Abstract
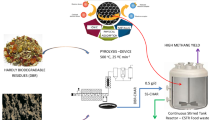
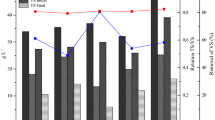
Chinese silver grass (CSG), a potential subtropical energy crop, was investigated as a co-substrate to enhance the anaerobic digestion of food waste for municipal solid waste treatment. Results showed that 88.1% of food wastes were degraded using CSG as a co-substrate with 45 days of digestion, where the food waste, CSG, and sludge on VS/TS/working volume was 93.14 g/111.55 g/1 L, in which the average biogas production was at 429.3 L/kg solids, and the average methane content was around 60%. During the digestion, the concentrations of ammonium and free ammonia gradually increased to 1448.2 and 265.2 mg/L respectively, without any significant inhibitory effects on biogas production, which is probably due to the buffering effects of CSG. Microbial community analysis showed that microorganisms from the class of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were dominant during digestion, and that the microbial community diversity increased with active methanogenesis, suggesting that the addition of substrates contribute to the increase of microbial diversity, and could be beneficial for biogas production. Therefore, using CSG as a co-substrate in the single-stage food waste anaerobic digestion system is a potential simple method to convert CSG into renewable energy and to simultaneously improve food waste treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Mata-Alvarez, J., S. Macé, and P. Llabrés (2000) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An over view of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 74: 3–16.
Cheng, H. and Y. Hu (2010) Municipal solid waste (MSW) as a renewable source of energy: Current and future practices in China. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 3816–3824.
Zhang, D. Q., S. K. Tan, and R. M. Gersberg (2010) Municipal solid waste management in China: Status, problems and challenges. J. Environ. Manage. 91: 1623–1633.
Kjeldsen, P., M. A. Barlaz, A. P. Rooker, A. Baun, A. Ledin, and T. H. Christensen (2002) Presentand long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: A review. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Technol. 32: 297–336.
Kastner, V., W. Somitsch, and W. Schnitzhofer (2012) The anaerobic fermentation of food waste: A comparison of two bioreactor systems. J. Clean. Prod. 34: 82–90.
Tawfik, A., A. Salem, and M. El-Qelish (2011) Two stage anaerobic baffled reactors for bio-hydrogen production from municipal food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 8723–8726.
Trzcinski, A. P. and D. C. Stuckey (2011) Parameters affecting the stability of the digestate from a two-stage anaerobic process treating the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Waste Manage. 31: 1480–1487.
Forster-Carneiro, T., M. Pérez, and L. I. Romero (2008) Anaerobic digestion of municipal solid wastes: Dry thermophilic performance. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 8180–8184.
Bouallagui, H., Y. Touhami, R. Ben Cheikh, and M. Hamdi (2005) Bioreactor performance in anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable wastes. Proc. Biochem. 40: 989–995.
Heo, N. H., S. C. Park, and H. Kang (2004) Effects of mixture ratio and hydraulic retention time on single-stage anaerobic codigestion of food waste and waste activated sludge. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part A. 39: 1739–1756.
Angelidaki, I. and B. K. Ahring (1993) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of livestock waste: The effect of ammonia. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 38: 560–564.
Chen, Y., J. J. Cheng, and K. S. Creamer (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 4044–4064.
El-Mashad, H. M., J. A. McGarvey, and R. Zhang (2008) Performance and microbial analysis of anaerobic digesters treating food waste and dairy manure. Biol. Eng. 1: 233–242.
Callaghan, F. J., D. A. J. Wase, K. Thayanithy, and C. F. Forster (1999) Co-digestion of waste organic solids: Batch studies. Bioresour. Technol. 67: 117–122.
Cuetos, M. J., C. Fernández, X. Gómez, and A. Morán (2011) Anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure with energy crop residues. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 16: 1044–1052.
Macias-Corral, M., Z. Samani, A. Hanson, G. Smith, P. Funk, H. Yu, and J. Longworth (2008) Anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste and agricultural waste and the effect of co-digestion with dairy cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 8288–8293.
Li, R., S. Chen, and X. Li (2010) Biogas production from anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with dairy manure in a two-phase digestion system. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 160: 643–654.
Liu, G., R. Zhang, H. M. El-Mashad, and R. Dong (2009) Effect of feed to inoculum ratios on biogas yields of food and green wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 5103–5108.
Zhu, H., W. Parker, R. Basnar, A. Proracki, P. Falletta, M. Béland, and P. Seto (2008) Biohydrogen production by anaerobic co-digestion of municipal food waste and sewage sludges. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 33: 3651–3659.
Guo, G. L., W. H. Chen, W. H. Chen, L. C. Men, and W. S. Hwang (2008) Characterization of dilute acid pretreatment of silvergrass for ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 6046–6053.
Nagao, N., N. Tajima, M. Kawai, C. Niwa, N. Kurosawa, T. Matsuyama, F. M. Yusoff, and T. Toda (2012) Maximum organic loading rate for the single-stage wet anaerobic digestion of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 118: 210–218.
Abbassi-Guendouz, A., D. Brockmann, E. Trably, C. Dumas, J. -P. Delgenès, J. -P. Steyer, and R. Escudié (2012) Total solids content drives high solid anaerobic digestion via mass transfer limitation. Bioresour. Technol. 111: 55–61.
Kleyböcker, A., M. Liebrich, W. Verstraete, M. Kraume, and H. Würdemann (2012) Earlywarning indicators for process failure due to organic overloading by rapeseed oil in one-stage continuously stirred tank reactor, sewage sludge and waste digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 123: 534–541.
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington D. C., USA.
Tawfik, A. and O. ElBatrawy (2012) Anaerobic biodegradation of personnel care products (PCPs) wastewater in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Desalin. Water Treat. 41: 232–239.
El-Mashad, H. M., G. Zeeman, W. K. P. van Loon, G. P. A. Bot, and G. Lettinga (2004) Effect of temperature and temperature fluctuation on thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 95: 191–201.
Poggi-Varaldo, H. M., R. Rodríguez-Vázquez, G. Fernández-Villagómez, and F. Esparza-García (1997) Inhibition of mesophilic solid-substrate anaerobic digestion by ammonia nitrogen. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 47: 284–291.
Wang, Q., G. M. Garrity, J. M. Tiedje, and J. R. Cole (2007) Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 73: 5261–5267.
Yu, Y., M. Breitbart, P. McNairnie, and F. Rohwer (2006) Fast-GroupII: A web-based bioinformatics platform for analyses of large 16S rDNA libraries. BMC Bioinformatics. 7: 57.
Tang, X. D., S. G. Wan, Y. C. Zhang, and W. S. Luo (2012) Influence of garden green wastes addition and freeze-thaw pretreatment on food waste anaerobic digestion efficiency. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2: 512–518.
Lin, J., J. Zuo, L. Gan, P. Li, F. Liu, K. Wang, L. Chen, and H. Gan (2011) Effects of mixture ratio on anaerobic co-digestion with fruit and vegetable waste and food waste of China. J. Environ. Sci. 23: 1403–1408.
Habiba, L., B. Hassib, and H. Moktar (2009) Improvement of activated sludge stabilisation and filterability during anaerobic digestion by fruit and vegetable waste addition. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 1555–1560.
Li, Y., S. Y. Park, and J. Zhu (2011) Solid-state anaerobic digestion for methane production from organic waste. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 15: 821–826.
He, Y. (1998) Anaerobic biological treatment of wastewater. 1 ed., China Light Industry Press, Beijing, China.
Hanaki, K., S. Hirunmasuwan, and T. Matsuo (1994) Protection of methanogenic bacteria from low pH and toxic materials by immobilization using polyvinyl alcohol. Water Res. 28: 877–885.
Viéitez, E. R. and S. Ghosh (1999) Biogasification of solid wastes by two-phase anaerobic fermentation. Biomass Bioenerg. 16: 299–309.
Leitão, R. C., A. C. van Haandel, G. Zeeman, and G. Lettinga (2006) The effects of operational and environmental variations on anaerobic wastewater treatment systems: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 97: 1105–1118.
Hansen, K. H., I. Angelidaki, and B. K. R. Ahring (1998) Anaerobic digestion of swine manure:inhibiton by ammonia. Water Res. 32: 5–12.
Koster, I. W. and G. Lettinga (1988) Anaerobic digestion at extreme ammonia concentrations. Biol. Wastes. 25: 51–59.
Liu, J. G., S. H. Zhao, and L. H. Zhang (2012) Study on anaerobic digestion performance of kitchen wastes: Inhibition of ammonia nitrogen and volatile acid on the anaerobic methanogenesis. Adv. Mater. Res. 347–353: 2497–2503.
Calli, B., B. Mertoglu, B. Inanc, and O. Yenigun (2005) Effects of high free ammonia concentrations on the performances of anaerobic bioreactors. Proc. Biochem. 40: 1285–1292.
Kashyap, D. R., K. S. Dadhich, and S. K. Sharma (2003) Biomethanation under psychrophilic conditions: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 87: 147–153.
Dearman, B., P. Marschner, and R. H. Bentham (2006) Methane production and microbial community structure in single-stage batch and sequential batch systems anaerobically co-digesting food waste and biosolids. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 69: 589–596.
Cardinali-Rezende, J., A. M. Moraes, L. D. B. Colturato, E. Carneiro, I. Marriel, E. Chartone-Souza, and A. M. A. Nascimento (2011) Phylogenetic and physiological characterization of organic waste-degrading bacterial communities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27: 245–252.
Garcia, S. L., K. Jangid, W. B. Whitman, and K. C. Das (2011) Transition of microbial communities during the adaption to anaerobic digestion of carrot waste. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 7249–7256.
Martín-González, L., R. Castro, M. A. Pereira, M. M. Alves, X. Font, and T. Vicent (2011) Thermophilic co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid wastes with FOG wastes from a sewage treatment plant: Reactor performance and microbial community monitoring. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 4734–4741.
Zhang, D., J. Li, P. Guo, P. Li, Y. Suo, X. Wang, and Z. Cui (2011) Dynamic transition of microbial communities in response to acidification in fixed-bed anaerobic baffled reactors (FABR) of two different flow directions. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 4703–4711.
Garcia-Peña, E. I., P. Parameswaran, D. W. Kang, M. Canul- Chan, and R. Krajmalnik-Brown (2011) Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion processes of vegetable and fruit residues: Process and microbial ecology. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 9447–9455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, S., Sun, L., Sun, J. et al. Biogas production and microbial community change during the Co-digestion of food waste with chinese silver grass in a single-stage anaerobic reactor. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 1022–1030 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0128-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0128-4