Abstract
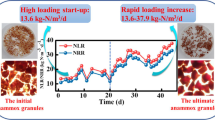
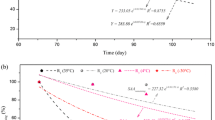
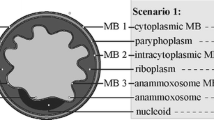
The physical properties and performance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) granules of different sizes (0.5 ∼ 1.0 mm, 1.0 ∼ 1.5 mm, and above 1.5 mm) have been investigated. The values of the settling velocity increased with increasing size of the granules. There was no significant difference in metal contents among granules of different sizes, in which calcium, magnesium and iron were the predominant ions. Different start-up periods showed that larger granules were better able to resist adverse impacts and their activities could quickly be recovered. The specific activities of granules of different sizes were 0.55, 0.62, and 0.52 g N/ (g/VSS/day), respectively, which implied the activity of 1.0 ∼ 1.5 mm granules was the highest. Larger anammox granules were better able to resist temperature shock and nitrogenous shock loading. However, larger granules were also shown to contain bigger gas tunnels and interior hollows, which decrease the stability of anammox granules. With the comprehensive consideration of bacteria activity, granule stability and shock resistance capacity, the properties of granules within the size range of 1.0 ∼ 1.5 mm were found superior to others in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, C. J., P. Zheng, C. H. Wang, Q. Mahmood, J. Q. Zhang, X. G. Chen, L. Zhang, and J. W. Chen (2011) Performance of high-loaded ANAMMOX UASB reactors containing granular sludge. Water Res. 45: 135–144.
Tsushima, I., Y. Ogasawara, T. Kindaichi, H. Satoh, and S. Okabe (2007) Development of high-rate anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) biofilm reactors. Water Res. 41: 1623–1634.
Qiao, S., Y. Kawakubo, Y. J. Cheng, T. Nishiyama, T. Fujii, and K. Furukawa (2009) Identification of bacteria coexisting with anammox bacteria in an upflow column type reactor. Biodegradation 20: 117–124.
Dapena-Mora, A., J. L. Campos, A. Mosquera-Corral, M. S. M. Jetten, and R. Mendez (2004) Stability of the ANAMMOX process in a gas-lift reactor and a SBR. J. Biotechnol. 110: 159–170.
van der Star, W. R. L., W. R. Abma, D. Blommers, J. W. Mulder, T. Tokutomi, M. Strous, C. Picioreanu, and Van Loosdrecht (2007) Startup of reactors for anoxic ammonium oxidation: Experiences from the first full-scale anammox reactor in Rotterdam. Water Res. 41: 4149–4163.
Zhang, X., S. Liu, and X. Chen (2011) Effect of Shear Stress on Activated Sludge Granular in Sequencing Batch Reactor. Ener. Procedia. 11: 2121–2126.
Tang, C. J., P. Zheng, and Q. Mahmood (2009) The shear force amendments on the slugging behavior of upflow Anammox granular sludge bed reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 69: 262–268.
Li, X., Y. Xiao, D. Liao, W. Zheng, T. Yi, Q. Yang, and G. Zeng (2011) Granulation of simultaneous partial nitrification and anammox biomass in one single SBR system. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 163: 1053–1065.
Imajo, U., T. Tokutomi, and K. Furukawa (2004) Granulation of Anammox microorganisms in up-flow reactors. Water Sci. Technol. 49: 155–163.
Arrojo, B., A. Mosquera-Corral, J. L. Campos, and R. Mendez (2006) Effects of mechanical stress on Anammox granules in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). J. Biotechnol. 123: 453–463.
Strous, M., J. J. Heijnen, J. G. Kuenen, and M. S. M. Jetten (1998) The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 50: 589–596.
APHA (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. United Book Press Inc., Baltimore, Maryland, USA.
Su, K. Z. and H. Q. Yu (2005) Formation and characterization of aerobic granules in a sequencing batch reactor treating soybean-processing wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39: 2818–2827.
Wang, X. H., H. M. Zhang, F. L. Yang, L. P. Xia, and M. M. Gao (2007) Improved stability and performance of aerobic granules under stepwise increased selection pressure. Enz. Microb. Tech. 41: 205–211.
Li, X. R., B. Du, H. X. Fu, R. F. Wang, J. H. Shi, Y. Wang, M. S. M. Jetten, and Z. X. Quan (2009) The bacterial diversity in an anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) reactor community. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 32: 278–289.
Saitou, N. and M. Nei (1987) The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Shi, X. Y., H. Q. Yu, Y. J. Sun, and X. Huang (2009) Characteristics of aerobic granules rich in autotrophic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in a sequencing batch reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 147: 102–109.
Zheng, Y. M., H. Q. Yu, and G. P. Sheng (2005) Physical and chemical characteristics of granular activated sludge from a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Proc. Biochem. 40: 645–650.
Vázquez-Padín, J., I. Fernádez, M. Figueroa, A. Mosquera-Corral, J. L. Campos, and R. Méndez (2009) Applications of Anammox based processes to treat anaerobic digester supernatant at room temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 2988–2994.
Tang, C. J., P. Zheng, L. Zhang, J. W. Chen, Q. Mahmood, X. -G. Chen, B. L. Hu, C. H. Wang, and Y. Yu (2010) Enrichment features of anammox consortia from methanogenic granules loaded with high organic and methanol contents. Chemosph. 79: 613–619.
Ji, G., F. Zhai, R. Wang, and J. Ni (2010) Sludge granulation and performance of a low superficial gas velocity sequencing batch reactor (SBR) in the treatment of prepared sanitary wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 9058–9064.
Teil, M. J., M. Blanchard, and M. Chevreuil (2006) Atmospheric fate of phthalate esters in an urban area (Paris-France). Sci. Total Environ. 354: 212–223.
Zandvoort, M. H., E. D. van Hullebusch, J. Gieteling, and P. N. L. Lens (2006) Granular sludge in full-scale anaerobic bioreactors: Trace element content and deficiencies. Enz. Microb. Tech. 39: 337–346.
Pevere, A., G. Guibaud, E. Goin, E. van Hullebusch, and P. Lens (2009) Effects of physico-chemical factors on the viscosity evolution of anaerobic granular sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 43: 231–238.
Ghangrekar, M. M., S. R. Asolekar, and S. G. Joshi (2005) Characteristics of sludge developed under different loading conditions during UASB reactor start-up and granulation. Water Res. 39: 1123–1133.
Batstone, D. J. and J. Keller (2001) Variation of bulk properties of anaerobic granules with wastewater type. Water Res. 35: 1723–1729.
Yang, J. C., L. Zhang, Y. Fukuzaki, D. Hira, and K. Furukawa (2010) High-rate nitrogen removal by the Anammox process with a sufficient inorganic carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 9471–9478.
Bhunia, P. and M. M. Ghangrekar (2007) Required minimum granule size in UASB reactor and characteristics variation with size. Bioresour. Technol. 98: 994–999.
Kindaichi, T., I. Tsushima, Y. Ogasawara, M. Shimokawa, N. Ozaki, H. Satoh, and S. Okabe (2007) In situ activity and spatial organization of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microb. 73: 4931–4939.
Okabe, S., M. Oshiki, Y. Takahashi, and H. Satoh (2011) N2O emission from a partial nitrification-anammox process and identification of a key biological process of N2O emission from anammox granules. Water Res. 45: 6461–6470.
Fux, C., M. Boehler, P. Huber, I. Brunner, and H. Siegrist (2002) Biological treatment of ammonium-rich wastewater by partial nitritation and subsequent anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in a pilot plant. J. Biotechnol. 99: 295–306.
Strous, M., E. Van Gerven, P. Zheng, J. G. Kuenen, and M. S. M. Jetten (1997) Ammonium removal from concentrated waste streams with the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) process in different reactor configurations. Water Res. 31: 1955–1962.
Dosta, J., I. Fernández, J. R. Vázquez-Padín, A. Mosquera-Corral, J. L. Campos, J. Mata-Álvarez, and R. Méndez (2008) Shortand long-term effects of temperature on the Anammox process. J. Hazard. Mater. 154:688–693.
Kimura, Y., K. Isaka, F. Kazama, and T. Sumino (2010) Effects of nitrite inhibition on anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 86: 359–365.
Dapena-Mora, A., I. Fernandez, J. L. Campos, A. Mosquera-Corral, R. Mendez, and M. S. M. Jetten (2007) Evaluation of activity and inhibition effects on anammox process by batch tests based on the nitrogen gas production. Enz. Microb. Technol. 40: 859–865.
Dolfing, J. (1985) Kinetics of methane formation by granular sludge at low substrate concentrations. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 22: 77–81.
Al-Muftah, A. E. and I. M. Abu-Reesh (2005) Effects of internal mass transfer and product inhibition on a simulated immobilized enzyme-catalyzed reactor for lactose hydrolysis. Biochem. Eng. J. 23: 139–153.
Alphenaar, P. A., M. C. Pérez, and G. Lettinga (1993) The influence of substrate transport limitation on porosity and methanogenic activity of anaerobic sludge granules. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 39: 276–280.
Chen, J., Q. Ji, P. Zheng, T. Chen, C. Wang, and Q. Mahmood (2010) Floatation and control of granular sludge in a high-rate anammox reactor. Water Res. 44: 3321–3328.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, P., Xu, X., Yang, F. et al. Comparison of the characteristics of anammox granules of different sizes. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 446–454 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0728-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0728-4