Abstract
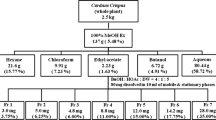
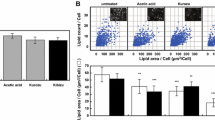
The adipocyte differentiation-inhibiting efficacies of cubic phase nanoparticle/herbal extract mixture suspensions were much higher than those of herbal extract suspensions (grape, apple, mugwort, barberry root, and green tea). Confocal laser scanning microscopy and fluorescenceactivated cell sorting analysis revealed that cubic phase nanoparticle promoted the internalization of a watersoluble dye (e.g. calcein) into adipocyte cell. Cubic phase nanoparticle/herbal extract mixture suspensions decreased the blood contents of aspartate aminotransferase, total cholesterol, triglyceride, urea nitrogen, and low density lipoprotein more than herbal extract suspensions. Cubic phase nanoparticle also promoted the efficacy of the herbal extracts in suppressing the body weight gain and the liver weight of rats. The amount permeated through hairless mouse skin was higher when cubic phase nanoparticle was included in barberry root extract suspension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong, S. K., J. Y. Ma, and J. -C. Kim (2012) In vitro skin permeation enhancement of KIOM-MA-128 by Monoolein Cubosomes. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 33: 1503–1508.
Mishra, N., N. P. Yadav, J. G. Meher, and P. Sinha (2012) Phytovesicles: Conduit between conventional and novel drug delivery system. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2: S1728–S1734.
Kwon, T. K. and J. -C. Kim (2010) In vitro skin permeation of monoolein nanoparticles containing hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin/ minoxidil complex. Int. J. Pharm. 392: 268–273.
Kwon, T. K., S. K. Hong, and J. -C. Kim (2012) In vitro skin permeation of cubosomes containing triclosan. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 18: 563–587.
Esposito, E., R. Cortesi, M. Drechsler, L. Paccamiccio, P. Mariani, C. Contado, E. Stellin, E. Menegatti, F. Bonina, and C. Puglia (2005) Cubosome dispersions as delivery systems for percutaneous administration of indomethacin. Pharmaceut. Res. 22: 2163–2173.
Kwon, T. K. and J. -C. Kim (2010) Preparation and in vitro skin permeation of cubosomes containing hinokitiol. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 31: 1004–1009.
Seo, S. R., G. Kang, J. W. Ha, and J. -C. Kim (2013) In vivo hair growth-promoting efficacies of herbal extracts and their cuboso-mal suspensions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19: 1331–1339.
Zhao, X. Y., J. Zhang, L. Q. Zheng, and D. H. Li (2005) Studies of cubosomes as a sustained drug delivery system. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 25: 795–799.
Baskaran, T. R., R. K. Thapa, J. Y. Rhyu, H. Y. Choi, J. O. Kim, C. S. Yong, and B. K. Yoo (2012) Design and in-vitro evaluation of finasteride-loaded liquid crystalline nanoparticles for topical delivery. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 14: 45–52.
Kwon, T. K., H. Y. Lee, J. -D. Kim, W. C. Shin, S. K. Park, and J. -C. Kim (2010) In vitro skin permeation of cubosomes containing water soluble extracts of Korean barberry. Colloid J. 72: 205–210.
Fang, J. Y., S. Y. Yu, P. C. Wu, Y. B. Huang, and Y. H. Tsai (2001) In vitro skin permeation of estradiol from various proniosome formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 215: 91–99.
Bao, Y., S. Zhang, and W. Shi (2012) Percutaneous absorption effects of Chinese herbal medicine. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmaco. 6: 389–396.
Nariya, M., V. Shukia, S. Jain, and B. Bavishankar (2009) Comparison of enteroprotective efficacy of triphala formulations (Indian Herbal Drug) on methotrexate-induced small intestinal damage in rats. Phytother. Res. 23: 1092–1098.
Um, J. Y., H. Chung, K. S. Kim, I. C. Kwon, and S. Y. Jeong (2003) In vitro cellular interaction and absorption of dispersed cubic particles. Int. J. Pharm. 253: 71–80.
Boyd, B. J., S. B. Rizwan, Y. D. Dong, S. Hook, and T. Rades (2007) Self-assembled geometric liquid-crystalline nanoparticles imaged in three dimensions: Hexosomes are not necessarily flat hexagonal prisms. Langmui. 23: 12461–12464.
Nguyen, T. H., T. Hanley, C. J. H. Proter, and B. J. Boyd (2011) Nanostructured liquid crystalline particles provide long duration sustained-release effect for a poor water soluble drug after oral administration. J. Control. Releas. 153: 180–186.
Rattanapak. T., K. Young, T. Rades, and S. Hook (2012) Comparative study of liposomes, transfersomes, ethosomes and cubosomes for transcutaneous immunisation: Characterisation and in vitro skin penetration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 64: 1560–1569.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Kim, JC. Effect of cubic phase nanoparticle on obesity-suppressing efficacy of herbal extracts. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 1005–1015 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0417-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0417-1