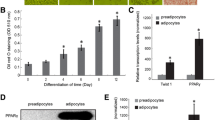
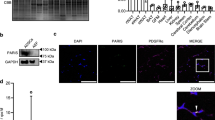
Abstract
Prohibitin (PHB) is a highly conserved protein in eukaryotic cells that are present in multiple cellular compartments and has potential roles as a tumor suppressor, an anti-proliferative protein, a regulator of cell-cycle progression and in apoptosis. In the present study, we generated PHB-deficient 3T3-L1 adipocytes and Clone 9 (C9) hepatocytes by oligonucleotide siRNA and investigated whether PHB affect lipid metabolism. It was revealed that PHB deficiency caused opposing lipid metabolism between the two cell models. PHB deficiency increased expression of adipogenic, lipogenic, and other lipid metabolic proteins in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, whereas significantly decreased the levels of those proteins in C9 cells. Collectively, PHB deficiency promoted lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes while it aggravated lipid metabolism in C9 hepatocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishra, S., L. C. Murphy, and L. J. Murphy (2006) The Prohibitins: Emerging roles in diverse functions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 10: 353–363.
Wang, S. and D. V. Faller (2008) Roles of prohibitin in growth control and tumor suppression in human cancers. Trans. Oncogenomics. 3: 23–37.
Mishra S., L. C. Murphy, B. L. Nyomba, and L. J. Murphy (2005) Prohibitin: A potential target for new therapeutics. Trends Mol. Med. 11: 192–197.
Jiang P., Y. Xiang, Y. J. Wang, S. M. Li, Y. Wang, H. R. Hua, G. Y. Yu, Y. Zhang, W. H. Lee, and Y. Zhang (2013) Differential expression and subcellular localization of Prohibitin 1 are related to tumorigenesis and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 15: 2092–2101.
Ko K. S., M. L. Tomasi, A. Iglesias-Ara, B. A. French, S. W. French, K. Ramani, J. J. Lozano, P. Oh, L. He, B. L. Stiles, T. W. Li, H. Yang, M. L. Martínez-Chantar, J. M. Mato, and S. C. Lu (2010) Liver-specific deletion of prohibitin 1 results in spontaneous liver injury, fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatol. 52: 2096–2108.
Sánchez-Quiles, V., V. Segura, E. Bigaud, B. He, B. W. O’Malley, E. Santamaría, J. Prieto, and F. J. Corrales (2012) Prohibitin-1 deficiency promotes inflammation and increases sensitivity to liver injury. J. Proteomics 75: 5783–5792.
Artal-Sanz, M. and N. Tavernarakis (2009) Prohibitin couples diapause signalling to mitochondrial metabolism during ageing in C. elegans. Nature 461: 793–797.
Artal-Sanz, M. and N. Tavernarakis (2010) Opposing function of mitochondrial prohibitin in aging. Aging 2: 1004–1011.
Gamble, S. C., D. Chotai, M. Odontiadis, D. A. Dart, G. N. Brooke, S. M. Powell, V. Reebye, A. Varela-Carver, Y. Kawano, J. Waxman, and C. L. Bevan (2007). Prohibitin, a protein downregulated by androgens, represses androgen receptor activity. Oncogene 26: 1757–1768.
Dai, Y., D. Ngo, J. Jacob, L. W. Forman, and D. V. Faller (2008). Prohibitin and the SWI/SNF ATPase subunit BRG1 are required for effective androgen antagonist-mediated transcriptional repression of androgen receptor-regulated genes. Carcinogenesis 29: 1725–1733.
He, B., Q. Feng, A. Mukherjee, D. M. Lonard, F. J. DeMayo, B. S. Katzenellenbogen, J. P. Lydon, and B. W. O’Malley (2008) A repressive role for prohibitin in estrogen signaling. Mol. Endocrinol. 22: 344–360.
Dart, D. A., B. Spencer-Dene, S. C. Gamble, J. Waxman, and C. L. Bevan (2009). Manipulating prohibitin levels provides evidence for an in vivo role in androgen regulation of prostate tumours. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 16: 1157–1169.
Sánchez-Quiles, V., E. Santamaría, V. Segura, L. Sesma, J. Prieto, and F. J. Corrales (2010) Prohibitin deficiency blocks proliferation and induces apoptosis in human hepatoma cells: molecular mechanisms and functional implications. Proteomics 10: 1609–1620.
Liu, D., Y. Lin, T. Kang, B. Huang, W. Xu, M. Garcia-Barrio, M. Olatinwo, R. Matthews, Y. E. Chen, and W. E. Thompson (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction and adipogenic reduction by prohibitin silencing in 3T3-L1 cells. PLoS One 7: e34315.
Ande, S. R., Z. Xu, Y. Gu, and S. Mishra (2012) Prohibitin has an important role in adipocyte differentiation. Int. J. Obes (Lond). 36: 1236–1244.
Chaudhari, H. N. and J. W. Yun (2014) Gender-dimorphic regulation of liver proteins in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 19: 93–107.
Aseer, K. R., S. W. Kim, D. G. Lee, and J. W. Yun (2014). Gender-dimorphic regulation of muscular proteins in response to high fat diet and sex steroid hormones. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 19: 93–107.
Chaudhari, H. N., S. W. Kim, and J. W. Yun (2014). Genderdimorphic regulation of antioxidant proteins in response to high-fat diet and sex steroid hormones in rats. Free Radic. Res. 48: 587–598.
Theiss, A. L. and S. V. Sitaraman (2011). The role and therapeutic potential of prohibitin in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813: 1137–1143.
Kahn, B. B., T. Alquier, D. Carling, and D. G. Hardie (2005) AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1: 15–25.
Koves, T. R., J. R. Ussher, R. C. Noland, D. Slentz, M. Mosedale, O. Ilkayeva, J. Bain, R. Stevens, J. R. Dyck, C. B. Newgard, G. D. Lopaschuk, and D. M. Muoio (2008) Mitochondrial overload and incomplete fatty acid oxidation contribute to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 7: 45–56.
Eberlé, D., B. Hegarty, P. Bossard, P. Ferré, and F. Foufelle (2004) SREBP transcription factors: Master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 86: 839–848.
Kasashima, K., M. Sumitani, M. Satoh, and H. Endo (2008) Human prohibitin 1 maintains the organization and stability of the mitochondrial nucleoids. Exp. Cell Res. 314: 988–996.
Knudsen, J., T. B. Neergaard, B. Gaigg, M. V. Jensen, and J. K. Hansen (2000) Role of acyl-CoA binding protein in acyl-CoA metabolism and acyl-CoA-mediated cell signaling. J. Nutr. 130: 294S–298S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.W., Yun, J.W. Prohibitin deficiency causes opposing lipid metabolism between 3T3-L1 adipocytes and Clone 9 hepatocytes. Biotechnol Bioproc E 21, 294–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-016-0249-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-016-0249-7