: 1–66.
Hadjmohammadi, M. R., S. M. Nikou, and K. Kamel (2006) Determination of fipronil residue in soil and water in the rice fields in north of Iran by RP-HPLC method. Acta Chim. Slov. 53: 517–520.
Dinham, B. (2000) Poisoning an island? Locust control in Madagascar. Pestic. News. 48: 3–6.
Lee, S. J., P. Mulay, B. Diebolt-Brown, M. J. Lackovic, L. N. Mehler, J. Beckman, J. Waltz, J. B. Prado, Y. A. Mitchell, S. A. Higgins, A. Schwartz, and G. M. Calvert (2010) Acute illnesses associated with exposure to fipronil-surveillance data from 11 states in the United States, 2001-2007. Clin. Toxic. 48: 737–744.
US Environmental Protection Agency (2011) Fipronil Summary Document Registration Review: Initial Docket June 2011. https://www.regulations.gov/document?D=EPA-HQ-OPP-2011-0448-0003.
Reuters, Contaminated eggs found in 40 countries as EU ministers meet: DPA. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-europe-ggs/contaminated-eggsfound-in-40-countries-as-eu-ministers-meet-dpa-idUSKCN1BG0LJ/.
FAO/WHO 2001, Report of the 2001 JMPR FAO/WHO Meeting of Experts. http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Reports_1991-2006/REPORT2001.pdf.
Guo, Q., S. Zhao, J. Zhang, K. Qi, Z. Du, and B. Shao (2018) Determination of fipronil and its metabolites in chicken egg, muscle and cake by a modified QuEChERS method coupled with LC-MS/MS. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 35: 1543–1552.
Vasylieva, N., K. C. Ahn, B. Barnych, S. J. Gee, and B. D. Hammock (2015) Development of an immunoassay for the detection of the phenylpyrazole insecticide fipronil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49: 10038–10047.
Tu, Q., M. E. Hickey, T. Yang, S. Gao, Q. Zhang, Y. Qu, X. Du, J. Wang, and L. He (2019) A simple and rapid method for detecting the pesticide fipronil on egg shells and in liquid eggs by Raman microscopy. Food Control. 96: 16–21.
Cho, E. J., J. W. Lee, and A. D. Ellington (2009) Applications of aptamers as sensors. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2: 241–264.
Xiao, Y., A. A. Lubin, A. J. Heeger, and K. W. Plaxco (2005) Label-free electronic detection of thrombin in blood serum by using an aptamer-based sensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 44: 5456–5459.
Tong, P., W. W. Zhao, L. Zhang, J. J. Xu, and H. Y. Chen (2012) Double-probe signal enhancing strategy for toxin aptasensing based on rolling circle amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 33: 146–151.
Shim, W. B., H. Mun, H. A. Joung, J. A. Ofori, D. H. Chung, and M. G. Kim (2014) Chemiluminescence competitive aptamer assay for the detection of aflatoxin B1 in corn samples. Food Control. 36: 30–35.
Farzin, L., M. Shamsipur, and S. Sheibani (2017) A review: Aptamer-based analytical strategies using the nanomaterials for environmental and human monitoring of toxic heavy metals. Talanta. 174: 619–627.
Mehlhorn, A., P. Rahimi, and Y. Joseph (2018) Aptamer-based biosensors for antibiotic detection: a review. Biosensors. 8: 54.
Hong, K. L. and L. J. Sooter (2018) In vitro selection of a single-stranded DNA molecular recognition element against the pesticide fipronil and sensitive detection in river water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19: 85.
Hussain, S. A. (2009) An introduction to fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). arXiv. arXiv:0908.1815.
Clegg, R. M. (1995) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 6: 103–110.
Nagatoishi, S., T. Nojima, E. Galezowska, B. Juskowiak, and S. Takenaka (2006) Quadruplex-based FRET probes with the thrombin-binding aptamer (TBA) sequence designed for the efficient fluorometric detection of the potassium in. Chembiochem. 7: 1730–1737.
Zhu, Y., Y. Cai, L. Xu, L. Zheng, L. Wang, B. Qi, and C. Xu (2015) Building an aptamer/graphene oxide FRET biosensor for one-step detection of bisphenol A. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7: 7492–7496.
Shi, J., F. Tian, J. Lyu, and M. Yang (2015) Nanoparticle based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) for biosensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. B. 3: 6989–7005.
Shaobo, C., S. Xu, H. Song, W. Xu, X. Chen, D. Zhou, Z. Yin, and W. Han (2015) Highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions based on up-conversion FRET from NaYF 4: Yb3+/Er3+ nanophosphors to CdTe quantum dots. RSC Adv. 5: 99099–99106.
Goud, K. Y., A. Sharma, A. Hayat, G. Catanante, K. V. Gobi, A. M. Gurban, and J. L. Marty (2016) Tetramethyl-6-carboxyrhodamine quenching-based aptasensing platform for aflatoxin B1: Analytical performance comparison of two aptamers. Anal. Biochem. 508: 19–24.
Sharma, A., G. Catanante, A. Hayat, G. Istamboulie, I. B. Rejeb, S. Bhand, and J. L. Marty (2016) Development of structure switching aptamer assay for detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk sample. Talanta. 158: 35–41.
Yüce, M. and H. Kurt (2017) How to make nanobiosensors: Surface modification and characterisation of nanomaterials for biosensing applications. RSC Adv. 7: 49386–49403.
Anastassiades, M., S. J. Lehotay, D. Stajnbaher, and F. J. Schenck (2003) Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and ‘dispersive solid-phase extraction’ for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC. Int. 86: 412–431.
Zhou, X., L. Wang, G. Shen, D. Zhang, J. Xie, A. Mamut, W. Huang, and S. Zhou (2018) Colorimetric determination of ofloxacin using unmodified aptamers and the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Mikrochim. Acta. 185: 355.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the main research program (E0192102-02) of the Korea Food Research Institute funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of South Korea. The authors declare no conflict of interest. Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, TY., Lim, J.W., Lim, MC. et al. Aptamer-based Fluorescent Assay for Simple and Sensitive Detection of Fipronil in Liquid Eggs. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 246–254 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0358-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0358-1