Abstract
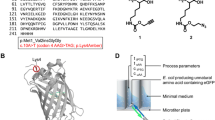
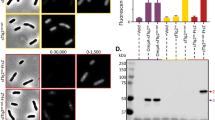
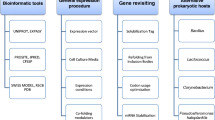
The optimization of aldose reductase (AR) expression levels and tracking of the AR expression sites within the cell is an essential step in developing a platform for the effective production of aldose reductase inhibitors (ARIs). In this study, we have demonstrated the use of both immunocytochemistry and quantum dots-based immunofluorescence techniques for observing and detecting the expression level and localization of AR in the cytoplasm and cell membrane of a eukaryotic cell model with high levels of AR protein expression. Our results show that high expression levels of human AR can be achieved using the eukaryotic cell model that we have developed. The overexpressed AR can be used for translational studies of hAR and the screening of ARIs. More importantly, the use of the established quantum dots-based immunofluorescence technique in the intracellular labeling of AR allows the determination of the expression and distribution of the AR gene. Overall, the use of the interdisciplinary approach of both genetic engineering and quantum dot-based immunofluorescence allows not only the effective production of a desired protein, but also the determination of the cellular localization of such an expressed protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petrash, J. M.} (2004) All in the family: Aldose reductase and closely related aldo-keto reductases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 61: 737–749.
Lee, A. Y. and S. S. Chung (1999) Contributions of polyol pathway to oxidative stress in diabetic cataract. FASEB J. 13: 23–30.
Obrosova, I. G. (2005) Increased sorbitol pathway activity generates oxidative stress in tissue sites for diabetic complications. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7: 1543–1552.
Ramana, K. V. and S. K. Srivastava (2010) Aldose reductase: A novel therapeutic target for inflammatory pathologies. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 42: 17–20.
Miller, S. I., R. K. Ernst, and M. W. Bader (2005) LPS, TLR4 and infectious disease diversity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3: 36–46.
Hotta, N., Y. Akanuma, R. Kawamori, K. Matsuoka, Y. Oka, M. Shichiri, T. Toyota, M. Nakashima, I. Yoshimura, N. Sakamoto, and Y. Shigeta (2006) Long-term clinical effects of epalrestat, an aldose reductase inhibitor, on diabetic peripheral neuropathy: The 3-year, multicenter, comparative aldose reductase inhibitor-diabetes complications trial. Diabetes Care. 29: 1538–1544.
Reddy, G. B., A. Satyanarayana, N. Balakrishna, R. Ayyagari, M. Padma, K. Viswanath, and J. M. Petrash (2008) Erythrocyte aldose reductase activity and sorbitol levels in diabetic retinopathy. Mol. Vis. 14: 593–601.
Kang, E. S., H. J. Kim, K. S. Paek, H. S. Jang, K. C. Chang, J. H. Lee, T. Nishinaka, C. Yabe-Nishimura, and H. G. Seo (2005) Phorbol ester up-regulates aldose reductase expression in A549 cells: A potential role for aldose reductase in cell cycle modulation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 62: 1146–1155.
Medintz, I. L., H. T. Uyeda, E. R. Goldman, and H. Mattoussi (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 4: 435–446.
Wu, X., H. Liu, J. Liu, K. N. Haley, J. A. Treadway, J. P. Larson, N. Ge, F. Peale, and M. P. Bruchez (2003) Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 41–46.
Jaiswal, J. K., H. Mattoussi, J. M. Mauro and S. M. Simon (2003) Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 47–51.
Gu, J., J. Yan, W. Wu, Q. Huang, and D. Ouyang (2010) Research progress in aldose reductase. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 35: 395–400.
Vedantham, S., H. Noh, R. Ananthakrishnan, N. Son, K. Hallam, Y. Hu, S. Yu, X. Shen, R. Rosario, Y. Lu, T. Ravindranath, K. Drosatos, L. A. Huggins, A. M. Schmidt, I. J. Goldberg, and R. Ramasamy (2011) Human aldose reductase expression accelerates atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein E-/-mice. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31: 1805–1813.
Hasuike, Y., T. Nakanishi, Y. Otaki, M. Nanami, T. Tanimoto, N. Taniguchi, and Y. Takamitsu (2002) Plasma 3-deoxyglucosone elevation in chronic renal failure is associated with increased aldose reductase in erythrocytes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 40: 464–471.
Alexiou, P., K. Pegklidou, M. Chatzopoulou, I. Nicolaou, and V. J. Demopoulos (2009) Aldose reductase enzyme and its implication to major health problems of the 21(st) century. Curr. Med. Chem. 16: 734–752.
Chen, X. P. and J. S. Shi (2012) HPLC-fluorescence detect the activity of aldose reductase. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 28: 1472–1475.
Du, M. M., J. Liu, B. Zhai, J. W. Liu, H. Yang, Z. H. Zhang, H. Yi, and L. Ye (2009) Construction and function study of a drug screening model based on aldose reductase gene and its inhibitor. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 25: 552–555.
Zhu, G. Q., Z. F. Wu, Y. F. Li, D. H. Hu, and Q. T. Wang (2006) Experimental study on dog's bone marrow stem cells transfected by pIRES2-EGFP-IGF-1 gene. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 41: 739–742.
Hu, Z. Y., S. T. Qi, X. Zhang, Q. Cao, and B. Y. Wu (2009) Construction of delta-pIRES2-EGFP plasmid and its expression in HEK293 cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 29: 1351–1353.
Scholz, O., A. Thiel, W. Hillen, and M. Niederweis (2000) Quantitative analysis of gene expression with an improved green fluorescent protein. p6. Europ. J. Biochem. / FEBS. 267: 1565–1570.
Haverkamp, S., D. Inta, H. Monyer, and H. Wassle (2009) Expression analysis of green fluorescent protein in retinal neurons of four transgenic mouse lines. Neurosci. 160: 126–139.
Chan, W. C. and S. Nie (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Sci. 281: 2016–2018.
Bruchez, M. ffixJr, M. Moronne, P. Gin, S. Weiss, and A. P. Alivisatos} (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Sci.. 281: 2013–2016.
Pitsillides, C. M., E. K. Joe, X. Wei, R. R. Anderson, and C. P. Lin (2003) Selective cell targeting with light-absorbing microparticles and nanoparticles. Biophys. J. 84: 4023–4032.
Alivisatos, P. (2004) The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat. Biotechnol. 22: 47–52.
Yong, K. T. (2011) Anti-claudin-4-conjugated highly luminescent nanoparticles as biological labels for pancreatic cancer sensing. Meth. Mol. Biol. 762: 427–438.
Monton, H., M. Roldan, A. Merkoci, E. Rossinyol, O. Castell, and C. Nogues (2012) The use of quantum dots for immunochemistry applications. Meth. Mol. Biol. 906: 185–192.
Plebani, A., L. D. Notarangelo, V. Monafo, L. Nespoli, and A. G. Ugazio (1984) A new immunoperoxidase assay for Lolium perenne-specific IgE in serum based on the biotin/avidin system (BAS). Clin. Aller. 14: 373–378.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Yang, C., Liu, J. et al. In Vitro evaluation and monitoring of the expression level and localization of aldose reductase using functionalized quantum dots and EGFP. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 800–806 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0022-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0022-3