Abstract
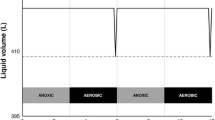
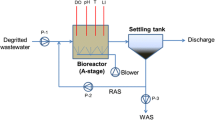
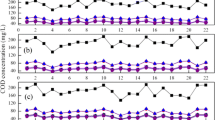
In the present study, a laboratory scale anoxic/oxic (A/O) reactor is used for the removal of nutrient and sludge reduction. Phosphorus removal was achieved through simultaneous precipitation, and sludge production was reduced through thermochemical pretreatment. The main objective of the study was to investigate the influence of sludge pretreatment on the nitrification rate. Total phosphorus in the effluent was maintained around 0.5 ∼ 1.0 mg/L by simultaneous precipitation, using coagulant alum at 2.2 mole ratio. Before simultaneous precipitation, the nitrification rate of the A/O reactor was found to be 0.050 g N-NH4 +/g MLVSS.d. The thermochemical sludge pretreatment began on the 120th day at pH 11 and 80°C. The initiation of sludge pretreatment brought about a significant reduction of the A/O reactor nitrification rate, which fell to 0.038 g N-NH4 +/g MLVSS/day. The effect of sludge pretreatment was reflected in the reduction of the nitrogen removal efficiency from 85 to 74%. Recycling of the thermochemically pretreated sludge accounted for 57% sludge reduction, which had an adverse influence on the nitrification rate of the system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tchobanoglous, G., F. L. Burton, and H. D. Stensel (2003) Wastewater engineering: Treatment, disposal and reuse. 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, NY, USA.
Banu, R. J., K. -U. Do, S. Kaliappan, and I. -T. Yeom (2009) Effect of alum on nitrification during simultaneous phosphorus removal in anoxic/oxic reactor. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 14: 543–548.
Oh, Y. -K., K. -R. Lee, K. -B. Ko, and I. -T. Yeom (2007) Effects of chemical sludge disintegration on the performances of wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor. Wat. Res. 41: 2665–2671.
Davis, R. D. and J. E. Hall (2007) Production, treatment and disposal of wastewater sludge in Europe from a UK perspective. Eur. Wat. Pollut. Control 7: 9–17.
Spellman, F. R. (1997) Wastewater biosolids to compost. pp. 223–235. Technomic Publishing Company, Lancaster, PA, USA.
Liu, Y. and J. H. Tay (2001) Strategy for minimization of excess sludge production from the activated sludge process. Biotechnol. Adv. 19: 97–107.
Do, K. -U., J. R. Banu, I. -J. Chung, and I. -T. Yeom (2009) Effect of thermochemical sludge disintegration on sludge reduction and on performances of anoxic-aerobic membrane bioreactor treating low strength domestic wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 84: 1350–1355.
Wei, Y. S., R. T. Van Houten, A. R. Borger, D. H. Eikelboom, and Y. B. Fan (2003) Minimization of excess sludge production for biological wastewater treatment. Wat. Res. 37: 4453–4467.
Muller, J. A. (2000) Disintegration as a key-step in sewage sludge treatment. Wat. Sci. Technol. 41: 123–130.
Ichinari, T., A. Ohtsubo, T. Ozawa, K. Hasegawa, K. Teduka, T. Oguchi, and Y. Kiso (2008) Wastewater treatment performance and sludge reduction properties of a household wastewater treatment system combined with an aerobic sludge digestion unit. Proc. Biochem. 43: 722–728.
Zhang, G., P. Zhang, J. Yang, and Y. Chen (2007) Ultrasonic reduction of excess sludge from the activated sludge system. J. Hazard. Mater. 145: 515–519.
Tanaka, S., T. Kobayashi, K. Kamiyama, and M. L. Bildan (1997) Effects of thermochemical pre-treatment on the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Wat. Sci. Technol. 8: 209–215.
Liu, Y. (2003) Chemically reduced excess sludge production in the activated sludge process. Chemosphere. 50: 1–7.
Xie, W. M., B. J. Ni, G. P. Sheng, H. Q. Yu, and M. Yang (2010) Substrate consumption and excess sludge reduction of activated sludge in the presence of uncouplers: A modeling approach. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85: 2001–2008.
Rocher, M., G. Goma, A. P. Begue, L. Louvel, and J. L. Rols (1999) Towards a reduction in excess sludge production in activated sludge processes: Biomass physicochemical treatment and biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51: 883–890.
Wei, Y., Y. Wang, X. Guo, and J. Liu (2009) Sludge reduction potential of the activated sludge process by integrating an oligochaete reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 163: 87–91.
Kim, J., C. Park, T. -H. Kim, M. Lee, S. -W. Kim, and J. Lee (2003) Effects of various pre-treatment for enhanced anaerobic digestion with waste activated sludge. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 95: 271–275.
Khursheed, A. and A. A. Kazmi (2011) Retrospective of ecological approaches to excess sludge reduction. Wat. Res. 45: 4287–4310.
Banu, J. R., K. -U. Do, and I. -T. Yeom (2008) Effect of ferrous sulphate on nitrification during simultaneous phosphorus removal from domestic wastewater using a laboratory scale anoxic/oxic reactor. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 2981–2986.
Valo, A., H. Carrere, and J. P. Delegenes (2004) Thermal, chemical and thermo-chemical pre-treatment of waste activated sudge for anaerobic digestion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 79: 1197–1203.
Neyens, E., J. Baeyens, and C. Creemers (2003) Alkaline thermal sludge hydrolysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 97: 295–314.
Do, K. -U, N. T. T. Ha, R. J. Banu, K. Kim, J. Heo, and I. -T. Yeom (2010). Effect of thermochemical pretreatment on the biodegradability of sludge from a biological wastewater treatment system. Maejo. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 4: 250–260.
Baeza, J. A., D. Gabriel, and J. Lafunente (2004) Effect of internal recycle on the nitrogen removal efficiency of an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2/O) wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Proc. Biochem. 39: 1615–1624.
APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 21st ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, USA.
Tanaka, S. and K. Kamiyama (2002) Thermochemical pre-treatment in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Wat. Sci. Technol. 46: 173–179.
Vlyssides, A. G. and K. P. Karlis (2004) Thermal-alkaline solubilisation of waste activated sludge as a pretreatment stage for anaerobic digestion. Biores. Technol. 91: 201–206.
Bougrier, C., J. P. Delgenès, and H. Carrère (2008) Impacts of thermal pre-treatments on the semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 34: 20–27.
Baier, U. and P. Schmidheiny (1997) Enhanced anaerobic degradation on mechanically disintegrated sludge. Wat. Sci. Technol. 36: 137–143.
Appels, J. D., B. Van der Bruggen, J. Van Impe, and R. Dewil (2010) Influence of low temperature thermal pre-treatment on sludge solubilisation, heavy metal release and anaerobic digestion. Biores. Technol. 101: 5743–5748.
Mervat, E. and A. W. Logan (1996) Removal of phosphorus from secondary effluent by a matrix filter. Desalination 106: 247–253.
de Haas, D. W., M. C. Wentzel, and G. A. Ekama (2000) The use of simultaneous chemical precipitation in modified activated sludge systems exhibiting biological enhanced phosphate removal. Part 1: Literature review. Water SA. 26: 439–452
Sakai, Y., T. Fukase, H. Yasui, and M. Shibata (1997) An activated sludge process without excess sludge production. Wat. Sci. Technol. 36: 163–170.
Yoon, S. H., H. S. Kim, and S. H. Lee (2004) Incorporation of ultrasonic cell disintegration into a membrane bioreactor for zero sludge production. Proc. Biochem. 39: 1923–1929.
Yasui, H. and M. Shibata (1994) An innovative approach to reduce excess sludge production in the activated sludge process. Wat. Sci. Technol. 30: 11–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, KU., Rajesh Banu, J., Kaliappan, S. et al. Influence of the thermochemical sludge pretreatment on the nitrification of A/O reactor with the removal of phosphorus by simultaneous precipitation. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 313–320 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0492-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0492-5