Abstract
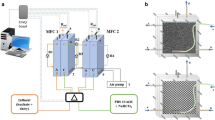
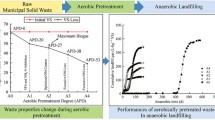
The biodrying pretreatment of municipal solid waste (MSW) and the treatment of leachate were investigated. The biological oxygen demand (BOD) and NH4 +-N concentration of leachate from MSW biodrying pretreatment were measured, and the optimal conditions for MSW biodrying pretreatment and microbial fuel cell (MFC) performance were established. The results show that the optimal temperature and time for biodrying pretreatment of MSW were 40°C and 6 day, resulting in 30% weight loss of MSW, 20,800 mg/L leachate BOD, and 1,410 mg/L leachate NH4 +-N. Effects of leachate properties on MFC performance were then studied. The optimal conditions for electricity generation of the MFC were neutral pH, 5,093 mg/L leachate BOD, and 341 mg/L leachate NH4 +-N. The stable voltage of MFC generated using diluted leachate was 0.32 V, and the removal efficiencies of BOD and NH4 +-N by the MFC were 86.0 and 88.8% after 7 day of treatment, respectively. These findings provide guidelines for the pretreatment of MSW and the treatment of leachate, and for further research and actual engineering application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, G. Q. (2000) The Engineering of Solid Waste Disposal. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Cao, Z. Z., H. C. Gao, and J. P. Chen (2001) Discussion on the development orientation of china’s current domestic refuse disposal. Eng. Technol. 2: 13–18.
Hu, J. P., X. X. Tang, and J. X. Li (2002) The pollution of municipal soild waste and its prevention technology. J. Vocat. Technical Coll. Jinhua 2: 43–45.
Logan, B. E. and J. M. Regan (2006) Microbial fuel cells-challenges and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40: 5172–5180.
Park, D. H. and J. G. Z. Zeikus (2003) Improved fuel cell and electrode designs for producing electricity from microbial degradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 81: 348–355.
Gil, G. C., I. S. Chang, B. H. Kim, M. Kim, J. K. Jang, H. S. Park, and J. M. Kim (2003) Operational parameters affecting the performance of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosens. Bioelectron. 18: 327–334.
Rabaey, K. and W. Verstraete (2005) Microbial fuel cells, novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol. 23: 291–298.
Min, B. and B. E. Logan (2004) Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38: 5809–5814.
Logan, B. E. (2005) Simultaneous wastewater treatment and biological electricity generation. Water Sci. Technol. 52: 31–37.
Sebastià, P., S. Marc, C. Marta, C. Marina, B. Dolors, and C. Jesús (2011) Microbial fuel cell application in landfill leachate treatment. J. Hazardous Mat. 185: 763–767.
Habermann, W. and E. H. Pommer (1991) Biological fuel cells with sulfide storage capacity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35: 128–133.
You, S.J., Q. L. Zhao, J. Q. Jiang, J. N. Zhang, and S. Q. Zhao (2006) Sustainable approach for leachate treatment, electricity generation in microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Health A. 41: 2721–2734.
Zhang, J. N., Q. L. Zhao, S. J. You, J. Q. Jiang, and N. Q. Ren (2008) Continuous electricity production from leachate in a novel upflowair-cathode membrane-free microbial fuel cell. Water Sci. Technol. 57: 1017–1021.
Greenman, J., A. Gálvez, L. Giusti, and I. Ieropoulos (2009) Electricity from landfill leachate using microbial fuel cells, Comparison with a biological aerated filter. Enz. Microb. Technol. 44: 112–119.
Gálvez, A., J. Greenman, and I. Ieropoulos (2009) Landfill leachate treatment with microbial fuel cells; Scale-up through plurality. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 5085–5091.
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. pp: 324–391. Architecture and Building Press, Beijing, China.
Deng, L. F., F. B. Li, S. G. Zhou, D. Y. Huang, and J. R. Ni (2009) A study of electron-shuttle mechanism in Klebsiella pneumoniae based-microbial fuel cells. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54: 2983–2987.
Yuan, H. R., L. F. Deng, Y. Chen, and S. G. Zhou (2012) Electricity generation from municipal solid waste leachate using microbial fuel cell technology. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 20: 800–810.
Kjeldsen, P., A. Morton Barlaz, A. P. Rooker, A. Baun, A. Ledin, and T. H. Christensen (2002) Present and long-term composition of Msw landfill leachate, a review. Critic. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32: 297–336.
Lou, Z. Y. and Y. C. Zhao (2006) Characterization of leachate generated in different seasons. Technol. Wat. Treatment 32: 38–40.
Wang, Y. C., Q. X. Yuan, J. H. Xie, and C. Y. Gao (2009) Characteristic studies on anaerobic fermentation for kitchen waste. Chin. J. Env. Eng. 3: 1677–1682.
Tatsi, A. A. and A. I. Zouboulis (2002) A field investigation of the quantity and quality of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill in a Mediterranean climate (Thessaloniki,Greece). Adv. Environ. Res. 6: 207–219.
Zhang, H., L. P. Sun, Y. An, and A. Q. Wang (2010) Research advances in characteristics of MSW landfill leachate. Sichuan Environ. 29: 113–118.
Park, D. H. and J. G. Zeikus (2000) Electricity generation in microbial fuel cells using neutral red as an electronophore. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 1292–1297.
Oh, S. E., B. Min, and B. E. Logan (2004) Cathode performance as a factor in electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38: 4900–4904.
Lu, N., B. Zhou, L. F. Deng, S. G. Zhou, and J. R. Ni (2009) Starch wastewater treatment using MnO2-catalyzed microbial fuel cells. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 17: 65–73.
Behera, M. and M. M. Ghangrekar (2009) Performance of microbial fuel cells in response to change in sludge loading rate at different anodic feed pH. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 5114–5121.
Behera, M., P. S. Jana, T. T. More, and M. M. Ghangreka (2010) Rice mill wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells fabricated using proton exchange membrane and earthen pot at different pH. Bioelectrochem. 79: 228–233.
He, Z., Y. L. Huang, A. K. Manohar, and F. Mansfeld (2008) Effect of electrolyte pH on the rate of the anodic and cathodic reactions in an air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Bioelectrochem. 74: 78–82.
Yuan, Y., S. G. Zhou, N. Xu, and L. Zhuang (2011) Electrochemical characterization of anodic biofilms enriched with glucose and acetate in single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Colloid Surf. B, Biointer. 82: 641–646.
Bond, D. R. and D. R. Lovley (2003) Electricity production by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69: 1548–1555.
Katuri, K. P., P. Kavanagh, S. Rengaraj, and D. Leech (2010) Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms developed under different growth conditions on glassy carbon electrodes, insights using cyclic voltammetry. Chem. Commun. 46: 4758–4760.
Liu, Y., F. Harnisch, K. Fricke, R. Sietmann, and U. Schröder (2008) Improvement of the anodic bioelectrocatalysis activity of mixed culture biofilm by simple consecutive electrochemical selection procedure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24: 1006–1011.
Kim, J. R., Y. Zuo, J. M. Regan, and B. E. Logan (2008) Analysis of ammonia loss mechanisms in microbial fuel cells treating animal wastewater. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 99: 1120–1127.
Puig, S., M. Serra, M. Coma, M. Cabré, M. D. Balaguer, and J. Colprim (2010) Effect of pH on nutrient dynamics and electricity production using microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 9594–9599.
Liu, H., S. Cheng, and B. E. Logan (2005) Power generation in fed-batch microbial fuel cells as a function of ionic strength, temperature, and reactor configuration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39: 5488–5493.
Liu, G. Y. (2010) Analysis of treatment process of municipal garbage leachate. Coastal Enterprises and Sci. Technol. 3: 39–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, H., Deng, L. & Chen, Y. Optimization of biodrying pretreatment of municipal solid waste and microbial fuel cell treatment of leachate. Biotechnol Bioproc E 19, 668–675 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0575-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0575-y