Abstract
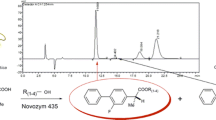
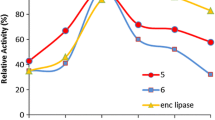
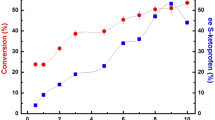
The Candida rugosa lipase catalyzed Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of racemic ibuprofen methyl ester produced (S)-ibuprofen in over 90% yield within 72 h at pH 7.6. The best concentration of various buffers for these reactions ranged from 0.2 to 0.5 M. The commercial lipase was found to be acidic altering the final pH of the reaction mixtures. Dimethylformamide co-solvent maintained the reaction pH better than dimethylsulfoxide. Lower concentrations of ibuprofen methyl ester and higher stirring rates led to faster conversions. The minimal amount of lipase needed was 20 mg/mL buffer. Reaction of (R)-ibuprofen methyl ester under the optimized conditions excluding the lipase led to no racemization, indicating that the conversion of (R)-ibuprofen methyl ester to (S)-ibuprofen is catalyzed by the enzyme, thus, indicating Candida rugosa lipase possess Isomerase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Persson, B. A., A. L. Larsson, M. Le Ray, and J. Bäckvall (1999) Ruthenium-and enzyme-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution of secondary alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121: 1645–1650.
Do, Y., I. Hwang, M. Kim, and J. Park (2010) Photoactivated racemization catalyst for dynamic kinetic resolution of secondary alcohols. J. Org. Chem. 75: 5740–5742.
Akai, S., R. Hanada, N. Fujiwara, Y. Kita, and M. Egi (2010) One-pot synthesis of optically active allyl esters via Lipasevanadium combo catalysis. Org. Lett. 12: 4900–4903.
Deska, J., C. del Pozo Ochoa, and J. Bäckvall (2010) Chemoenzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution of axially chiral allenes. Chem. Eur. J. 16: 4447–4451.
Kim, M., W. Kim, K. Han, Y. K. Choi, and J. Park (2007) Dynamic kinetic resolution of primary amines with a recyclable Pd nanocatalyst for racemization. Org. Lett. 9: 1157–1159.
Stirling, M., J. Blacker, and M. I. Page (2007) Chemoenzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution of secondary amines. Tetrahedron Lett. 48: 1247–1250.
Fransson, A. L., L. Borén, O. Pàmies, and J. Bäckvall (2005) Kinetic resolution and chemoenzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution of functionalized γ-hydroxy amides. J. Org. Chem. 70: 2582–2587.
Baxter, S., S. Royer, G. Grogan, F. Brown, K. E. Holt-Tiffin, I. N. Taylor, I. G. Fotheringham, and D. J. Campopiano (2012) An improved racemase/acylase biotransformation for the preparation of enantiomerically pure amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134: 19310–19313.
Engström, K., M. Shakeri, and J. Bäckvall (2011) Dynamic kinetic resolution of ß-amino esters by a heterogeneous system of a palladium nanocatalyst and candida antarctica lipase A. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 10: 1827–1830.
Rodríguez-Docampo, Z., C. Quigley, S. Tallon, and S. J. Connon (2012) The dynamic kinetic resolution of azlactones with thiol nucleophiles catalyzed by arylated, deoxygenated cinchona alkaloids. J. Org. Chem. 77: 2407–2414.
Rodríguez, C., G. de Gonzalo, A. Rioz-Martínez, D. E. T. Pazmino, M. W. Fraaije, and V. Gotor (2010) BVMO-catalysed dynamic kinetic resolution of racemic benzyl ketones in the presence of anion exchange resins. Org. Bimol. Chem. 8: 1121–1125.
Pamies, O. and J. Baeckvall (2002) Efficient lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution and dynamic kinetic resolution of ß-hydroxy nitriles. correction of absolute configuration and transformation to chiral ß-hydroxy acids and γ-amino alcohols. Adv. Synth. Catal. 344: 947–952.
Kiełbasiński, P., M. Rachwalski, M. Miko ajczyk, M. A. Moelands, B. Zwanenburg, and F. P. Rutjes (2005) Lipase-promoted dynamic kinetic resolution of racemic ß-hydroxyalkyl sulfones. Tetrahedron: Asymm. 16: 2157–2160.
Shiina, I., K. Ono, and K. Nakata (2012) Non-enzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution of racemic a-arylalkanoic acids: An advanced asymmetric synthesis of chiral nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Catal. Sci. Tech. 2: 2200–2205.
Ng, I. and S. Tsai (2006) Characterization and application of Carica papaya lipase to the dynamic kinetic resolution of (R,S)-naproxen thioester. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 37: 375–382.
Yuchun, X., L. Huizhou, and C. Jiayong (2000) Kinetics of base catalyzed racemization of ibuprofen enantiomers. Int. J. Pharm. 196: 21–26.
Liu, Y., F. Wang, and T. Tan (2009) Cyclic resolution of racemic ibuprofen via coupled efficient lipase and acid/base catalysis. Chirality 21: 349–353.
Xin, J., Y. Zhao, Y. Shi, C. Xia, and S. Li (2005) Lipase-catalyzed naproxen methyl ester hydrolysis in water-saturated ionic liquid: significantly enhanced enantioselectivity and stability. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21: 193–199.
Fazlena, H., A. Kamaruddin, and M. Zulkali (2006) Dynamic kinetic resolution: alternative approach in optimizing S-ibuprofen production. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 28: 227–233.
Chavez-Flores, D. and J. M. Salvador (2012) Facile conversion of racemic ibuprofen to (S)-ibuprofen. Tetrahedron: Asym. 23:237–239.
Lin, H. and S. Tsai (2003) Dynamic kinetic resolution of (R,S)-naproxen 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl ester via lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis in micro-aqueous isooctane. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 24-25: 111–120.
Xin, J., S. Li, Y. Xu, J. Chui, and C. Xia (2001) Dynamic enzymatic resolution of naproxen methyl ester in a membrane bioreactor. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 76: 579–585.
Chang, C., S. Tsai, and J. Kuo (1999) Lipase-catalyzed dynamic resolution of naproxen 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl thioester by hydrolysis in isooctane. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 64: 120–126.
Chen, C., Y. Cheng, and S. Tsai (2002) Lipase-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution of (R, S)-fenoprofen thioester in isooctane. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 77:699–705.
Lin, C. and S. Tsai (2000) Dynamic kinetic resolution of suprofen thioester via coupled trioctylamine and lipase catalysis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 69: 31–38.
Ong, A. L., A. H. Kamaruddin, and S. Bhatia (2005) Current technologies for the production of (S)-ketoprofen: Process perspective. Process Biochem. 40:3526–3535.
Chavez-Flores, D. and J. M. Salvador (2009) Commercially viable resolution of ibuprofen. Biotechnol. J. 4: 1222–1224.
Yamaji, T., T. Saito, K. Hayamizu, M. Yanagisawa, and O. Yamamoto Spectral Database for Organic Compounds SDBS. Http://Sdbs.Db.Aist.Go.Jp. http://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp
Koul, S., J. L. Koul, B. Singh, M. Kapoor, R. Parshad, K. S. Manhas, S. C. Taneja, and G. N. Qazi (2005) Trichosporon beigelli esterase (TBE): A versatile esterase for the resolution of economically important racemates. Tetrahedron: Asymm. 16: 2575–2591.
Takaç, S. and D. Mutlu (2007) A parametric study on biphasic medium conditions for the enantioselective production of naproxen by Candida rugosa lipase. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 141: 15–26.
Mathews, A. (1909) The spontaneous oxidation of the sugars. J. Biol. Chem. 6: 3–20.
Hardegger, E., K. Kreis, and H. E. Khadem (1952) Oxidation of several mono-and disaccharides with alkali and oxygen. Helv. Chim. Acta 35: 618–623.
Good, N. E., G. D. Winget, W. Winter, T. N. Connolly, S. Izawa, and R. M. Singh (1966) Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochem. 5: 467–477.
Doonan, S. (2004) Making and changing buffers. Methods Mol. Biol. 244: 91–99.
Steenkamp, L. and D. Brady (2008) Optimisation of stabilised Carboxylesterase NP for enantioselective hydrolysis of naproxen methyl ester. Proc. Biochem. 43: 1419–1426.
Liu, X., J. Xu, J. Pan, and J. Zhao (2010) Efficient production of (S)-Naproxen with (R)-substrate recycling using an overexpressed carboxylesterase BsE-NP01. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 162: 1574–1584.
Quax, W. and C. Broekhuizen (1994) Development of a newBacillus carboxyl esterase for use in the resolution of chiral drugs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 41: 425–431.
Gonawan, F. N., L. S. Yon, A. H. Kamaruddin, and M. H. Uzir (2012) Effect of co-solvent addition on the reaction kinetics of the lipase-catalyzed resolution of ibuprofen ester. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 88: 672–679.
Lee, W. H., K. Kim, M. G. Kim, and S. B. Lee (1995) Enzymatic resolution of racemic ibuprofen esters: Effects of organic cosolvents and temperature. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 80: 613–615.
Qu, X., A. Allan, G. Chui, T. J. Hutchings, P. Jiao, L. Johnson, W. Y. Leung, P. K. Li, G. R. Steel, and A. S. Thompson (2013) Hydrolysis of ibuprofenoyl-CoA and other 2-APA-CoA esters by human acyl-CoA thioesterases-1 and-2 and their possible role in the chiral inversion of profens. Biochem. Pharmacol. 86: 1621–1625.
Woodman, T. J., P. J. Wood, A. S. Thompson, T. J. Hutchings, G. R. Steel, P. Jiao, M. D. Threadgill, and M. D. Lloyd (2011) Chiral inversion of 2-arylpropionyl-CoA esters by human a-methylacyl-CoA racemase 1A (P504S)-a potential mechanism for the anti-cancer effects of ibuprofen. Chem. Commun. 47: 7332–7334.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortazavi, S.S., Chavez-Flores, D. & Salvador, J.M. Isomerase activity of Candida rugosa lipase in the optimized conversion of racemic ibuprofen to (S)-ibuprofen. Biotechnol Bioproc E 21, 634–640 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-016-0231-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-016-0231-4