Abstract
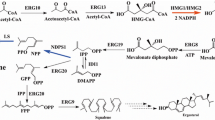
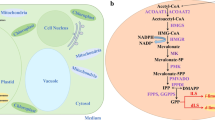
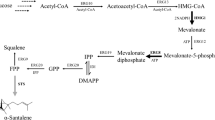
As an alternative terpenoid producer, non-conventional oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica was chosen for limonene production. Y. lipolytica can give high biomass yield and metabolize a broad range of substrates such as glycerol, alkanes, fatty acid, fats, and oils. As previously reported, optimization of limonene synthesis pathway and mevalonate (MVA) pathway leads to the accumulation of 112-fold higher limonene as compared to an initial strain. In this study, we introduced an additional copy of limonene synthesis gene (LS), which resulted in an increase of limonene production. This engineered strain was used to carry out further optimization study. Amongst all the carbon sources tested, the highest level of limonene production was obtained from glycerol, and citrate was selected as an auxiliary carbon source. In fed-batch fermentation with an optimized medium, the engineered strain was found to produce 165.3 mg/L limonene, which corresponds to the highest yield till date for the production of limonene in Y. lipolytica.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, J. (2007) D-limonene: Safety and clinical applications. Altern. Med. Rev. 12: 259–264.
Duetz, W. A., H. Bouwmeester, J. B. van Beilen, and B. Witholt (2003) Biotransformation of limonene by bacteria, fungi, yeasts, and plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 61: 269–277.
Ndayishimiye, J., D. J. Lim, and B. S. Chun (2017) Impact of extraction conditions on bergapten content and antimicrobial activity of oils obtained by a co-extraction of citrus by-products using supercritical carbon dioxide. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E 22: 586–596.
Nichkova, M., X. Fu, Z. Yang, P. Zhong, J. R. Sanborn, D. Chang, S. J. Gee, and B. D. Hammock (2009) Immunochemical screening of pesticides (simazine and cypermethrin) in orange oil. J. Agr. Food Chem. 57: 5673–5679.
Serra, S., C. Fuganti, and E. Brenna (2005) Biocatalytic preparation of natural flavours and fragrances. Trends Biotechnol. 23: 193–198.
Alonso-Gutierrez, J., R. Chan, T. S. Batth, P. D. Adams, J. D. Keasling, C. J. Petzold, and T. S. Lee (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for limonene and perillyl alcohol production. Metab. Eng. 19: 33–41.
Jongedijk, E., K. Cankar, J. Ranzijn, S. van der Krol, H. Bouwmeester, and J. Beekwilder (2015) Capturing of themonoterpene olefin limonene produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 32: 159–171.
Alonso-Gutierrez, J., E. M. Kim, T. S. Batth, N. Cho, Q. J. Hu, L. J. G. Chan, C. J. Petzold, N. J. Hinson, P. D. Adams, J. D. Keasling, H. G. Martin, and T. S. Lee (2015) Principal component analysis of proteomics (PCAP) as a tool to direct metabolic engineering. Metab. Eng. 28: 123–133.
Groenewald, M., T. Boekhout, C. Neuveglise, C. Gaillardin, P. W. M. van Dijck, and M. Wyss (2014) Yarrowia lipolytica: Safety assessment of an oleaginous yeast with a great industrial potential. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 40: 187–206.
Cao, X., L. J. Wei, J. Y. Lin, and Q. Hua (2017) Enhancing linalool production by engineering oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresource Technol. 245: 1641–1644.
Gao, S. L., Y. Y. Tong, L. Zhu, M. Ge, Y. A. Zhang, D. J. Chen, Y. Jiang, and S. Yang (2017) Iterative integration of multiple-copy pathway genes in Yarrowia lipolytica for heterologous beta-carotene production. Metab. Eng. 41: 192–201.
Yang, X., K. Nambou, L. J. Wei, and Q. Hua (2016) Heterologous production of alpha-farnesene in metabolically engineered strains of Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresource Technol. 216: 1040–1048.
Cao, X., Y. B. Lv, J. Chen, T. Imanaka, L. J. Wei, and Q. Hua (2016) Metabolic engineering of oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for limonene overproduction. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9: 11.
Michely, S., C. Gaillardin, J. M. Nicaud, and C. Neuveglise (2013) Comparative physiology of oleaginous species from the Yarrowia clade. PLoS One 8.
Barth, G. and C. Gaillardin (1997) Physiology and genetics of the dimorphic fungus Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 19: 219–237.
Du, F. L., H. L. Yu, J. H. Xu, and C. X. Li (2014) Enhanced limonene production by optimizing the expression of limonene biosynthesis and MEP pathway genes in E. coli. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 1: 10.
Kim, J. H., S. W. Kim, D. Q. A. Nguyen, H. Li, S. B. Kim, Y. G. Seo, J. K. Yang, I. Y. Chung, D. H. Kim, and C. J. Kim (2009) Production of beta-carotene by recombinant Escherichia coli with engineered whole mevalonate pathway in batch and fed-batch cultures. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E. 14: 559–564.
Huang, Y. Y., X. X. Jian, Y. B. Lv, K. Q. Nian, Q. Gao, J. Chen, L. J. Wei, and Q. Hua (2018) Enhanced squalene biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica based on metabolically engineered acetyl-CoA metabolism. J. Biotechnol. 281: 106–114.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21776081, 21576089) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (18ZR1410000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Materials
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, BQ., Wei, LJ., Lv, YB. et al. Elevating Limonene Production in Oleaginous Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica via Genetic Engineering of Limonene Biosynthesis Pathway and Optimization of Medium Composition. Biotechnol Bioproc E 24, 500–506 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0497-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0497-9