Abstract
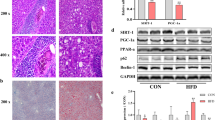
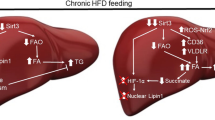
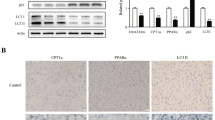
Imbalance in lipid metabolism within hepatocytes can lead to hepatosteatosis, which is a cause of numerous hepatic dysfunctions. Previous studies have demonstrated the roles of DJ-1 in Parkinson’s disease, diet-induced oxidative stress, obesity, and diabetes. Although recent studies have shown that DJ-1 is involved in metabolic complications, the roles of DJ-1 in steatosis are largely unknown. Therefore, the aim of the current study was to elucidate the potential roles of DJ-1 in hepatosteatosis in vitro. Normal rat liver cells Clone 9 (C9) were treated with 1 mM oleic acid (OA) for 24 h for establishment of a steatosis model, after which various biochemical parameters, including triglyceride, total cholesterol, and free fatty acid contents, were determined after knockdown with Dj1- specific siRNA. Silencing of Dj1 prevented hepatic steatosis by suppressing expression of hepatic lipogenic markers, which was confirmed by immunoblotting and real-time PCR analysis. Up-regulation of mitochondrial and β- oxidation-associated proteins showed potential to reduce fat accumulation in the liver. Silencing of Dj1 resulted in alleviation of steatosis by reducing lipogenesis and improving mitochondrial biogenesis. Further in vivo studies will be required to understand the molecular mechanism behind the role of DJ-1 in steatosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yilmaz, Y. (2012) Review article: Is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease a spectrum, or are steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis distinct conditions? Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 36: 815–823.
Kwon, E. Y., U. J. Jung, T. Park, J. W. Yun, and M. S. Choi (2015) Luteolin attenuates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance through the interplay between the liver and adipose tissue in mice with diet-induced obesity. Diabete. 64: 1658–1669.
Krawczyk, M., L. Bonfrate, and P. Portincasa (2010) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 24: 695–708.
Lonardo A., S. Bellentani, V. Ratziu, and P. Loria (2011) Insulin resistance in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Necessary but not sufficient-death of a dogma from analysis of therapeutic studies? Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 5: 279–289.
Amarapurkar, D., P. Kamani, N. Patel, P. Gupte, P. Kumar, S. Agal, R. Baijal, S. Lala, D. Chaudhary, and A. Deshpande (2007) Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Population based study. Ann. Hepatol. 6: 161–163.
Zhou, Y. J., Y. Y. Li, Y. Q. Nie, J. X. Ma, L. G. Lu, S. L. Shi, M. H. Chen, and P. J. Hu (2007) Prevalence of fatty liver disease and its risk factors in the population of South China. World J. Gastroenterol. 13: 6419–6424.
Duarte, M. A. and G. A. Silva (2011) Hepatic steatosis in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. 87: 150–156.
Marrero, J. A., R. J. Fontana, G. L. Su, H. S. Conjeevaram, D. M. Emick, and A. S. F. Lok (2002) NAFLD may be a common underlying liver disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Hepatol. 36: 1349–1354.
Caldwell, S. H., D. M. Crespo, H. S. Kang, and A. M. Al-Osaimi (2004) Obesity and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol. 127: 97–103.
Kim, H. Y., S. Y. Park, M. H. Lee, J. H. Rho, Y. J. Oh, H. U. Jung, S. H. Yoo, N. Y. Jeong, H. J. Lee, S. Suh, S. Y. Seo, J. Cheong, J. S. Jeong, and Y. H. Yoo (2015) Hepatic STAMP2 alleviates high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 63: 477–485.
Kim, D. I., M. J. Park, S. K. Lim, J. I. Park, K. C. Yoon, H. J. Han, J. Å. Gustafsson, J. H. Lim, and S. H. Park (2015) PRMT3 regulates hepatic lipogenesis through direct interaction with LXRá. Diabete. 64: 60–71.
Takaki, Y., Y. Saito, A. Takasugi, K. Toshimitsu, S. Yamada, T. Muramatsu, M. Kimura, K. Sugiyama, H. Suzuki, E. Arai, H. Ojima, Y. Kanai, and H. Saito (2014) Silencing of microRNA-122 is an early event during hepatocarcinogenesis from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Cancer Sci. 105: 1254–1260.
Katsura, A., A. Morishita, H. Iwama, J. Tani, T. Sakamoto, M. Tatsuta, Y. Toyota, K. Fujita, K. Kato, E. Maeda, T. Nomura, H. Miyoshi, H. Yoneyama, T. Himoto, S. Fujiwara, H. Kobara, H. Mori, T. Niki, M. Ono, M. Hirashima, and T. Masaki (2015) MicroRNA profiles following metformin treatment in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 35: 877–884.
Choi, Y. J., C. H. Lee, K. Y. Lee, S. H. Jung, and B. H. Lee (2015) Increased hepatic fatty acid uptake and esterification contribute to tetracycline-induced steatosis in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 145: 273–282.
Kim, H. M., E. S. Lee, B. R. Lee, D. Yadav, Y. M. Kim, H. J. Ko, K. S. Park, E. Y. Lee, and C. H. Chung (2015) C-C chemokine receptor 2 inhibitor ameliorates hepatic steatosis by improving ER stress and inflammation in a type 2 diabetic mouse model. PLoS One. 10: e0120711.
Bandopadhyay, R., A. E. Kingsbury, M. R. Cookson, A. R. Reid, I. M. Evans, A. D. Hope, A. M. Pittman, T. Lashley, R. Canet-Aviles, D. W. Miller, C. McLendon, C. Strand, A. J. Leonard, P. M. Abou-Sleiman, D. G. Healy, H. Ariga, N. W. Wood, R. de Silva, T. Revesz, J. A. Hardy, and A. J. Lees (2004) The expression of DJ-1 (PARK7) in normal human CNS and idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Brain. 127: 420–430.
Kim, R. H., P. D. Smith, H. Aleyasin, S. Hayley, M. P. Mount, S. Pownall, A. Wakeham, A. J. You-Ten, S. K. Kalia, P. Horne, D. Westaway, A. M. Lozano, H. Anisman, D. S. Park, and T. W. Mak (2005) Hypersensitivity of DJ-1-deficient mice to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrindine (MPTP) and oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 102: 5215–5220.
Giaime, E., H. Yamaguchi, C. A. Gautier, T. Kitada, and J. Shen (2012) Loss of DJ-1 does not affect mitochondrial respiration but increases ROS production and mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. PLoS One. 7: e40501.
Chaudhari, H. N., S. W. Kim, and J. W. Yun (2014) Genderdimorphic regulation of antioxidant proteins in response to highfat diet and sex steroid hormones in rats. Free Radic. Res. 48: 587–598.
Chaudhari, H. N., S. W. Kim, and J. W. Yun (2015) Genderdimorphic regulation of DJ-1 and its interactions with metabolic proteins in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Cell Mol. Med. 19: 996–1009.
Inberg, A. and M. Linial (2010) Protection of pancreatic betacells from various stress conditions is mediated by DJ-1. J. Biol. Chem. 285: 25686–25698.
Waanders, L. F., K. Chwalek, M. Monetti, C. Kumar, E. Lammert, and M. Mann (2009) Quantitative proteomic analysis of single pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 106: 18902–18907.
Jain, D., R. Jain, D. Eberhard, J. Eglinger, M. Bugliani, L. Piemonti, P. Marchetti, and E. Lammert (2012) Age-and dietdependent requirement of DJ-1 for glucose homeostasis in mice with implications for human type 2 diabetes. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 4: 221–230.
Das, U. N. (2006) Essential fatty acids: Biochemistry, physiology and pathology. Biotechnol. J. 1: 420–439.
Kim, K. S., J. S. Kim, J. Y. Park, Y. H. Suh, I. Jou, E. H. Joe, and S. M. Park (2013) DJ-1 associates with lipid rafts by palmitoylation and regulates lipid rafts-dependent endocytosis in astrocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22: 4805–4817.
Kim J. M., H. J. Jang, S. Y. Choi, S. A. Park, I. S. Kim, Y. R. Yang, Y. H. Lee, S. H. Ryu, and P. G. Suh (2014) DJ-1 contributes to adipogenesis and obesity-induced inflammation. Sci. Rep. 4: 4805.
den Boer, M., P. J. Voshol, F. Kuipers, L. M. Havekes, and J. A. Romijn (2004) Hepatic steatosis: A mediator of the metabolic syndrome. Lessons from animal models. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24: 644–649.
Wouters, K., P. J. van Gorp, V. Bieghs, M. J. Gijbels, H. Duimel, D. Lütjohann, A. Kerksiek, R. van Kruchten, N. Maeda, B. Staels, M. van Bilsen, R. Shiri-Sverdlov, and M. H. Hofker (2008) Dietary cholesterol, rather than liver steatosis, leads to hepatic inflammation in hyperlipidemic mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. 48: 474–486.
Kim, K. Y., M. V. Stevens, M. H. Akter, S. E. Rusk, R. J. Huang, A. Cohen, A. Noguchi, D. Springer, A. V. Bocharov, T. L. Eggerman, D. F. Suen, R. J. Youle, M. Amar, A. T. Remaley, and M. N. Sack (2011) Parkin is a lipid-responsive regulator of fat uptake in mice and mutant human cells. J. Clin. Invest. 121: 3701–3712.
Cookson, M. R. (2012) Parkinsonism due to mutations in PINK1, parkin, and DJ-1 and oxidative stress and mitochondrial pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2: a009415.
Hardie, D. G. (2008) AMPK: A key regulator of energy balance in the single cell and the whole organism. Int. J. Obes. 32: 7–12.
Thomson, D. M., B. B. Porter, J. H. Tall, H. J. Kim, J. R. Barrow, and W. W. Winder (2007) Skeletal muscle and heart LKB1 deficiency causes decreased voluntary running and reduced muscle mitochondrial marker enzyme expression in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292: E196–202.
Hardie, D. G., F. A. Ross, and S. A. Hawley (2012) AMPK: A nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13: 251–262.
Li, Y., S. Xu, M. M. Mihaylova, B. Zheng, X. Hou, B. Jiang, O. Park, Z. Luo, E. Lefai, J. Y. Shyy, B. Gao, M. Wierzbicki, T. J. Verbeuren, R. J. Shaw, R. A. Cohen, and M. Zang (2011) AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab. 13: 376–388.
Seo, M. S., J. H. Kim, H. J. Kim, K. C. Chang, and S. W. Park (2015) Honokiol activates the LKB1-AMPK signaling pathway and attenuates the lipid accumulation in hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 284: 113–124.
Brown M. S. and J. L. Goldstein (2009) Cholesterol feedback: From Schoenheimer's bottle to Scap's MELADL. J. Lipid Res. 50: 15–27.
Gao, M., Y. Ma, and D. Liu (2015) High-fat diet-induced adipos ity, adipose inflammation, hepatic steatosis and hyperinsulinemia in outbred CD-1 mice. PLoS One. 10: e0119784.
Higuchi, N., M. Kato, Y. Shundo, H. Tajiri, M. Tanaka, N. Yamashita, M. Kohjima, K. Kotoh, M. Nakamuta, R. Takayanagi, and M. Enjoji (2008) Liver X receptor in cooperation with SREBP-1c is a major lipid synthesis regulator in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 38: 1122–1129.
Nakamuta, M., T. Fujino, R. Yada, M. Yada, K. Yasutake, T. Yoshimoto, N. Harada, N. Higuchi, M. Kato, M. Kohjima, A. Taketomi, Y. Maehara, M. Nakashima, K. Kotoh, and M. Enjoji (2009) Impact of cholesterol metabolism and the LXRalpha-SREBP-1c pathway on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 23: 603–608.
Wang, M., S. Sun, T. Wu, L. Zhang, H. Song, W. Hao, P. Zheng, L. Xing, and G. Ji (2013) Inhibition of LXRá/SREBP-1c-Mediated Hepatic Steatosis by Jiang-Zhi Granule. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2013: 584634.
Park, M. J., D. I. Kim, J. H. Choi, Y. R. Heo, and S. H. Park (2015) New role of irisin in hepatocytes: The protective effect of hepatic steatosis in vitro. Cell Signal. 27: 1831–1839.
Timchenko, L. T., E. Salisbury, G. L. Wang, H. Nguyen, J. H. Albrecht, J. W. Hershey, and N. A. Timchenko (2006) Age-specific CUGBP1-eIF2 complex increases translation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta in old liver. J. Biol. Chem. 281: 32806–32819.
Gao, L. L., M. Li, Q. Wang, S. A. Liu, J. Q. Zhang, and J. Cheng (2015b) HCBP6 Modulates Triglyceride Homeostasis in Hepatocytes via the SREBP1c/FASN Pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 116: 2375–2384.
Schroeder-Gloeckler, J. M., S. M. Rahman, R. C. Janssen, L. Qiao, J. Shao, M. Roper, S. J. Fischer, E. Lowe, D. J. Orlicky, J. L. McManaman, C. Palmer, W. L. Gitomer, W. Huang, R. M. O'Doherty, T. C. Becker, D. J. Klemm, D. R. Jensen, L. K. Pulawa, R. H. Eckel, and J. E. Friedman (2007) CCAAT/enhancerbinding protein beta deletion reduces adiposity, hepatic steatosis, and diabetes in Lepr(db/db) mice. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 15717–15729.
Matsusue, K., M. Haluzik, G. Lambert, S. H. Yim, O. Gavrilova, J. M. Ward, B. Jr. Brewer, M. L. Reitman, and F. J. Gonzalez (2003) Liver-specific disruption of PPARγ in leptin-deficient mice improves fatty liver but aggravates diabetic phenotypes. J. Clin. Invest. 111: 737–747.
Auguet, T., A. Berlanga, E. Guiu-Jurado, S. Martinez, J. A. Porras, G. Aragonès, F. Sabench, M. Hernandez, C. Aguilar, J. J. Sirvent, D. Del Castillo, and C. Richart (2014) Altered fatty acid metabolism-related gene expression in liver from morbidly obese women with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15: 22173–22187.
Oshida, K., N. Vasani, R. S. Thomas, D. Applegate, M. Rosen, B. Abbott, C. Lau, G. Guo, L. M. Aleksunes, C. Klaassen, and J. C. Corton (2015) Identification of modulators of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a mouse liver gene expression compendium. PLoS One 10: e0112655.
Ambade A., D. Catalano, A. Lim, A. Kopoyan, S. A. Shaffer, and P. Mandrekar (2014) Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 alleviates steatosis and macrophage activation in murine alcoholic liver injury. J. Hepatol. 61: 903–911.
Wheeler, M. C. and N. Gekakis (2014) Hsp90 modulates PPARγ activity in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Lipid Res. 55: 1702–1710.
Knobbe C. B., T. J. Revett, Y. Bai, V. Chow, A. H. Jeon, C. Böhm, S. Ehsani, T. Kislinger, H. T. Mount, T. W. Mak, P. St George-Hyslop, and G. Schmitt-Ulms (2011) Choice of biological source material supersedes oxidative stress in its influence on DJ-1 in vivo interactions with Hsp90. J. Proteome Res. 10: 4388–4404.
Hardwick, J. P., D. Osei-Hyiaman, H. Wiland, M. A. Abdelmegeed, and B. J. Song (2009) PPAR/RXR Regulation of fatty acid metabolism and fatty acid omega-hydroxylase (CYP4) Isozymes: Implications for prevention of lipotoxicity in fatty liver disease. PPAR Res. 2009: 952734.
Tzeng, T. F., S. S. Liou, C. J. Chang, and I. M. Liu (2015) [6]-Gingerol dampens hepatic steatosis and inflammation in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Phytomed. 22: 452–461.
Zhao, F., P. Xie, J. Jiang, L. Zhang, W. An, and Y. Zhan (2014) The effect and mechanism of tamoxifen-induced hepatocyte steatosis in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 5: 4019–4030.
Zhou, J., L. Zhang, J. Zhang, and X. Wan (2014) Aqueous extract of post-fermented tea reverts the hepatic steatosis of hyperlipidemia rat by regulating the lipogenic genes expression and hepatic fatty acid composition. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 14:263.
Zhu, W., S. Chen, Z. Li, X. Zhao, W. Li, Y. Sun, Z. Zhang, W. Ling, and X. Feng (2014) Effects and mechanisms of resveratrol on the amelioration of oxidative stress and hepatic steatosis in KKAy mice. Nutr. Metab. 11:35.
Austin, S. and J. St-Pierre (2012) PGC-1α and mitochondrial metabolism—emerging concepts and relevance in ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. J. Cell Sci. 125: 4963–4971.
LeBleu, V. S., J. T. O'Connell, K. N. Gonzalez Herrera, H. Wikman, K. Pantel, M. C. Haigis, F. M. de Carvalho, A. Damascena, L. T. Domingos Chinen, R. M. Rocha, J. M. Asara, and R. Kalluri (2014) PGC-1α mediates mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cells to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 16: 992–1003.
Nassir, F. and J. A. Ibdah (2014) Role of mitochondria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15: 8713–8742.
Puigserver, P. (2005) Tissue-specific regulation of metabolic pathways through the transcriptional coactivator PGC1-α. Int. J. Obes. 29: 5–9.
Irrcher, I., H. Aleyasin, E. L. Seifert, S. J. Hewitt, S. Chhabra, M. Phillips, A. K. Lutz, M. W. Rousseaux, L. Bevilacqua, A. Jahani-Asl, S. Callaghan, J. G. MacLaurin, K. F. Winklhofer, P. Rizzu, P. Rippstein, R. H. Kim, C. X. Chen, E. A. Fon, R. S. Slack, M. E. Harper, H. M. McBride, T. W. Mak, and D. S. Park (2010) Loss of the Parkinson's disease-linked gene DJ-1 perturbs mitochondrial dynamics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19: 3734–3746.
Thomas, K. J., M. K. McCoy, J. Blackinton, A. Beilina, M. van der Brug, A. Sandebring, D. Miller, D. Maric, A. Cedazo-Minguez, and M. R. Cookson (2011) DJ-1 acts in parallel to the PINK1/parkin pathway to control mitochondrial function and autophagy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 20: 40–50.
Nakamura, S., T. Takamura, N. Matsuzawa-Nagata, H. Takayama, H. Misu, H. Noda, S. Nabemoto, S. Kurita, T. Ota, H. Ando, K. Miyamoto, and S. Kaneko (2009) Palmitate induces insulin resistance in H4IIEC3 hepatocytes through reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 284: 14809–14818.
Serviddio, G., A. M. Giudetti, F. Bellanti, P. Priore, T. Rollo, R. Tamborra, L. Siculella, G. Vendemiale, E. Altomare, and G. V. Gnoni (2011) Oxidation of hepatic carnitine palmitoyl transferase-I (CPT-I) impairs fatty acid beta-oxidation in rats fed a methionine-choline deficient diet. PLoS One. 6: e24084.
Handa, P., B. D. Maliken, J. E. Nelson, V. Morgan-Stevenson, D. J. Messner, B. K. Dhillon, H. M. Klintworth, M. Beauchamp, M. M. Yeh, C. T. Elfers, C. L. Roth, and K. V. Kowdley (2014) Reduced adiponectin signaling due to weight gain results in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through impaired mitochondrial biogenesis. Hepatol. 60: 133–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhari, H.N., Yun, J.W. DJ-1 deficiency alleviates steatosis in cultured hepatocytes. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 1152–1161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0689-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0689-5